ai-coding

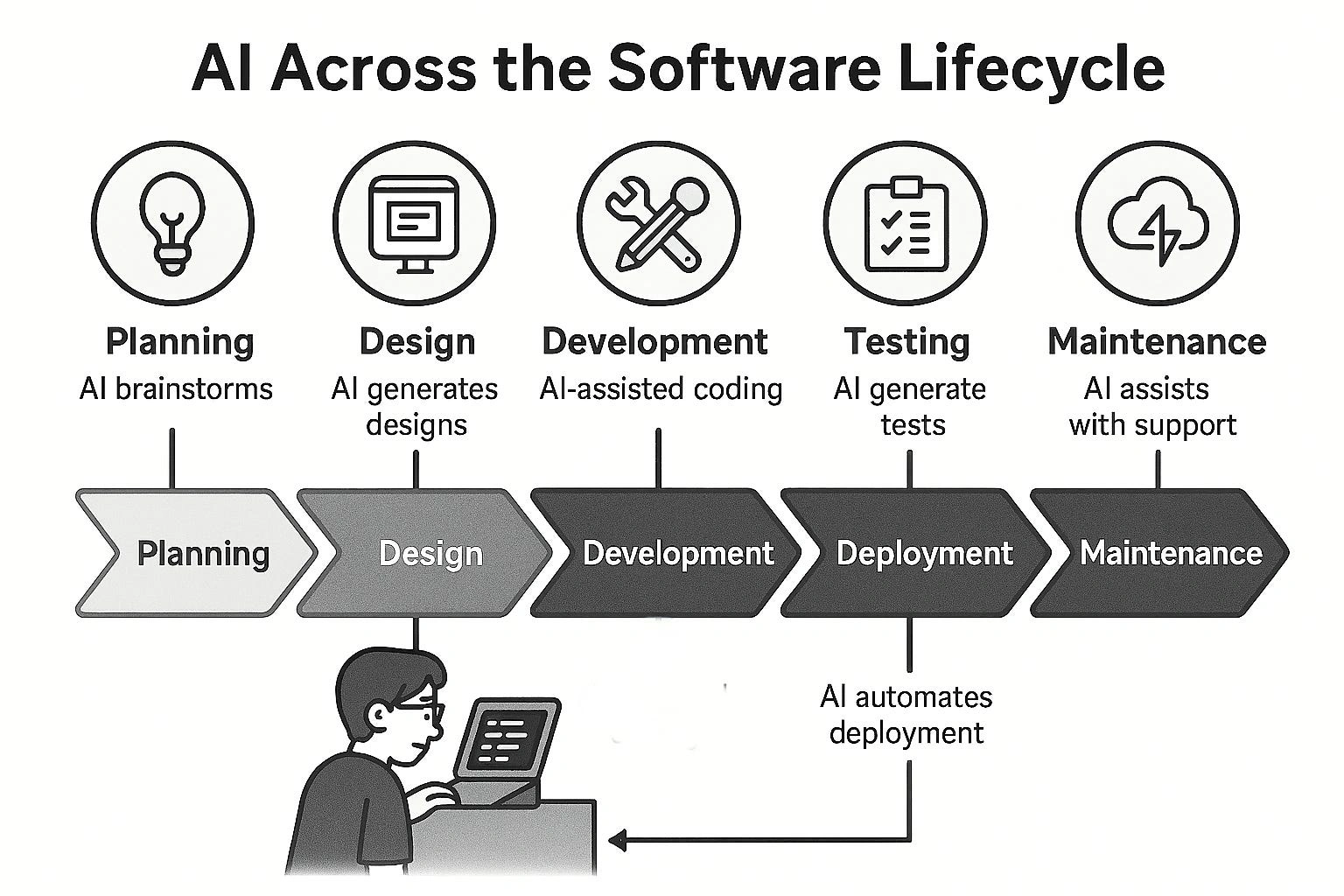
The advent of sophisticated AI coding assistants, such as GitHub Copilot and Kiro, has introduced a transformative dimension to project documentation. Historically, documentation primarily served human developers, offering explanations and guidelines in natural language. However, with AI tools now capable of generating and modifying code, a new imperative has emerged: the need for machine-interpretable instructions. These specialized documents guide AI behavior, ensuring that the code produced aligns precisely with project-specific conventions, architectural patterns, and predefined quality standards. This marks a significant paradigm shift, moving documentation beyond passive information repositories to active, prescriptive guidance systems that directly influence automated development processes.
