STARTUP
Am I Ready?
- there's no such thing as ready
- if you feel ready, you've waited too long
Pitch
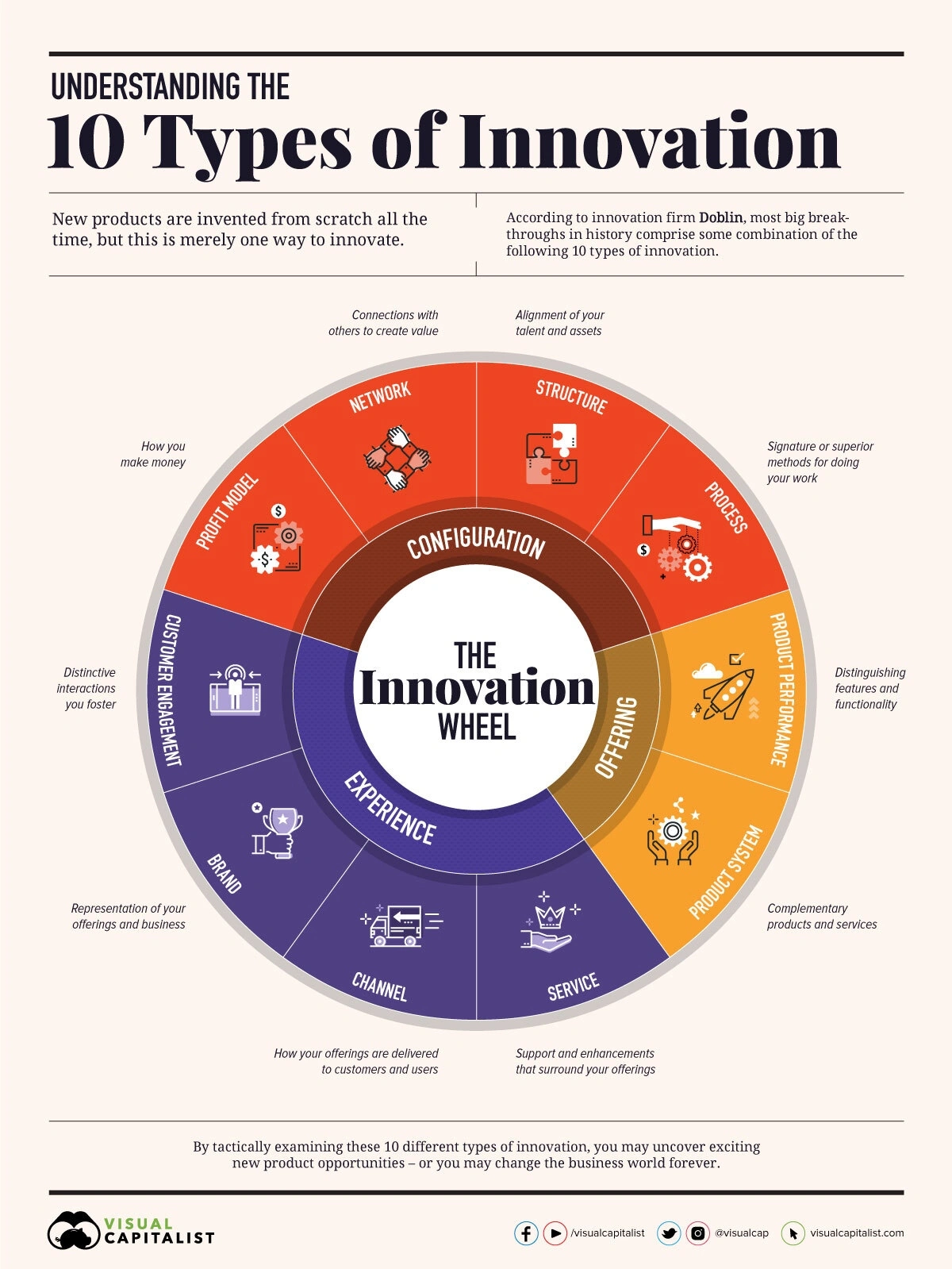
a pitch requires clear and concise communication that highlights the value proposition for the audience.
