Junior Software Engineer Interview
Start by clearly defining the technical skills, programming languages, frameworks, and other qualifications necessary for the software developer role. This will serve as a benchmark against which you can evaluate candidates' skills.
An interview typically includes both technical and soft skills.
-
Company Slide Presentation: This part usually involves the interviewer or a representative from the company presenting an overview of the organization, its culture, and the specific role the candidate is applying for. This helps the candidate understand the company's mission, values, and the work environment.
-
Soft Skills Questions: These questions aim to evaluate the candidate's interpersonal and communication abilities. Examples include asking about how the candidate handles conflicts, adapts to change, and collaborates with team members. The STAR (Situation, Task, Action, Result) method is often used to structure answers, providing context and outcomes of past experiences.
-
Question: “In our startup, you’ll work with non-technical teams like marketing. Describe a time you explained a technical concept to someone without a coding background.” (Tests ability to bridge technical and non-technical worlds.)
-
Follow-up if no example: “How would you approach explaining a bug to a marketing teammate?”
-
Technical Skills Questions: These questions focus on assessing the candidate's knowledge of programming languages, data structures, algorithms, and software development concepts. Common topics include explaining the differences between data structures like hash tables and dictionaries, implementing a binary search tree, and understanding concepts such as recursion, dynamic programming, and big O notation.
-
Coding Test: This is a crucial part of the interview process where candidates are asked to solve coding problems either on a whiteboard or through a take-home assignment. The test evaluates the candidate's ability to write clean, efficient, and maintainable code. Examples of coding challenges might include optimizing sorting algorithms for large datasets or implementing a graph data structure.
-
Behavioral Interview Questions: These questions are designed to understand how the candidate has handled past situations in their work experience. For example, candidates might be asked to describe a project they worked on, how they managed bugs and issues, and how they prioritized their workload when working on multiple projects simultaneously.
-
Live Coding Interview: In this part, candidates are asked to write code in real-time, either on a whiteboard or a shared coding environment. This helps assess their problem-solving skills and coding proficiency under pressure.
-
Take-Home Coding Test: Some interviews include a take-home coding assignment where candidates have a set amount of time to complete a coding challenge. This allows candidates to demonstrate their coding skills in a more relaxed environment.
Each of these components helps the hiring team evaluate the candidate's suitability for the role, ensuring they have the necessary technical and soft skills to succeed as a junior software engineer.
technical assessment
Design a technical assessment or coding challenge that allows candidates to showcase their coding abilities and problem-solving skills. This could involve solving coding problems, building small projects, or reviewing and debugging existing code. Assess their ability to write clean, efficient, and maintainable code.
Review GitHub profile
Request candidates to provide samples of their past work, such as projects they have contributed to or personal coding projects. Review their code quality, structure, and documentation to assess their proficiency and coding best practices.
Skill Gaps
Walk me through how you’d debug a failing API call in a language you’re familiar with
How would you learn a new framework if we needed it for a project?
we need team members that accomplish our goals quickly and efficiently
-[ ] Define a function? It's a reusable block of logic. -[ ] Define a class? A blueprint for creating objects. -[ ] Define an object? An instance of a class with specific values. -[ ] Define a variable? A named container that stores data.
Ethical Dilemma Questions
You discover a severe privacy flaw in a legacy codebase that could expose user data. The fix is complex, risky, and would delay a major product launch. What is your priority, and how do you communicate this?
- Focus: Data security, risk assessment, technical debt vs. user safety.
Your team is tasked with developing an algorithm for content moderation (e.g., for user-generated reviews). You realize the training data has inherent biases that could lead to unfair suppression of certain viewpoints or demographics. What actions do you take?
- Focus: Algorithmic bias, fairness in AI, data ethics, advocating for more inclusive data sets.
A client requests a custom data integration that, while technically feasible, could inadvertently create a 'shadow profile' of users by combining data points they wouldn't expect to be linked. How do you approach this request?
