Sales
Sales: selling products or services to customers. Prospecting, Lead Generation (identify potential customers), make sales calls, negotiate contracts, and close deals.
Table of Contents
Sales Process Management
Manage the entire sales process, from initial contact to closing deals. Track sales activities, follow up on leads, negotiate contracts, and handle objections to maximize conversion rates and achieve sales targets.
Collaboration
Collaborate with cross-functional teams, such as marketing, product development, and customer support, to align sales strategies, gather customer feedback, and ensure a positive customer experience.
Sales Reporting
Maintain accurate records of sales activities, customer interactions, and sales forecasts. Generate regular reports to analyze sales performance, identify trends, and provide insights for improvement.
Market Research
Stay updated on industry trends, competitor activities, and market dynamics. Conduct market research to identify new business opportunities, understand customer needs, and refine sales strategies accordingly.
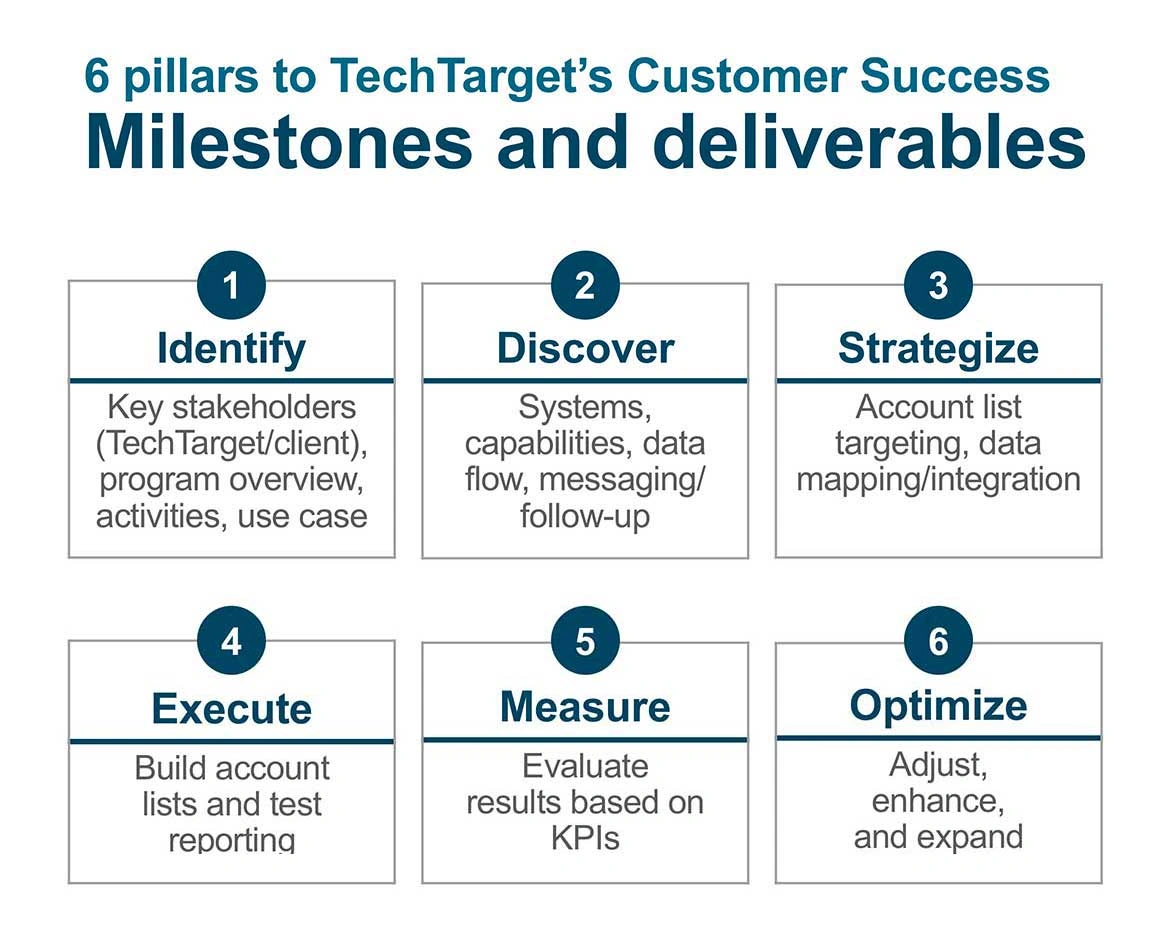
Customer Success
Support customers after the sale by addressing any post-sales concerns, ensuring customer satisfaction, and promoting upselling or cross-selling opportunities.
