Cloud
data warehouse: A data warehouse is a centralized repository that stores structured, historical data from multiple sources. It is designed for query and analysis rather than transaction processing. Data warehouses are optimized for complex queries, reporting, and data analysis to support decision-making processes.
IaC (Infrastructure as Code)
Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is the practice of managing and provisioning computing infrastructure through machine-readable definition files, rather than physical hardware configuration or interactive configuration tools. IaC allows infrastructure to be defined, managed, and versioned in a code-like manner, providing consistency, repeatability, and automation in infrastructure deployment and management processes.
- the popularity of Dockerfiles and containers, IaC, and other cloud-native technologies has increased greatly (2023/2024)
Multi-cloud / hybrid strategies
Cloud data warehouses (CDWs)
offering scalability, flexibility, and accessibility. They enable advanced analytics, business intelligence, and various use cases such as DApp development, market intelligence, personal data management, and fraud detection.
- data integration
- security
- and consistency
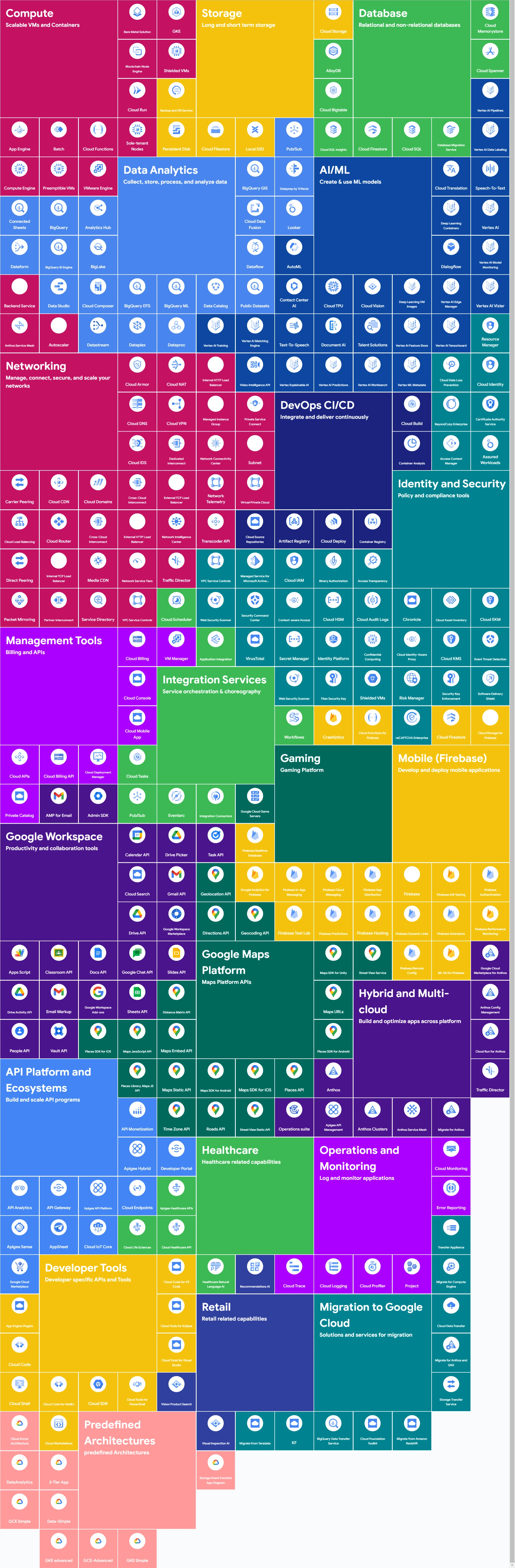
https://googlecloudcheatsheet.withgoogle.com/
An RDBMS (Relational Database Management System) like SQL Server and a cloud platform like AWS (Amazon Web Services) are two different concepts that serve different purposes in the context of data storage and management.