Clearly Define the Innovation: Start by clearly defining the disruptive innovation or IP exploitation that your pitch is centered around. This should be done in simple and understandable terms, so that the audience understands the core concepts of your pitch.
Highlight the Unique Value Proposition: It's important to clearly articulate the unique value proposition of the innovation, and how it will benefit the target market. This should focus on the benefits that set the innovation apart from existing solutions, and how it solves a specific problem or addresses a gap in the market.
Use Examples: Using examples can help to illustrate the value proposition of the innovation, and how it solves a real-world problem. This can include case studies, testimonials, or examples of successful implementations.
Address Potential Concerns: It's important to address any potential concerns or objections that the audience may have, such as potential barriers to adoption or competition in the market. This can help to build trust and credibility with the audience, and demonstrate that the innovation has been thoroughly considered.
Emphasize the IP Protection: If the innovation is based on IP exploitation, it's important to highlight the IP protection measures that have been taken, such as patents or trademarks. This can help to build confidence with potential investors or partners, and demonstrate that the innovation has a strong foundation for long-term success.
Overall, conveying disruptive innovation or IP exploitation in a pitch requires clear and concise communication that highlights the unique value proposition of the innovation, addresses potential concerns, and emphasizes the IP protection measures that have been taken. By effectively communicating these concepts, you can increase the likelihood of securing investment or partnerships for your innovation.
Focus your pitch deck on problem-solving, not technology
Set Boundaries
- Remember how you felt being treated as an employee
- Good places
- Bad places
- Set boundaries, ppl have no chill
- Too much friendship is bad for the business
- Friendship can damage relationships with clients
Videos
- 10 Reasons To Start A Business During A Recession https://instagram.com/startupdevelopmenthouse?igshid=YmMyMTA2M2Y=
- Product discovery
- Early go to market
- Idea validation
- User interviews
- MVP budgeting
What is a Private Practice?
Private practice refers to a professional or medical practice in which an individual practitioner operates independently, typically in a non-institutional setting such as a private office or clinic. In a private practice, the practitioner provides services directly to clients or patients without being employed by a larger organization or institution.
Private practices are commonly found in various fields, including medicine, law, psychology, counseling, therapy, accounting, and architecture, among others. The practitioner in a private practice is responsible for managing their own business affairs, including scheduling appointments, maintaining records, billing, and handling administrative tasks.
One of the primary advantages of private practice is the autonomy it provides to the practitioner. They have greater control over their work environment, the services they offer, and the clients or patients they choose to work with. Additionally, private practitioners often have the opportunity to establish long-term relationships with their clients or patients, which can contribute to continuity of care.
However, private practitioners also face challenges such as managing the financial aspects of running a business, marketing their services, and dealing with administrative tasks. They do not have the same level of institutional support or resources as practitioners working within larger organizations or institutions.
Overall, private practice offers professionals the opportunity to work independently and tailor their services to meet the specific needs of their clients or patients, but it also requires them to take on the responsibilities of running a business.
Difference between "private practice," "side hustle," and "freelancer"
While they all involve independent work, there are differences in their meanings and usage:
-
Private Practice: Private practice typically refers to a professional or medical practice in which an individual practitioner operates independently, providing services directly to clients or patients. It is commonly associated with fields such as medicine, law, psychology, counseling, therapy, and other professional services. Private practitioners often have their own office or clinic and manage their business affairs. They may work full-time or part-time in their private practice and usually have a specific area of expertise.
-
Side Hustle: A side hustle refers to a secondary job or income stream that someone pursues in addition to their primary occupation. It is typically an extra source of income that is pursued outside of regular working hours. Side hustles can take various forms, such as freelancing, gig work, online businesses, or part-time jobs. Unlike private practice, a side hustle is often not a professional or specialized practice but rather a way to earn additional money or explore personal interests.
-
Freelancer: A freelancer is a self-employed individual who offers services to clients on a project-by-project basis. Freelancers are not committed to a single employer and instead work independently, often remotely. They may provide services in various fields such as writing, graphic design, web development, marketing, consulting, and more. Freelancers are typically hired for specific assignments or contracts and have the flexibility to choose their clients and projects.