The Three Core Stages: Lead Gen, Lead Qual, to Close
This process is often visualized as a sales funnel, where a large number of potential leads are narrowed down to a few high-quality customers.
| SALES PROCESS | STAGE |
|---|---|
| Prospecting | This is the stage where the salesperson identifies potential customers who may be interested in the product or service. Prospecting can be done through a variety of methods, such as cold calling, referrals, or networking. |
| Lead Qualification | This is the stage where the salesperson determines if the potential customer is a good fit for the product or service. Qualifying involves asking questions to understand the customer's needs, budget, and decision-making process. |
| Requirements Gathering | Needs assessment: This is the stage where the salesperson works with the customer to identify their specific needs and pain points. The salesperson may ask questions, listen carefully to the customer's responses, and provide information about how the product or service can solve the customer's problems. |
| Sales Pitch | Explain benefits (Sales Presentation) This is the stage where the salesperson presents the product or service to the customer. The presentation may involve a demonstration of the product or service, a proposal outlining the benefits and features of the product or service, or a comparison with competitors. |
| Negotiation | (Handling objections) This is the stage where the salesperson addresses any objections or concerns that the customer may have about the product or service. The salesperson may provide additional information, offer a solution to the customer's concern, or provide social proof in the form of customer testimonials. |
| Closing | This is the stage where the salesperson asks for the customer's commitment to purchase the product or service. The salesperson may use techniques such as trial closes or assumptive closes to move the customer towards a decision. |
| Follow-up | This is the stage where the salesperson follows up with the customer after the sale to ensure that they are satisfied with the product or service, answer any questions or concerns, and potentially upsell or cross-sell additional products or services. |

Glossary of Sales Terms
Table of All Relevant Sales Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Sales Enablement | Sales enablement is the strategic, cross-functional process of providing sales professionals with the essential content, tools, training, and knowledge needed to engage buyers effectively and close more deals. |
| Cold Lead | A contact or business who has no prior interaction with your brand and shows no known intent to purchase. |
| Cold Prospect | Similar to a cold lead but actively being researched or contacted by a rep (email, call, DM). |
| Cold Outreach | Unsolicited outbound communication to someone who has never engaged with your brand. |
| Cold Call / Cold Email | Direct contact with a cold lead with the goal of generating awareness or booking a meeting. |
| Cold Pipeline / Cold Funnel | The earliest stage of pipeline where leads have no qualification and no engagement signals. |
| ICP (Ideal Customer Profile) | The archetype of your best-fit customer based on firmographics, needs, and budget. |
| Lead Sourcing | Finding potential leads manually or via tools (e.g., website audits, social media, databases). |
| Lead List Building | Compiling a structured list of prospects that match the ICP. |
| Lead Enrichment | Adding missing data to a lead (industry, revenue, pain points, tech stack). |
| Lead Research | Studying a prospect’s business, website, tech stack, and needs before outreach. |
| Lead Qualification | The earliest stage of pipeline where leads have no qualification and no engagement signals. |
| Lead Qualification | The earliest stage of pipeline where leads have no qualification and no engagement signals. |
| ICP (Ideal Customer Profile) | The archetype of your best-fit customer based on firmographics, needs, and budget. |
| Lead Sourcing | Finding potential leads manually or via tools (e.g., website audits, social media, databases). |
| Lead List Building | Compiling a structured list of prospects that match the ICP. |
| Lead Enrichment | Adding missing data to a lead (industry, revenue, pain points, tech stack). |
| Lead Research | Studying a prospect’s business, website, tech stack, and needs before outreach. |
| Prospecting Sequence | A structured multi-touch outreach plan: emails, calls, DMs, social engagement. |
| Top-of-Funnel (TOFU) Prospecting | Activities designed to generate awareness and first contact, not conversion. |
| Awareness Stage | The first stage in the customer journey where the goal is to make prospects aware your company exists. |
| Brand Awareness | The degree to which your target market recognizes and recalls your company. |
| Reach | The number of unique people exposed to your brand on any channel. |
| Impressions | The total number of times your content or brand was displayed (not unique). |
| Engagement Rate (ER%) | A measure of how much people interact (likes, reactions, comments, shares). |
| Share of Voice (SOV) | Your brand’s visibility compared to competitors across social or search. |
| Top-of-Funnel (TOFU) Marketing | Marketing efforts designed to attract and expose new audiences to the brand. Examples: social posts, blogs, short videos, awareness ads. |
| Brand Positioning | How your brand is perceived relative to competitors. |
| Brand Messaging | The core narrative: value prop, tagline, tone, and story. |
| Marketing Qualified Impression (MQI) | Awareness-level metric indicating content generated visibility from the target audience. |
| MQL (Marketing Qualified Lead) | A lead who has shown light engagement or interest but is not yet sales-ready. |
| SQL (Sales Qualified Lead) | A lead vetted by sales as having intent, need, and potential fit. |
| Inquiry / Hand-Raiser | A cold or warm lead who takes a small action (download, submit form, click, reply). |