- Focus: Data privacy by design, unintended data aggregation, advocating for user transparency and consent.
You are asked to implement a tracking mechanism that is intentionally difficult for users to opt-out of (a 'dark pattern'). Your manager insists it's a business requirement. How do you handle this?
- Focus: Professional ethics vs. managerial pressure, user experience, advocating for ethical design patterns.
Your manager asks you to quickly push a feature to production without thorough testing to meet a tight deadline. You suspect there might be critical bugs that could impact data integrity or user experience. What do you do?
- Focus: Code quality, professional responsibility, risk to users/data, advocating for proper testing procedures.
guesstimate interview questions
understanding of development complexity, realistic timelines, and the factors that influence them.
Core Feature/App Development Time Guesstimates:
- "Imagine you need to build a fully functional contact form for a website, including client-side validation, sending data to a backend, and storing it in a database. From scratch, how long do you estimate it would take a single full-stack developer?"
- Follow-up: "What are the biggest time sinks you anticipate for this?"
- "How long do you think it would take a single developer to build a basic To-Do List mobile app (create, read, update, delete tasks) for iOS and Android, connected to a simple backend for data storage?"
- Follow-up: "What factors would make this project take significantly longer?"
- "If you were tasked with creating a simple login/registration system (user accounts, password hashing, session management) for a web application, how many hours or days do you estimate it would take?"
- Follow-up: "What are the security considerations that might add time?"
- "Estimate the time required for a single developer to implement a 'Forgot Password' feature with email verification for an existing web application."
- Follow-up: "What external services or integrations would you need to consider?"
- "How long would it take to build a basic blogging platform (with user accounts, post creation, commenting, and a simple public view) for a single full-stack developer?"
- Follow-up: "What would be the most challenging part of this project?"
Feature Extension/Complexity Guesstimates:
- "If you've built a basic e-commerce product page, how much additional time do you think it would take to add a user review and rating system to it?"
- Follow-up: "What are the key components of a reliable rating system?"
- "Suppose you have a simple static website. How long would it take to integrate a real-time chat widget (like a customer support chat) that connects to a backend service?"
- Follow-up: "What technologies would you consider for real-time communication?"
- "You've developed a simple photo-sharing app. How much extra time would you estimate to add a feature for users to 'like' photos and see a count of likes?"
- Follow-up: "How would you handle showing likes in real-time or near real-time?"
- "How long would it take to implement user profile pages (displaying basic user info and their public posts) if you already have a user database?"
- Follow-up: "What kind of data would you need to fetch to display on these profiles?"
- "Estimate the time to add a search functionality to a web application that allows users to search across various content types (e.g., posts, users, comments)."
- Follow-up: "Would you consider a full-text search engine, and why or why not?"
Deployment & Maintenance Guesstimates:
- "Once a simple full-stack app is developed, how long do you anticipate it would take to deploy it to a cloud platform (like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure) and make it publicly accessible for the first time?"
- Follow-up: "What are the steps involved in a first-time deployment?"
- "If a critical bug is reported in production for a feature you developed, how long do you estimate it would take to identify, fix, and deploy the hotfix?"
- Follow-up: "What tools or processes would help you find the bug faster?"
- "How much time per week do you think a full-stack developer typically spends on debugging and testing compared to writing new code?"
- Follow-up: "Why is that balance important?"
- "Estimate the time required to set up continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) for a simple full-stack application from scratch."
- Follow-up: "What are the benefits of CI/CD for a development team?"
- "If a client requests a seemingly small UI change on the frontend, but it requires adjustments to the backend API, what's your initial estimate for how long that seemingly 'small' change might take?"
- Follow-up: "What are the hidden complexities in seemingly simple changes?"
Key for You:
- Listen to their thought process: The "how" they arrive at the number is more important than the number itself. Do they break it down? Do they consider different layers (frontend, backend, database)? Do they think about testing, deployment, and edge cases?
- Encourage assumptions: Prompt them to state their assumptions about technology stack, team size (assume single developer for most), and level of polish.