While there may be some overlap between the concepts, private practice, side hustle, and freelancer are distinct terms that describe different forms of independent work. Private practice is more specific to certain professions, side hustle refers to a secondary income activity, and freelancer is a broad term for self-employed individuals offering services on a project basis.
Pre-revenue startup valuation for Seed Round Funding
Pre-revenue startup valuation for seed round funding is the process of determining the worth of a startup company that has not yet generated any significant revenue. This valuation is typically based on factors such as the strength of the team, the market potential of the product or service, the level of innovation, the competitive landscape, and the company's progress in product development or customer acquisition, among other relevant factors.
Walking Skeleton
- End to end
- Main architectural components
- Iterative
"UNICORN PROCESS"

Y Combinator
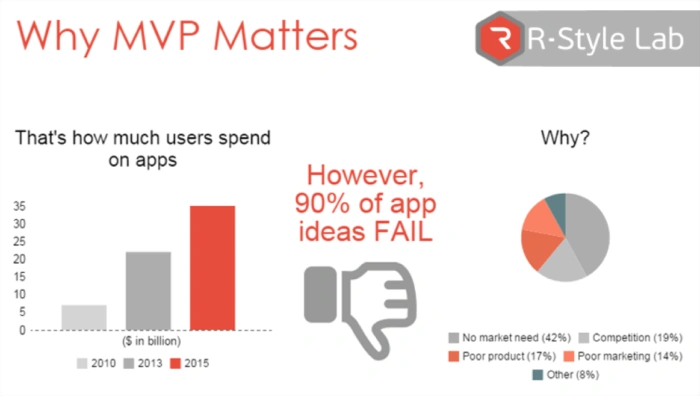

Stealth Mode?
People who live in fear of others stealing their ideas generally don’t have many good ideas.
Creativity is abundant. Execution is scarce
What prevails is not the best idea but the best implementation.
novelty arrives in a flash
- cheaper
- faster
- lighter
- easier
- more popular
https://startupstash.com/ https://www.producthunt.com/alternatives/techstars-entrepreneur-s-toolkit
“product smoke test” >> validation problem / vision statements
1. how do i balance running two llcs?
Balancing the management of two LLCs can be challenging, but here are some tips to help you manage both effectively:
Set clear priorities: Determine which LLC requires the most attention and prioritize your time accordingly. You may need to allocate more time to one LLC over the other based on their respective needs.
Delegate responsibilities: If possible, delegate responsibilities to trusted employees or partners. This can allow you to focus on high-level tasks and strategic planning.
Create a schedule: Create a schedule that outlines your daily, weekly, and monthly tasks for each LLC. Stick to the schedule as much as possible to stay organized and on track.
Use technology: Use technology to help you manage both LLCs efficiently. For example, use project management software to track tasks and deadlines, or use cloud-based bookkeeping software to manage finances.
Communicate effectively: Communicate regularly with employees, partners, and stakeholders of both LLCs to keep them informed and ensure that everyone is on the same page.
Get help if needed: Consider hiring a business consultant or coach to help you manage both LLCs effectively. They can provide guidance and support to help you balance your responsibilities and achieve your business goals.
Social Impact / Investor Appeal
A capped-profit company is a business structure that places a limit on the amount of profit its owners can earn. It combines aspects of for-profit and non-profit organizations. Here's a breakdown of the key features:
-
Profit Limit: There's a pre-determined maximum profit that owners can take out of the company. Any profits exceeding this cap are handled differently depending on the specific company's structure.
-
Profit Distribution: Surplus profits after reaching the cap can be directed towards various purposes:
- Reinvested in the company's growth and development.
- Used to fund social or charitable initiatives aligned with the company's mission.
- Channeled to a separate non-profit organization.
-
Motivation: Capped-profit companies are often established with a dual mission: achieving financial success while also creating a positive social impact. They aim to attract investors who are interested in both financial return and contributing to a cause.
-
Example: OpenAI, a research company focused on artificial intelligence, is a well-known example of a capped-profit company. Their goal is to ensure responsible development of AI while still attracting investment.
Benefits:
- Social Impact: Capped-profit companies can ensure profits are used for a cause beyond simply maximizing shareholder returns.