| Lead Nurturing | Follow-up content designed to move awareness-level contacts into consideration. |
| Outbound | Proactive outreach initiated by sales reps (calls, emails, DMs). |
| Touchpoint | Any interaction between your team and the prospect. |
| Cadence | Structured sequence of touchpoints over a period of time. |
| Connect Rate | Percentage of attempts that result in actual conversations. |
| Inside Sales Channels | Inside sales channels refer to the process of selling products directly to customers through digital and telephonic means, without face-to-face interaction. This approach typically involves activities like cold calling, outbound emails, and social selling. Inside sales teams use these methods to engage with prospects, qualify leads, and close deals remotely. This strategy allows startups to reach a broader audience without the need for a large, on-the-ground sales force, making it a cost-effective option for many SaaS companies. |
| Contract | A contract is the final document that you’ve been working toward so you can begin efforts on the new project. The contract will take into account the various details as specified in the original request for information and may very well be adjusted in a number of ways, based on the parameters that you went through when developing the request for proposal. A contract serves as a legal agreement that your organization and the other party sign. The contract will specify payments and timing of work to be done, as well as any reporting requirements and the duties of the contracting parties. Expanding your knowledge and skills to move ahead in your career is not a task to take lightly, but it will definitely set you apart from others as you take on more responsibilities in managing projects for your company. In fact, when it comes to project management, while it will take some time to learn the ropes, you can feel confident that with experience will come greater confidence and the ability to sort out the contract’s needs and requirements in keeping with what your team can deliver. Becoming more familiar with terms such as RFI, RFP, SOW, MSA and how they are different from one another will prepare you to work out the terms of a contract for your next project. |
| Inside sales | the practice of selling products or services remotely, typically through phone, email, or online communication channels, rather than in person. This approach is often used by companies that sell to a large number of customers or operate in geographically dispersed markets. Inside sales teams may use a variety of tools and technologies to manage their sales process, such as customer relationship management (CRM) software, video conferencing platforms, and automated email marketing tools. They may also rely on data analytics and market research to identify potential customers and tailor their sales approach accordingly. One of the advantages of inside sales is that it allows companies to reach a much larger audience than traditional face-to-face sales methods, while also reducing travel and other associated costs. Inside sales can also provide a more flexible and convenient experience for customers, who can interact with sales representatives at their own convenience. However, it does require a strong focus on building relationships and engaging with customers through remote channels, which can be challenging for some salespeople. |
| Lead Qualification | identifying potential clients who are a good fit for your services and determining whether they are ready to engage in a project. |
| Lumpy followup | In phone sales, a lumpy follow-up is an inconsistent and poorly timed series of contact attempts—characterized by large, unpredictable gaps followed by sudden, overwhelming bursts of calls—that fails to maintain the necessary, predictable cadence to nurture a prospect effectively. |
| MSA (Master Service Agreement) | A Master Services Agreement or MSA serves to define how your company and the other company will work together. One key element of this document will be the terms of payment. The decisions you make on payments timing and amounts will naturally involve your CFO and accounting department, such as whether it would be best to offer a discounted rate to win a particular job or whether your revenue cycle is strong enough to withstand later payment terms that you would otherwise object to. |
| Overhead | In sales, overhead refers to the ongoing expenses that a business incurs in order to operate and maintain its sales operations, but which are not directly tied to the production or delivery of the product or service being sold. These expenses may include things like rent, utilities, salaries and benefits for sales staff and support personnel, office equipment and supplies, marketing and advertising costs, travel expenses, and other general administrative expenses. |
| Requirements: | A representation of the application from the perspective of the user, or the business. |
| Value Propositions | a cost vs. benefits formula that is evaluated subconsciously and automatically in your prospect’s mind when they encounter your marketing touchpoint. Think of it as an equation, balancing the perceived benefits and perceived cost of transacting with your brand. |
| RFI (Request for Information) | Receiving a Request for Information will often be the first way you learn about the organization that you might soon be contracting with to do work. The RFI is used to explore options before creating a contract for the project. A company or other organization will issue an RFI to gain information about which businesses are best suited to take on the job, as well as meet internal requirements for competitive bidding on all jobs. This is your time to shine. The existence of an RFI should indicate that the bidding process will be fair to all companies that want to throw their hat into the ring. Examine the RFI carefully to determine if your company can meet its objectives within budget. |