- Look for factors: Do they mention things like design, testing, debugging, environment setup, learning curves, or only the "happy path" coding?
- The "Why": Their explanations will give you insight into their understanding of the full development lifecycle.
situational
- "You're assigned to lead a new software development project. How would you go about gathering project requirements and ensuring clear communication with stakeholders throughout the development process?"
- You're tasked with optimizing the performance of a slow-performing web application. How would you approach identifying the bottlenecks and improving the application's performance?"
- "You're working on a complex software project that requires integrating multiple third-party APIs. How would you ensure the reliability and stability of the integrations, considering potential failure points and error handling?"
"You're tasked with designing a scalable and fault-tolerant architecture for a high-traffic web application. What factors would you consider, and what technologies or design patterns would you employ to achieve these goals?"
Scenario: "A customer reports a critical issue in your software. How would you handle the situation, including troubleshooting, communication with the customer, and coordinating with the development team to resolve the problem?"
Scenario: "You're working on a distributed team with members located in different time zones. How would you ensure effective collaboration and communication within the team, considering the time zone differences?"
Scenario: "You're assigned to mentor a junior software engineer who is new to the team. How would you approach mentoring and guiding them to help them grow their skills and become an effective contributor?"
behavioral
How did you handle a project where you didn’t know the tech?” to map their skills. If they say “I don’t know” or lack examples, follow up with, “What steps would you take to learn this skill if needed?” to test initiative. This approach ensures you hire someone who can grow into the role despite gaps.
Stress management
“Our dev team often pushes code under tight timelines—describe a time you debugged a critical issue while the clock was ticking.”
Independence
“We need coders who can figure out complex bugs solo—give an example of when you tackled a tricky technical problem on your own.”
Cross-functional
“You’ll work with designers and PMs to ship features—tell me about a time you collaborated with non-technical teammates to meet a goal.”
-