- Investor Appeal: The structure can attract investors who value both financial gain and social responsibility.
- Sustainable Growth: By reinvesting profits, the company can focus on long-term growth and stability.
Challenges:
- Complexity: Setting up and managing a capped-profit company can be more complex than a traditional for-profit structure.
- Transparency: Clear guidelines and oversight are needed to ensure the profit cap and distribution plan are followed fairly.
- Balancing Interests: Finding a balance between maximizing profits and social impact can be challenging.
Overall, capped-profit companies offer a unique approach to business, aiming to achieve financial success while also addressing social concerns.
Longevity
In the 1920s, the average lifespan of a company included in the S&P 500 (a list of the biggest 500 companies in the US) was 67 years. Today, it’s 15 years.
While it is true that many companies do not last past 100 years, the statement that less than 1% of companies survive beyond a century is an approximation and may not be entirely accurate. The longevity of a company depends on various factors such as industry dynamics, market conditions, management decisions, and adaptability to changing times. While it is challenging for companies to maintain their success over such a long period, there are certainly examples of companies that have surpassed the 100-year mark and continue to thrive.
Some well-known companies that have been in existence for more than a century include:
-
Coca-Cola: Founded in 1886, Coca-Cola is one of the most iconic and enduring brands in the world.
-
IBM: International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) was established in 1911 and has evolved over the years to become a leading technology company.
-
Ford Motor Company: Founded in 1903, Ford has played a significant role in the automotive industry and continues to be a major player today.
-
General Electric: Established in 1892, General Electric has been involved in various industries and has had a substantial impact on the global economy.
-
Procter & Gamble: P&G was founded in 1837 and has successfully built a diverse portfolio of consumer goods brands.
-
Siemens: Siemens, a multinational conglomerate, was founded in 1847 and operates in various sectors, including energy, healthcare, and transportation.
These are just a few examples, and there are numerous other companies that have achieved longevity. While it is true that many companies face challenges and do not survive for a century, it is difficult to provide an exact percentage or statistic regarding the survival rate of companies beyond the 100-year mark.
growth hacking
mendoza line
https://www.scalevp.com/blog/understanding-the-mendoza-line-for-saas-growth
s curve growth
Georgia Tech Startup Exchange https://launchx.com/ https://www.startupschool.org/
Internal growth focuses on improving the existing operational efficiency and cost efficiencies. On the other hand, external growth emphasizes branding, marketing, advertising, etc. Implementation of an internal growth strategy takes a longer period to yield results, while external growth is a relatively faster approach.
Mentor
https://www.npr.org/2019/10/25/773158390/how-to-find-a-mentor-and-make-it-work
is it right for me?
- review your business idea and start-up plan with trusted industry pros and mentors
Let’s build without burnout
the elephant in the room is that most start-ups fail
73% of founders burnout
31 million entrepreneurs in US 61 million employees work for entrepreneurs 47% of workforce
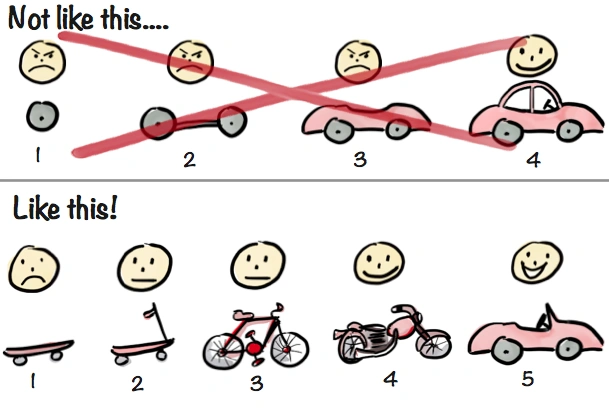
Minimum Viable Mockup
- stop chasing investors and have investors chase you instead because you have a customer list of willing and able buyers?
- skip the trial and error period and get a proven system that captures, nurtures, and converts your prospects?
(MLP) Minimum Loveable Product https://www.reforge.com/blog/the-product-strategy-stack
How long to create MVP?