| RFP (Request for Proposal) | A Request for Proposal is a document that is used to obtain comprehensive proposals from capable and interested companies, to demonstrate their skills, experience and knowledge will enable them to take on the described project. You will often receive an RFP after reading the advanced details in the RFI. It’s important to take your time and do your due diligence when developing an RFI, which will include budget details, timing of work and a thorough description of the project scope. All requirements of the project will be addressed, with you showing the specific steps or solutions you will follow from day one to completion. |
| SOW (Statement of Work) | The Statement of Work is a document that the companies will use to describe what will be happening during the project. For example, the SOW should indicate all items that will be delivered, the timeline or timelines involved and when invoicing will take place. You are spelling out everything that will be done, and the terms may be done for a fixed cost or on the basis of the materials and time expended, subject to negotiations, of course. The SOW declares what expectations and underlying assumptions are associated with the project. Your organization will be legally obligated to deliver what you agreed to in the SOW’s terms when it comes time to formalize the contract. |
| Specifications: | A representation of the application from the perspective of the engineering team. |
| Internal applications | software applications that are designed to be used within an organization's own network or infrastructure, and are not intended to be accessed over the public internet. These applications may include line-of-business (LOB) applications such as ERP, CRM, HR, finance, and other enterprise applications that are critical for the organization's day-to-day operations. |
| Lead / Contact | A person or company that has shown some interest in your product but has not been qualified. |
| Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL) | A lead that marketing has deemed ready for sales based on engagement (e.g., downloaded a key asset, visited pricing page). |
| Sales Qualified Lead (SQL) | A lead that a sales rep has qualified and accepts as a genuine potential customer. |
| Opportunity | A qualified lead that has a clear need, budget, and timeline; it's a potential deal in the pipeline. |
| Account | A company or organization that is a customer or prospect. |
| Buying Committee | The group of multiple stakeholders within a prospect's company involved in the purchase decision. |
| Champion | An internal advocate within the prospect's company who supports your solution. |
| Decision Maker | The person with the ultimate authority to approve the purchase. |
| Buyer Persona | A semi-fictional representation of your ideal customer based on market research and real data. |
| Sales Funnel | Pipeline |
| Sales Pipeline | The stages a prospect goes through in the sales process. It represents the active deals being worked on. |
| Sales Forecast | A sales forecast is a prediction of what future sales (revenue/deals) are expected to close based on historical data, market trends, and other factors in a given period. This typically includes a breakdown of expected sales by product or service, as well as by geographic region or customer segment. |
| Cold Calling | The act of initiating contact with a potential customer who has no prior relationship with your company. |
| Cold Email | A unsolicited email sent to a potential customer to generate interest. |
| Demo | Demonstration |
| Proof of Concept (POC) | A limited trial or test to prove that your product works in the prospect's specific environment. |
| Value Proposition | A clear statement that explains how your product solves customers' problems, delivers specific benefits, and why it's better than alternatives. |
| Objection | A concern or reason for hesitation raised by a prospect that prevents them from buying. |
| Quote (Quotation) | A formal document stating the fixed price for the proposed products or services. |
| Proposal | A formal document outlining the solution, scope, timeline, and cost, often used to secure a deal. |
| Contract (Agreement) | A legally binding document between the seller and the buyer outlining the terms of the sale. |
| Close-Lost | An opportunity that did not result in a sale. |
| Close-Won | An opportunity that successfully became a paying customer. |
| Annual Contract Value (ACV) | The average annualized revenue per customer contract. |
| Total Contract Value (TCV) | The total value of a contract over its entire lifespan. |
| Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) | The predictable revenue a company can expect to receive every month. |
| Average Selling Price (ASP) | The average revenue received per sold unit of a product or service. |
| Conversion Rate | The percentage of leads that move from one stage of the funnel to the next (e.g., MQL to SQL). |
| Sales Cycle Length | The average amount of time it takes to close a deal from first contact to signed contract. |
| Net Promoter Score (NPS) | A measure of customer loyalty and satisfaction. |
| Sales Rollout | launch event, promotion, press release |
| Skim Pricing | Charging premium prices to target high-value clients, focusing on exclusivity and delivering superior value. |
| Competitive Pricing | Setting prices in line with competitors to appeal to a broad client base and not "stand out" pricing-wise |
| Penetration Pricing | Offering lower prices to attract clients quickly, build market share, or enter competitive markets. In some cases known as "loss leader" if is sold at or under cost |
| Bundle Pricing | Can combine them, aka: Penetration (or "loss leader") in one service, but bundled with a Skim priced service) |
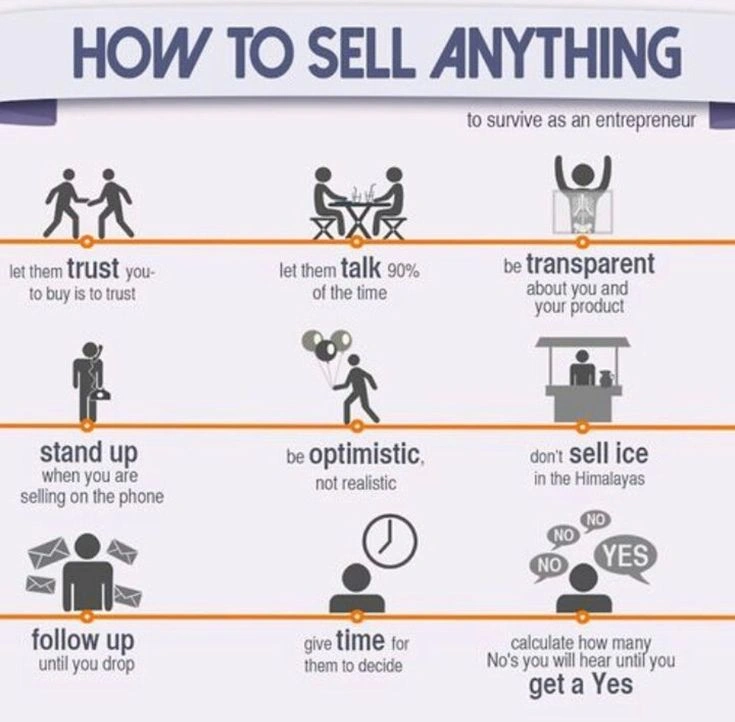
Consultative Selling

Sales Ethics
Sales ethics refers to the principles and guidelines that govern ethical behavior in the field of sales and marketing. It involves conducting sales activities in an honest, transparent, and responsible manner, while respecting the rights and interests of customers.
