NPM
npm is the standard for installing global executable tools, while yarn is the standard for managing your project's dependencies.
NPM Setup
PATH setup for NPM export PATH="/usr/bin:$PATH"
export PATH="/home/your-username/.npm-global/bin:\$PATH" # Add npm bin PATH
Verify
which npm
npm root -g
List Global Packages
npm list --g
Updating npm dependencies
Find out the packages that need to be updated
npm outdated
npm outdated -g --depth=0
Update local packages according to package.json
npm update
Upgrade packages manually
npm update [-g] [<pkg>...]
npm install --save[-dev] <package_name>@latest
Alternatively, you can use npm-check to perform an interactive upgrade:
npm-check -u --skip-unused
Locking package versions
Starting from npm@5 a new package-lock.json file is
automatically generated when using npm install commands, to ensure a
reproducible dependency tree and avoid unwanted package updates.
If you use a previous npm version, it is recommended to use npm shrinkwrap to lock down all your dependencies version:
npm shrinkwrap --dev
This will create a file npm-shrinkwrap.json alongside your package.json files.
Do not forget to run shrinkwrap each time you manually update your dependencies!
aliases: up, upgrade
Setup
Proxy Variables
npm config ls -l | grep config
initialize new project
- Create an empty directory and initialize it as npm using npm init.
- It will ask you to construct your package.json file.
- If you feel lazy like me to hit enter many times, then go with shorthand script npm init --yes.
License Question
- ISC is default
if you do not wish to grant others the right to use a private or unpublished package under any terms:
{ "license": "UNLICENSED" }
Consider also setting "private": true to prevent accidental publication.
npm install
-S or --save if you need the package for the application to run -D or --save-dev if it's for testing
NPX
- Executing one-off commands
- Run commands with different Node.js versions
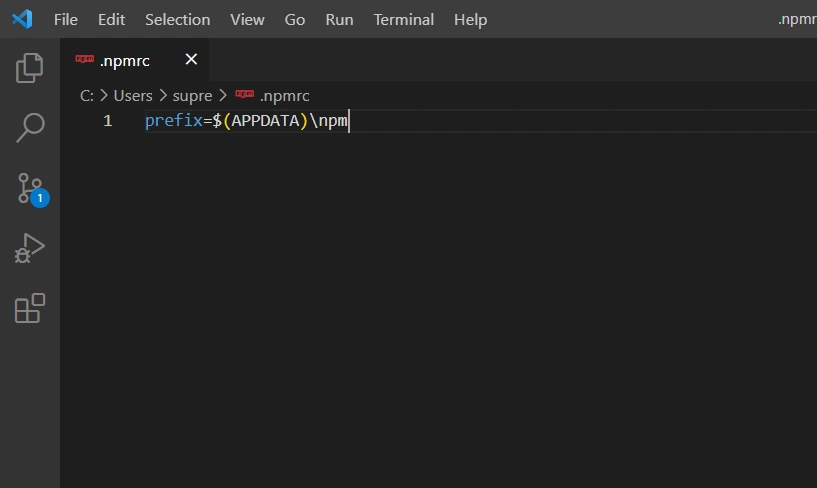
your customizable NPM profile
npm Dependencies
- Dev vs Prod: Your app needs Dev dependencies to build and test, and Prod dependencies to run.
- Direct vs Indirect: Your app only explicitly requires Direct dependencies, but your quality, legal and security reviews should cover the (larger number of) Indirect dependencies as well.
- Package vs Version: Your deployed app is impacted by the specific Version of each dependency, but your project relies on each dependent Package to keep working.
- Logical vs Disk: The Logical tree of dependencies in your app can change substantially when installed on Disk, be sure to versions that were actually installed.
- Path vs Unique: When counting your dependencies, be sure to separate the number of unique dependencies from dependency paths, to properly estimate the size of a task or problem.
Loading from node_modules Folders
Loading from node_modules Folders#
If the module identifier passed to require() is not a core module, and does not begin with '/', '../', or './', then Node.js starts at the parent directory of the current module, and adds /node_modules, and attempts to load the module from that location. Node.js will not append node_modules to a path already ending in node_modules.
If it is not found there, then it moves to the parent directory, and so on, until the root of the file system is reached.
For example, if the file at '/home/ry/projects/foo.js' called require('bar.js'), then Node.js would look in the following locations, in this order:
/home/ry/projects/node_modules/bar.js/home/ry/node_modules/bar.js/home/node_modules/bar.js/node_modules/bar.js
This allows programs to localize their dependencies, so that they do not clash.
It is possible to require specific files or sub modules distributed with a module by including a path suffix after the module name. For instance require('example-module/path/to/file') would resolve path/to/file relative to where example-module is located. The suffixed path follows the same module resolution semantics.