- https://startup.exchange/
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/linkedin-top-voices-entrepreneurship-small-business-10-jordyn-dahl/
- https://www.harpersbazaar.com/uk/people-parties/bazaar-at-work/a38459809/what-makes-a-great-start-up-founder/
- https://startup.exchange/
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/1249901/leading-startup-accelerators-exits-usa/ Grow Startup
- Grow Customer List (platform agnostic)
- emails
- phone numbers
- names
- Pre-Sell minimum viable mock-up
Startup vs scaleup
identify primary needs
- customer acquisition
- talent
- funding
always double check the scope of the project to ensure that everyone is on the same page
https://www.1517fund.com/take-action
Kadence Core
findkadence.com/apply https://toolkit.techstars.com/
community, grants, investments
verified by user feedback
Customer acquisition and customer acquisition cost (CAC)
Venture capitalists want to see healthy user acquisition numbers.
Product Modelling
https://www.primary.app/solutions/product-modelling/
scaling-up / traction
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/getting-your-app-from-zero-critical-mass-marc-fischer/
- https://medium.com/immutable/critical-mass-937355e1f179
Success Stories
Growth Planning
- pivot
- S Corporation
| Legal Hurdles | description |
|---|---|
| Intellectual property | Startups need to be mindful of intellectual property issues when creating and sharing content on social media. This includes copyright, trademark, and patent issues. For example, if you use an image or video that is owned by someone else, you could be liable for copyright infringement. Similarly, if you use a logo or trademark that belongs to another company, you could be liable for trademark infringement. |
| Privacy | Startups also need to be aware of privacy considerations when using social media and marketing. This includes complying with data privacy laws, such as the GDPR and the CCPA, as well as protecting the privacy of your customers and users. For example, if you collect personal information from users, you may need to obtain their consent and provide them with notice of how their information will be used. |
| Advertising regulations | Startups need to comply with advertising regulations when creating and sharing ads on social media. This includes complying with the Federal Trade Commission's guidelines for sponsored content, which require disclosure of any material connections between the advertiser and the endorser. Startups also need to be aware of specific regulations that apply to their industry, such as those that apply to healthcare or financial services. |
Beta Testing
What a valuable user segment we just created together.
If you have a segment of users that are opted in to beta test new features for you, you can run some tech magic by flagging them in your database somewhere that makes sense as beta users.
When are writing your code, you can have a simple statement like this:
if (User.betaUser == true) {
showNewFeature()
}
Now you have the ability to roll out features only to those that want these early gems and you can speak with them directly for feedback. I’ve done this in the real world with outstanding results every single time and I always recommend this to startups that I advise.
In all of my experience in the fast paced world of tech startups, even in enterprise level companies with hundreds of millions of users, failing quickly is the safest path to product success. There are other ways to get there, but this removes the most risk from a time and cash flow perspective.
- Branding
- Company Vision
- Growth Planning
- Competitor Differentiation
- Market Research
- Legal Documents
src: 'https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eJdtzT11Li0'
Q1: how do I prioritize tasks as a startup?
Prioritizing tasks as a startup can be a challenging process, as there are typically many tasks to complete and limited resources available. Here are some steps that you can take to prioritize tasks effectively:
Define your goals and objectives: Start by defining your startup's goals and objectives. This will help you to focus on tasks that are aligned with your overall strategy.
Identify urgent and important tasks: Make a list of tasks that are urgent and important, and prioritize them accordingly. These tasks are typically time-sensitive and critical to your startup's success.