"Imagine you're working on a project with tight deadlines, and your team discovers a critical bug in the code that is affecting the production environment. What steps would you take to address the issue quickly and effectively?"
Ans: 1. alert code maintainer 2.
- alert the team and manager
- try to solve it myself
-
Tell me about a time when you had to explain complex technical concepts to a non-technical audience.
How did you ensure effective communication, and how did you adapt your approach to suit their level of understanding?
are you comfortable working full-stack?
- What have you been working on?
- "Describe the project you've worked on that you're most proud of. What did you do that worked out particularly well?”
- Describe your programming habits
- Source control
- Testing
- Variable/file/class/whatever naming
- Application architecture decisions
- Marketing Skills
- Email Marketing software skills
- SEO skills
- blogging skills
- CI / DevOps
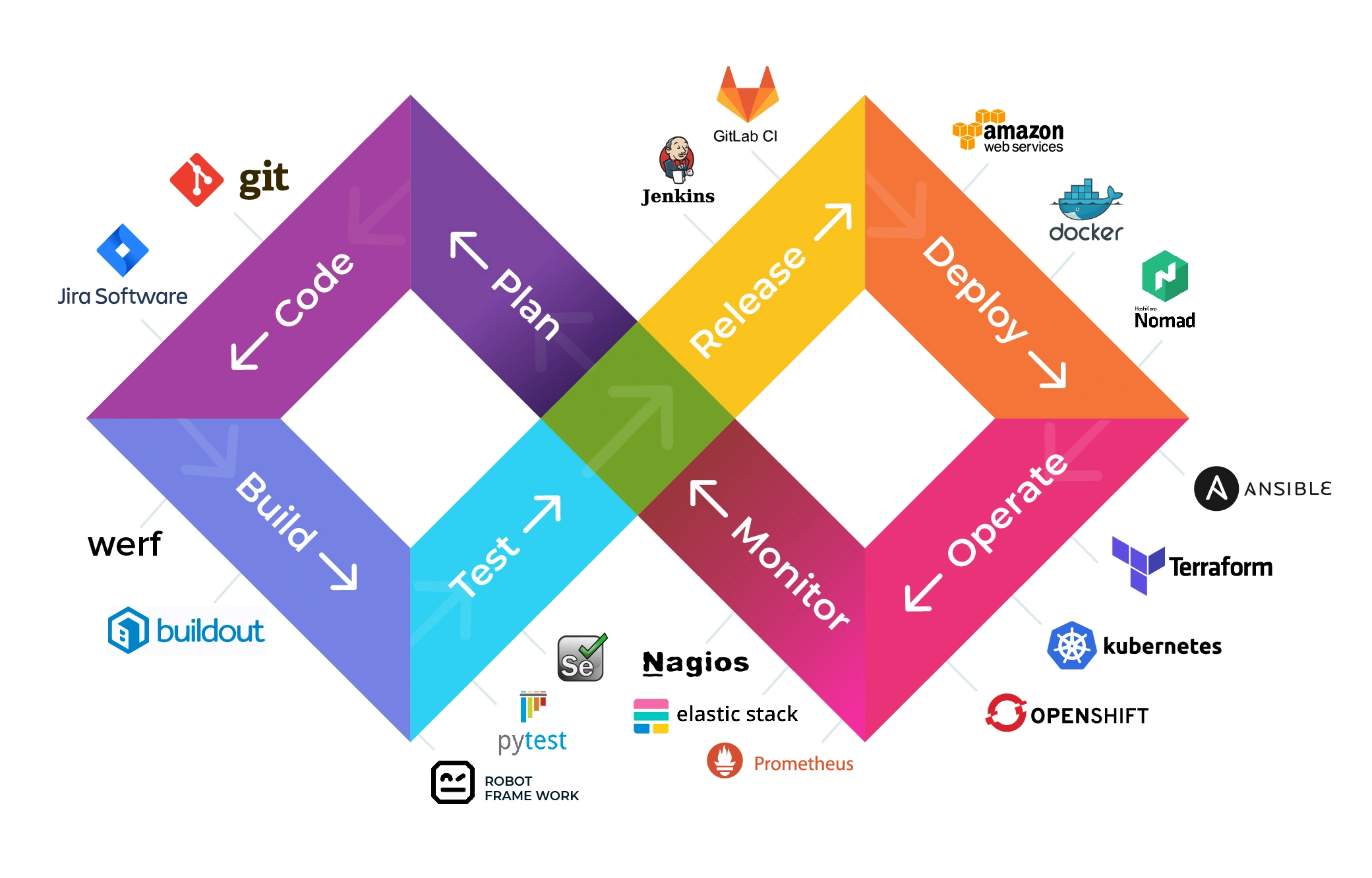
The DevOps Lifecycle is an infinite iteration of:
- Plan
- Code
- Build
- Test
- Release
- Deploy
- Operate
- Monitor
- what are you looking for from working here?
- Discuss your resume
- what do you do for fun
Describe your programming habits
- Source control
- Testing
- Variable/file/class/whatever naming
- Application architecture decisions
How do you approach your documentation?
Version Control System
How do you use source control to manage releases?
What is your experience with version control systems such as Git?
- Repository
- Repository Cloning
- Code Commit
- Branching
- Merging
Tools
How would you handle an emergency release?
FRONT END
What level of experience do you have with web design and development?
Are you able to create nice website designs in Photoshop / Illustrator? Are you able to convert PSDs to pixel perfect HTML & CSS?
I occasionally use Photoshop/illustrator for small tasks and light editing.
I would probably use Figma to create website designs.
I'm seeking a role where the bulk of my time is spent convert PSDs to HTML/CSS, however since I already know how to code if I'm doing a side hustle website from scratch I would skip the prototyping step and jump straight into coding.
I'm not able to write PHP, I choose to work on front end.
I have experience working in DevOps on large projects doing systems engineering. in 2015. At PointRoll, now renamed to Sizmek, I was working on a scrum team configuring web applications, virtual machines, and servers. so I believe I could handle any sys admin task given to me easily.