This evolution from descriptive to prescriptive documentation is a notable trend. Traditional documents explain what a project is and how humans should interact with it. In contrast, AI-driven documentation explicitly dictates how the AI should operate and what rules it must follow during code generation or modification. This requires authors to consider not only human clarity but also the unambiguous, structured interpretation by machines. The quality of AI-generated output becomes directly contingent upon the precision and comprehensiveness of these prescriptive documents.
Github Copilot
more AI creates more bugs > developer jobs will go up not down
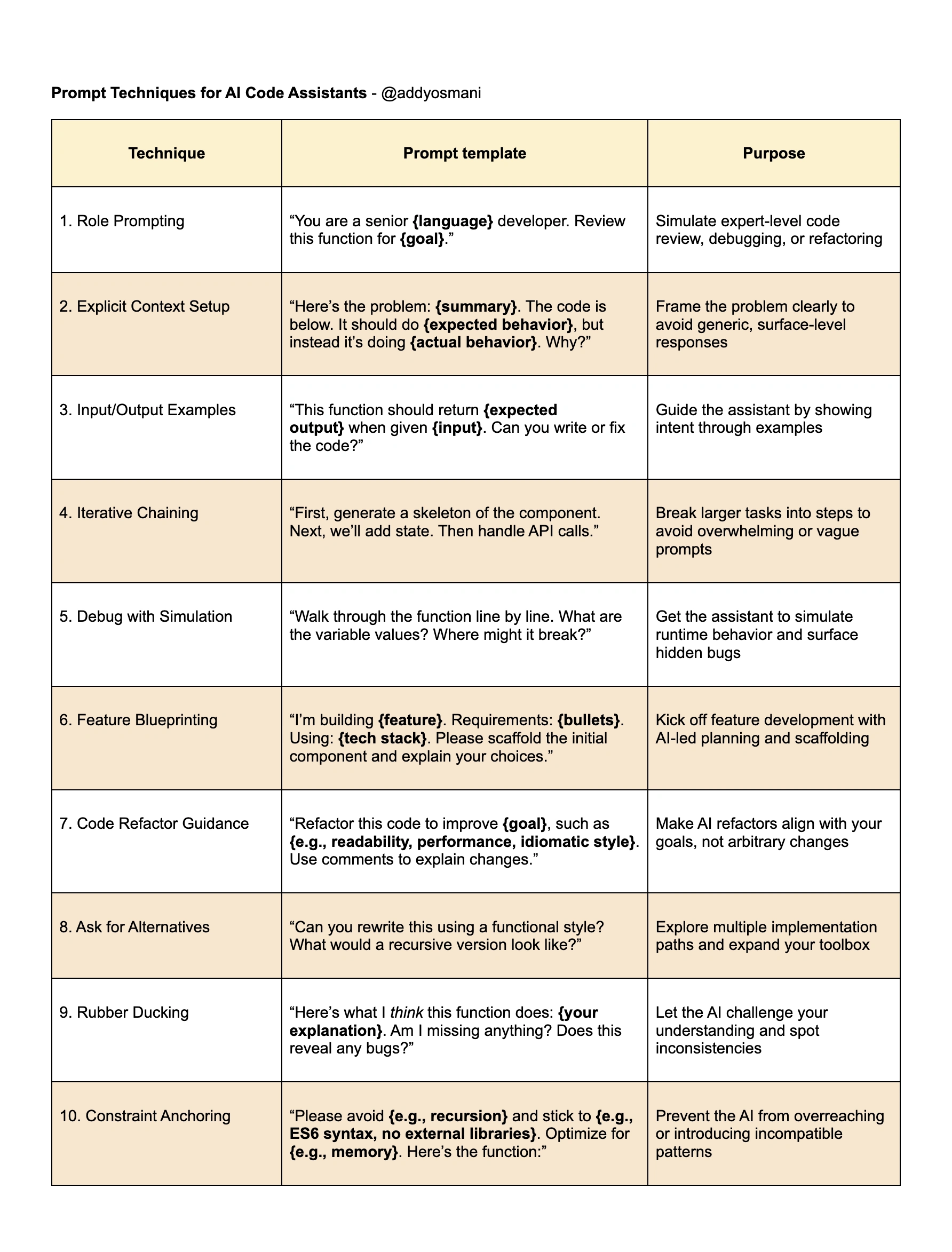
Prompt Engineering
Stochastic response
The model's output is always randomly determined
Chain of thought prompting
- To encourage the Al model to be factual or correct by forcing it to follow a series of steps in its "reasoning"
AI-powered code completion tool developed by OpenAI in collaboration with GitHub
Duet
https://cloud.google.com/duet-ai/docs/discover/developers#ide