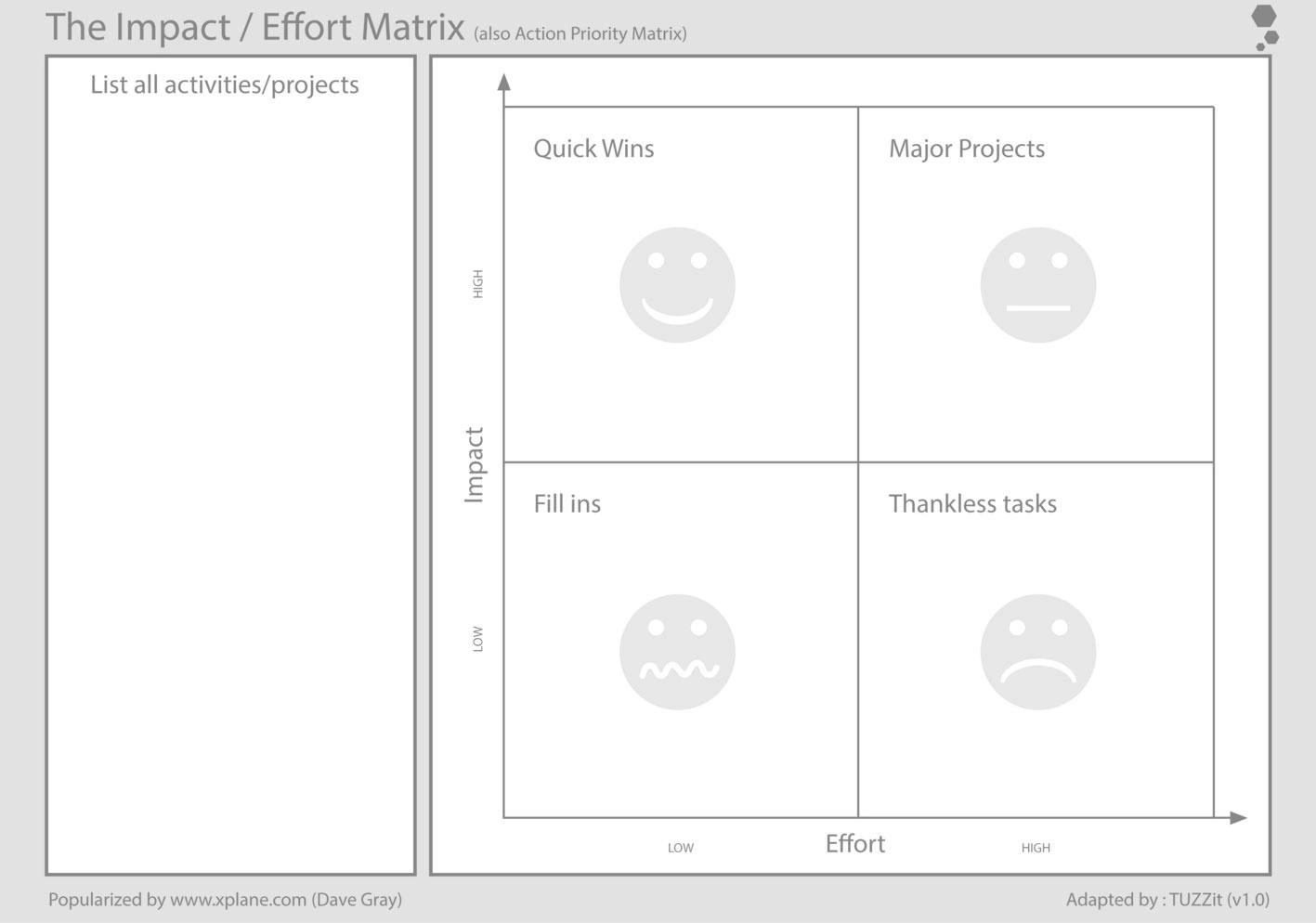
Consider the impact and effort required: Evaluate each task based on the impact it will have on your startup's goals and the effort required to complete it. Prioritize tasks that have a high impact and require less effort.
Use the Eisenhower Matrix: The Eisenhower Matrix is a popular tool for prioritizing tasks based on their urgency and importance. It involves dividing tasks into four quadrants: urgent and important, important but not urgent, urgent but not important, and neither urgent nor important. Prioritize tasks in the urgent and important quadrant first.
Involve your team: Involve your team in the prioritization process to gain their input and ensure that everyone is aligned on the priorities. This can also help to distribute tasks more effectively and increase accountability.
Review and adjust regularly: Regularly review and adjust your task priorities based on changes in your startup's goals, feedback from customers, and other factors. This will help to ensure that you are always focused on the most important tasks at any given time.
By following these steps, you can prioritize tasks effectively and ensure that your startup is focused on the tasks that are most critical to its success.