One important aspect of sales ethics is understanding the distinction between persuasion and manipulation. Persuasion involves using logical arguments, presenting relevant information, and appealing to the customer's needs and desires in order to influence their decision-making process. It aims to provide customers with the necessary information to make informed choices that align with their best interests.
On the other hand, manipulation involves using deceptive or unethical tactics to exploit the vulnerabilities or lack of knowledge of customers. It often involves misleading or withholding information, using high-pressure tactics, or creating a false sense of urgency to manipulate customers into making a decision that may not be in their best interest.
In the context of sales ethics, it is crucial to ensure that persuasion is conducted ethically and responsibly. Here are some guidelines to persuade the interested in an ethical manner:
-
Transparency and Honesty: Be transparent about the features, benefits, limitations, and pricing of the product or service. Provide accurate and truthful information to help customers make informed decisions.
-
Customer-Centric Approach: Understand the needs and preferences of the customer. Listen actively, ask questions, and tailor your approach to address their specific requirements. Focus on how the product or service can genuinely benefit the customer.
-
Education and Information: Provide objective and comprehensive information about the product or service. Highlight its unique value proposition and how it can meet the customer's needs. Avoid exaggerations or false claims.
-
Respect Boundaries: Respect the customer's decision-making process and personal boundaries. Avoid using aggressive or manipulative tactics to pressure them into making a purchase.
-
Long-Term Relationships: Prioritize building long-term relationships with customers based on trust and mutual benefit. Focus on providing value and excellent customer service even after the sale is made.
-
Ethical Standards: Adhere to legal and industry regulations, as well as your organization's code of ethics. Avoid engaging in activities that could harm customers or undermine their trust.
By following these ethical guidelines, sales professionals can build trust, maintain customer satisfaction, and contribute to a positive reputation for themselves and their organization.
Cross-Selling
Cross-selling is a valuable technique that can maximize sales opportunities and enhance customer satisfaction. By training your salesman on cross-selling strategies, you can encourage customers to purchase additional products or services that complement their initial purchase. Here are a few cross-selling opportunities you can explore:
Remember, successful cross-selling requires understanding the client's needs and aligning the additional products or services with their goals. Encourage your salesman to actively listen to customers, identify pain points, and propose relevant solutions that can enhance their overall experience and achieve their business objectives.
cross-selling to existing clients
Certainly! Here are some sales and marketing processes and terms that can help with cross-selling to existing clients and nurturing long-term relationships for continued service purchases:
-
Account Mapping: Conduct an in-depth analysis of the client's organization to identify additional departments, business units, or individuals who may benefit from your services. Map out the relationships and decision-making structures within the client's company to understand how to approach cross-selling opportunities effectively.
-
Cross-Selling/Cross-Promotion: Identify complementary services or products that align with the client's needs and offer cross-selling opportunities. Develop targeted campaigns or personalized recommendations to introduce these offerings to the client. Cross-promotion can involve promoting related services or products through various marketing channels to create awareness and generate interest.
-
Upselling: Present higher-tier or advanced versions of your existing services that provide added value to the client. Highlight the enhanced features, benefits, and potential ROI to encourage the client to upgrade their service package.
-
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Utilize a CRM system to track and manage client interactions, preferences, and purchase history. This information helps tailor marketing and sales efforts and ensures personalized and relevant communication with the client.
-
Customer Segmentation: Segment your client base based on various criteria such as industry, company size, or service usage. This allows you to develop targeted marketing campaigns and communication strategies that cater to the specific needs and pain points of each segment.
-
Thought Leadership Content: Develop and share insightful content such as blogs, whitepapers, case studies, or webinars that showcase your expertise and provide value to the client. Position yourself as a thought leader in your industry and establish credibility, which can lead to increased trust and loyalty from clients.
-
Referral Programs: Encourage satisfied clients to refer your services to their network by implementing a referral program. Offer incentives or rewards to clients who refer new business, such as discounts, exclusive access, or monetary incentives.
-
Customer Success Managers: Assign dedicated customer success managers to key accounts. These individuals act as trusted advisors, proactively engaging with clients to understand their evolving needs, address concerns, and identify opportunities for additional services. They play a crucial role in nurturing long-term relationships and ensuring customer satisfaction.
-
Regular Check-ins and Reviews: Schedule periodic check-ins and project reviews to assess the client's satisfaction, gather feedback, and identify areas for improvement. Use these opportunities to discuss their future goals and challenges, and explore how your services can continue to support them.