What technologies do you love that you don't see others in the industry doing yet?
AFrame.io, webVR
Please share links to work of yours that has gone live and a description of what you did and challenges you overcame. You may also include links to your code repositories on git or other sites
bit.ly/abhi-ray-portfolio
What will building for the web look like in 5 years?
"Static websites are an evolutionary dead end. Extremely fast, inexpensive cloud functions mean it doesn't make sense to spend developer time on brittle pre-rendering when you can easily deploy dynamic code that scales forever. Doing work is what computers are for! I think the future of web development is fully dynamic, and the development model will be centered on cloud functions talking to low latency managed databases, all deployed with Infra-as-Code (IaC). No more janky spinners or client-side fetches to render a page. Just pure cloud functions returning markup, often as real-time WebSocket streams, flowing straight from the backend to the frontend. That's why we created arc.codes and begin.com to build modern dynamic apps."
Define Refactoring
what is N-Tier Architecture?
What is debugging?
- How do you approach testing and debugging hybrid mobile apps? What tools and techniques do you use?
Agile development methodologies
These questions are designed to gauge your experience with Agile development methodologies and your ability to work collaboratively in a development team. It's important to be able to showcase your technical knowledge, as well as your ability to communicate effectively with your team and stakeholders. Make sure to prepare examples from your previous work experience that demonstrate your ability to work in an Agile environment and deliver high-quality front-end code.
- What is your experience with Agile development methodologies?
- How do you prioritize the tasks on your backlog?
- How do you ensure that your code is maintainable and scalable?
- How do you approach testing in an Agile development environment?
- How do you measure the success of your work as a front-end developer?
app development frameworks
- Which hybrid mobile app development frameworks have you used, and which do you prefer? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each?
How do you stay up-to-date with the latest trends in technologies and best practices in software development? What resources do you use to continue learning and growing in your craft?
Can you describe some of the projects you've worked on?
How do you manage app data and storage? What strategies do you use to optimize performance and minimize bandwidth usage?
How do you ensure the security of apps and protect them against security threats, such as data breaches and hacking?
How do you collaborate with other developers, designers, and stakeholders in a hybrid mobile app development project? What communication and project management tools do you use to stay organized and efficient?
- "How do you use technology to improve your productivity and organization? What tools or applications do you find most helpful?" (This assesses their ability to leverage technology to enhance their organizational skills.)
The Fundamental Paradox
Professional developers have identified a cruel irony: vibe coding works best for those who don't need it. Experienced developers can guide AI tools effectively and catch their mistakes because they already understand the domain deeply.
This creates a devastating catch for junior developers:
- They need experience to use AI tools effectively
- But vibe coding prevents them from gaining that experience
- They end up trapped in a cycle of dependency without real skills
Vibe Coding skills degradation happens across multiple dimensions:
No Debugging Abilities: When AI-generated code fails, vibe coders can't identify or fix the problems. They become dependent on AI for every technical challenge, never developing the problem-solving skills that separate real developers from code generators.
No Architecture Understanding: They can't make informed technical decisions about system design, performance optimization, or scalability because they don't understand the underlying principles.
No Code Review Skills: They can't assess code quality, security vulnerabilities, or maintainability because they've never learned to read code properly.
No Fundamental Knowledge: They miss the foundation that allows developers to adapt to new technologies, understand trade-offs, and make architectural decisions.
Experienced engineers report reviewing significantly more code than in previous years, but struggling to maintain quality standards when so much of it is AI-generated. The volume of code increases, but the understanding decreases.
The problems compound because:
- Poor Code Quality: AI generates verbose, poorly structured code that's difficult to maintain
- Missing Edge Cases: AI often ignores error handling and unusual scenarios
- Performance Issues: Generated code frequently has bottlenecks and inefficiencies
- No Documentation: AI-generated code typically lacks proper documentation
- Security Vulnerabilities: AI doesn't think adversarially like human attackers