-
Functionality and Purpose:
-
RDBMS: An RDBMS is a software system designed to manage relational databases. It provides a structured way to store, organize, and retrieve data using tables with predefined schemas, relationships, and SQL (Structured Query Language) for querying and manipulating data. RDBMSs like SQL Server are typically installed on-premises or on dedicated servers and offer features like data integrity, transaction management, and advanced querying capabilities.
-
Cloud Platform (AWS): AWS is a cloud computing platform that offers a wide range of services, including storage, computing power, networking, and database management. AWS provides scalable and on-demand resources that can be accessed over the internet. In the context of databases, AWS offers services like Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service), Amazon DynamoDB (NoSQL database), Amazon Redshift (data warehousing), and more. These services abstract the underlying infrastructure and provide managed database solutions in the cloud.
-
-
Deployment and Infrastructure:
-
RDBMS: RDBMSs like SQL Server are traditionally deployed on dedicated servers or on-premises infrastructure. Organizations need to manage the installation, configuration, maintenance, and scaling of the hardware and software components themselves. This requires expertise in server administration and infrastructure management.
-
Cloud Platform (AWS): AWS, being a cloud platform, provides a fully managed infrastructure for deploying and running applications and databases. AWS abstracts the underlying hardware and infrastructure, allowing users to focus on the application and data without worrying about server management. AWS offers various database services that can be provisioned and scaled in a few clicks, reducing the operational overhead.
-
-
Scalability and Flexibility:
-
RDBMS: Traditional RDBMSs may have limitations in terms of scalability. Scaling an RDBMS often involves upgrading hardware or manually partitioning the data across multiple servers. This process can be complex and time-consuming.
-
Cloud Platform (AWS): Cloud platforms like AWS offer elastic scalability, allowing users to scale their database resources up or down based on demand. With AWS, you can easily provision additional database instances, add read replicas, or leverage auto-scaling capabilities. This flexibility enables organizations to handle varying workloads and accommodate growth without significant upfront investments.
-
-
Cost Model:
-
RDBMS: Traditional RDBMSs typically involve upfront costs for software licenses, hardware infrastructure, and ongoing maintenance expenses. Organizations need to plan and budget for these costs, which can vary based on factors like server capacity, software versions, and support agreements.
-
Cloud Platform (AWS): AWS follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model, where you pay for the resources you consume. This can be more cost-effective for many organizations, especially those with variable workloads. With AWS, you can choose the appropriate database service and size it according to your needs, paying only for the actual usage. Additionally, cloud platforms often offer pricing models that allow you to reserve capacity in advance for further cost optimization.
-
It's important to note that AWS itself provides managed RDBMS services like Amazon RDS for SQL Server, which combines the benefits of traditional RDBMS with the flexibility and scalability of the cloud.
Snowflake Cloud Data Warehouse
Snowflake is a cloud data warehouse that offers a fully managed service for data storage, processing, and analytics. It is known for its scalability, performance, and ease of use. Snowflake uses a unique architecture that separates storage and compute, allowing users to independently scale resources based on their needs. This separation enables efficient query processing and cost optimization.
Key Features of Snowflake:
- Scalability: Snowflake can automatically scale up or down to handle varying workloads without manual intervention. Users can allocate resources dynamically based on demand.
- Concurrency: Snowflake supports multiple users and workloads concurrently, ensuring consistent performance even under heavy loads.
- Data Sharing: Snowflake enables secure data sharing across organizations, allowing users to share data without copying or moving it.
- Security: Snowflake provides robust security features, including encryption, access controls, and compliance certifications to protect data at rest and in transit.
- Performance: Snowflake's architecture optimizes query performance by separating storage and compute, resulting in faster query execution and reduced latency.
- Integration: Snowflake integrates seamlessly with various data sources, BI tools, and data processing frameworks, making it easy to ingest, analyze, and visualize data.
Overall, Snowflake offers a modern cloud data warehouse solution that addresses the challenges of traditional data warehousing by providing scalability, performance, and flexibility in a cost-effective manner.