-
Client Loyalty Programs: Implement loyalty programs that reward clients for their ongoing partnership and purchases. These programs can include exclusive benefits, discounts, or access to special events or resources, fostering a sense of loyalty and incentivizing continued engagement.
Remember, the key is to consistently demonstrate the value of your services, maintain open lines of communication, and actively seek opportunities to support your clients' evolving needs. By employing these processes and terms, you can effectively cross-sell to existing clients and cultivate long-term relationships for ongoing service purchases.
Solution architecture
Solution architecture refers to the process of designing and defining the structure, components, and interactions of a software solution to meet specific business requirements. It involves creating a blueprint or plan that outlines how different software elements will work together to address the needs of an organization.
The role of a solution architect is to understand the business requirements and constraints, analyze existing systems and infrastructure, and design a solution that aligns with the organization's goals and objectives. The solution architect considers factors such as scalability, performance, security, reliability, and cost-effectiveness when designing the solution.
The solution architecture typically includes the following elements:
-
Requirements Analysis: The solution architect works closely with stakeholders to gather and understand the business requirements, functional and non-functional requirements, and constraints.
-
System Design: Based on the requirements, the solution architect designs the overall system architecture, including the high-level structure, components, and their interactions. This may involve selecting appropriate technologies, platforms, and frameworks.
-
Integration and Interoperability: Solution architecture involves determining how different components of the solution will integrate and interact with each other, as well as with existing systems or third-party applications. This includes defining data exchange formats, communication protocols, and interfaces.
-
Performance and Scalability: The solution architect considers factors such as system performance, scalability, and capacity planning to ensure that the solution can handle the expected workload and user demands.
-
Security: Solution architecture addresses security requirements by designing appropriate security measures, such as access controls, authentication mechanisms, data encryption, and secure communication protocols.
-
Reliability and Resilience: The solution architect designs the solution to be reliable and resilient, ensuring that it can recover from failures, handle exceptions, and continue to function in the event of disruptions or system failures.
-
Documentation: Throughout the solution architecture process, the architect creates documentation, including architectural diagrams, design specifications, and guidelines, to communicate the solution design to stakeholders, development teams, and other relevant parties.
Overall, solution architecture aims to provide a comprehensive plan for developing a software solution that meets the business needs, aligns with the organization's goals, and considers various technical and operational aspects.
Philosophy
In China, there is a saying, "the more you talk, the more mistakes you make."
- Engaging with customers to understand their technology needs and preferences
- Demonstrating and explaining the features and benefits of technology products and services
- Recommending appropriate products and services based on customer needs and budget
- Closing sales and processing transactions
- Following up with customers after the sale to ensure satisfaction and promote customer retention
- Keeping up-to-date with the latest technology trends and developments
- Collaborating with other sales associates, managers, and technical support staff to provide a seamless customer experience
- Account Manager: An Account Manager is responsible for managing relationships with existing customers. ensure customer satisfaction, identify opportunities for upselling or cross-selling, and work to renew customer contracts.
- Handling inbound sales and product inquiries by telephone, email, and chat
- prepare e-commerce sales pitch presentations for local brick and mortar businesses
- understand & communicate the value realization gap.
ebooks ● How to ebooks ● Industry case studies ● InformationI'm about product or service pamphlet ● how to bring the solution to market ● streamlined project workflow ○ template ○ customization ○ delivery ○ retainer- WHAT IS THE LIFETIME VALUE FOR THE PRODUCT? future-proof ■ support ■ upgrades ■ blogging ■ advertising ○ word of mouth references ● quality control Average sales cycle who??
- 3 meetings for requirements ○ board members & owners
- 4 days market research & content drafting ○ CREATE A FORM ■ save me time ○ keywords ○ text for each page
- 3 weeks for design and development
- 1 week edits & approval
- 1 week launch prep & email campaign
- support and hosting retainers
- continue to engage client
B2C
Local SEL Campaign Management Creative Design Project Planning
Web E-Commerce
Effectively manage your web store metrics with their powerful reporting. Modular eCommerce solution that allows for an open and flexible system architecture. With third party integrations and built in features like upsell and cross-sell you can build fantastic eCommerce websites.
-
glgroup / glgresearch
Revenue Sharing E-Commerce Consulting Agreement
title: Retail Store Consulting Agreement Example
subtitle: Store Web Development Contract
url: /admin/legal/consulting-agreements/Consulting Agreement with E-Commerce Revenue Sharing.docx
Making it RAIN
- Rapport
- Aspirations and Afflictions
- Impact
- New Reality
small talk
- What's going on in your business these days?
- Location based: local weather, local news, sport teams, good restaurants, city/region
- Company based: admire recent social media post, admire their office artwork
- Give compliments:
10 Steps to a Successful First Interaction!
Step into business entity Identify who you are talking to (ie business owner / employee) Build Rapport talking about random everyday topics Start conversing about general business Listen to their problems Understand their opportunities Identify their need Reveal that you are a digital marketing mastermind!!! Say that you love their products / services and want to help them grow Ask if they are available to set up a meeting
Sales Pipeline
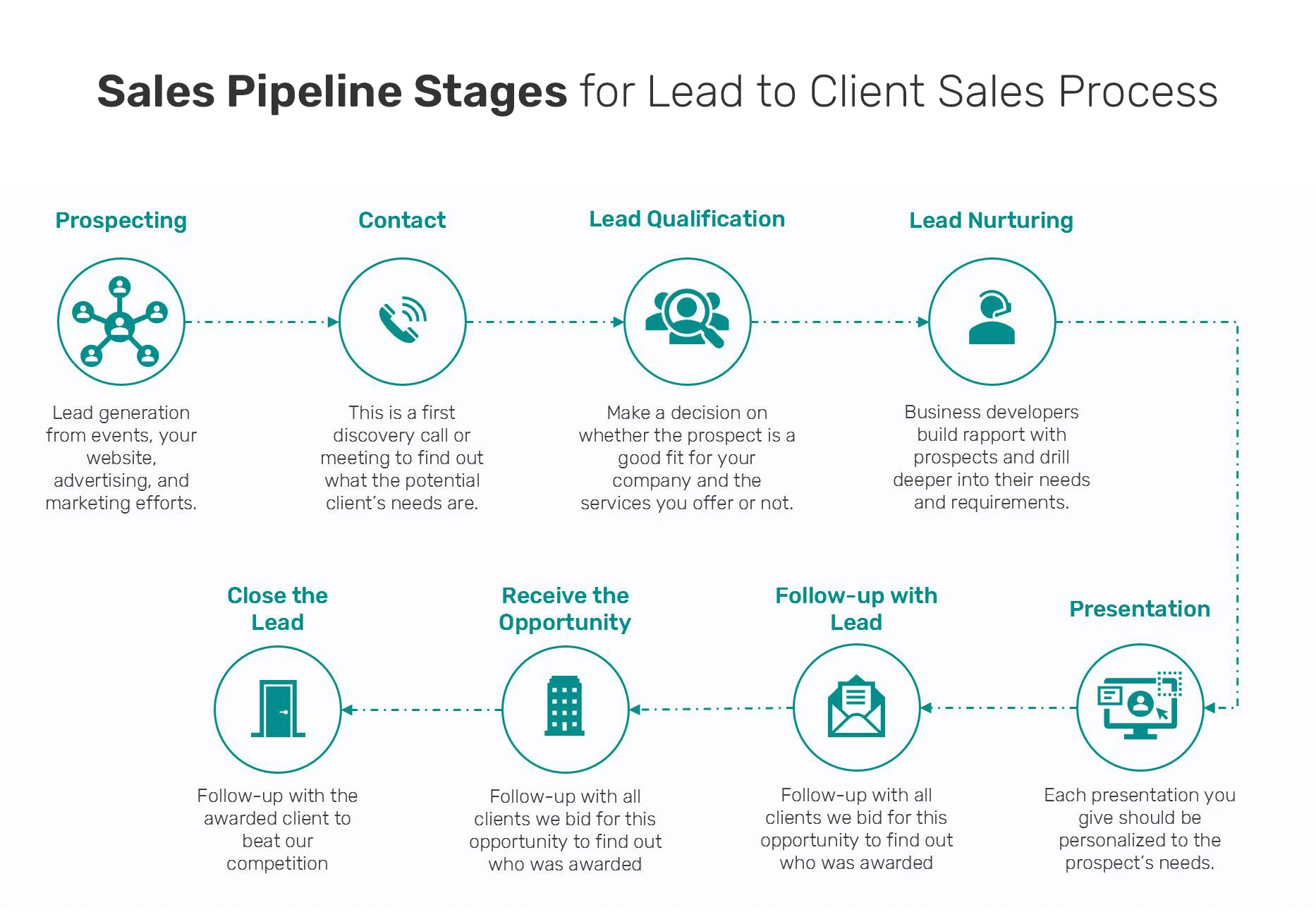
https://www.shellblack.com/whiteboard/salesforce-opportunities-part-2-creating-a-sales-process/
Defining your sales stages: Key strategies for managing your pipeline
Most sales professionals have been trained to follow a sales process that includes defined steps for assessing a deal's potential and moving the deal forward. Any effective sales process model is designed to:
- Build rapport with the customer
- Uncover customer needs, goals, and pain points
- Identify options that could solve the customer's problems
- Propose solutions that will deliver the outcome the customer wants
- Come to an agreement and close the deal
Whether you're working for a small, medium, or enterprise-sized business, the basic process is the same. Sales organizations typically track deals through six or seven stages,
For each stage, you should also define required outcomes to advance the deal from one stage to the next. By defining both stages and outcomes, you'll gain greater visibility into the true health and value of your pipeline while giving your sales team a roadmap to success.
For example, a B2B product company---regardless of size---might map its stages and outcomes like this:
Common Growth Fears
- Being forced to add services that the firm doesn't want to support
- Overburdening staff already at max capacity
- Budget concerns
- Changing technology and the implementation process
4 Contract
Submit the contract and final proposal to the customer and begin the final negotiation process.
Outcomes
- Negotiation concluded
- Contract terms/conditions agreed upon
- Contract submitted for signature
5 Win/Loss
Record the final disposition of the opportunity, along with any next steps.
Outcomes
- Contract signed
- Contract not signed
Next steps
By combining workflows and stage alerts, you can help sales managers keep a sharp eye on the progress of every team member, quickly identify any breakdown in the sales process, and determine how to best solve the problem with coaching or re-tasking. Your sales team can also use these features to monitor progress, open tasks for each stage, and stay on track to effectively maximize every opportunity.
Consider setting up these simple but highly effective alerts using workflow:
- Lead alert -- Notifies specified users or groups when a lead remains in status "pending" for more than a specified number of days
- Stage alert -- Notifies specified users or groups when an opportunity remains in a particular stage for more than a specified number of days
- Update open opportunity close date -- Notifies the opportunity owner when an open opportunity is approaching or is past its scheduled close date
- Stage alert -- Closed Lost
- Stage alert -- Closed Won
Summary
Sales Workflow should provide for unified collaboration to ensure sales process alignment and execution.
- Keep it simple
- Create specific outcomes for each stage
It pays to take the time to define the stages and then monitor the progress of those stages against your industry's or company's identified best practices to ensure maximum pipeline throughput.
Contact Info
Customer list is high value
Vision
Value
- Acquisition
- total visits
- unique visits
- hourly/daily/weekly/monthly/quarterly/yearly unique visits
- Geolocation: Country/Region/City/State/DMA
- Time Zones
- demographics
- tld domains of origin
- Engagement -404 page errors
- single page visit abandons
- content metrics
- total page views
- time spent per visit
- trends
- trends by hierarchy
- page flow previous/next path analysis
- reloads
- clicks
- entry pages
- exit pages
- Persuasion
- Conversion
- Advocacy
- Retention
Recommendations
- Boost developer productivity by empowering their teams with integrated tools that help them navigate and use vast code repositories from a single interface.
- Mitigate software security risks by encouraging their teams to try application security tools that detect and prevent unsecure code early in the development process.
- Improve the developer onboarding experience, and reduce toil by encouraging their teams to experiment with browser-based integrated development environments (IDEs).
Strategic Planning
-
By 2025, 30% of large enterprises will use browser-based integrated development environments to streamline development workflows and enable better manageability.
-
By 2026, more than 75% of organizations will pay for curated open-source artifacts, up from less than 1% in 2022.
-
By 2026, application security will become the most desired software engineering skill for more than 75% of organizations, up from less than 20% in 2022.
How to Make a website for free
Upscaling your Web Dev Biz
https://riptutorial.com/html/topic/10000004/upscaling-your-web-development-business
- https://www.intercom.com/blog/podcasts/shop-whats-in-store/
- https://marmalead.com/
- https://www.aeropay.com/admin/legal/privacy-policy
- https://www.aeropay.com/
"When it comes to selling and servicing agricultural and industrial equipment, the last twenty years has taught us plenty. Operators throughout Central Queensland demand quality, not only famous names, but equipment that can handle the toughest job, and stay reliable. That time IS money and that our service people have to be quick to get your equipment back into action. You'll know the Milne Bros name by reputation. Chances are you've dealt with us over the years. Well, now, Milne Bros has developed an even wider Sales, Service and Spare Parts service for an amazing array of equipment. Please take a moment to scan this directory for services that'll help YOU. And then call. We'd like to hear from you."
https://www.wix.com/studio/community/partners/build-then-market
Getting Gigs online
FREELANCER
DM: Hey there, I’m a front end developer managing a consulting business out of New Jersey since 2014. I’ve gone through your project requirements and it’s a match for my skills. let’s get it done together.
LinkedIn
BONUS – Connecting with LinkedIn:
There is a way you can send private messages on LinkedIn to anyone for free, even if you don’t have them as a connection. It’s also a great way to find and connect with your market in general... It probably deserves it’s own post, but here is the short version.
Step 1: Log on to LinkedIn and under interests, search for groups in your market. You will likely find lots... Join those groups... SIDE NOTE: Sometimes if there is someone I REALLY want to get in contact with I’ll use the tips above to google their name... If I can’t find the email, I’ll search the person’s name plus LinkedIn (for example, Jane Smith LinkedIn). Click their LinkedIn profile, and see the groups they joined. Then Ill join those groups too so I can message them.
Step 2: Once accepted to these groups, if you click people from within the group you can send a private message without needing to be contacts yet. All you have to do is go to the group, click on the persons name, and click the dropdown next to where it says “follow..”. Then click send message. Another great way to connect is to read some of the treads people are commenting on in the group. Then you can reply to peoples comments either publicly or privately. If you do this, and you ask a question or make a comment related to what the people are talking about it is a really good way to connect.