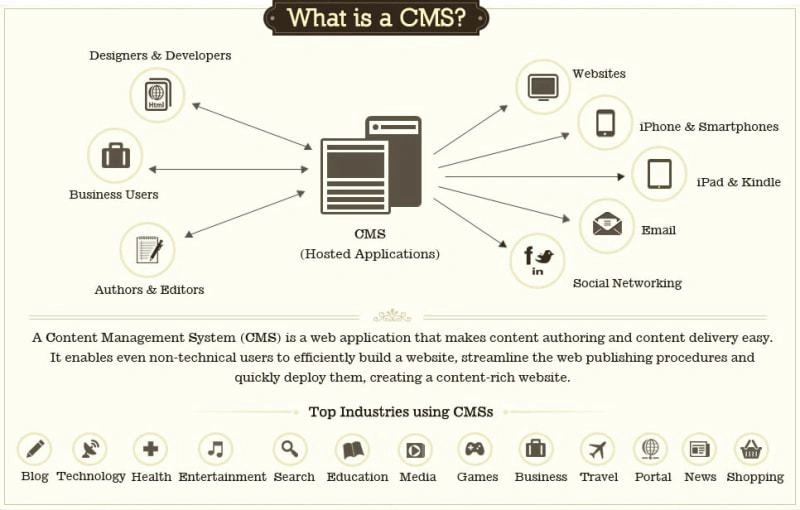
CMS
Table of Contents
content entry
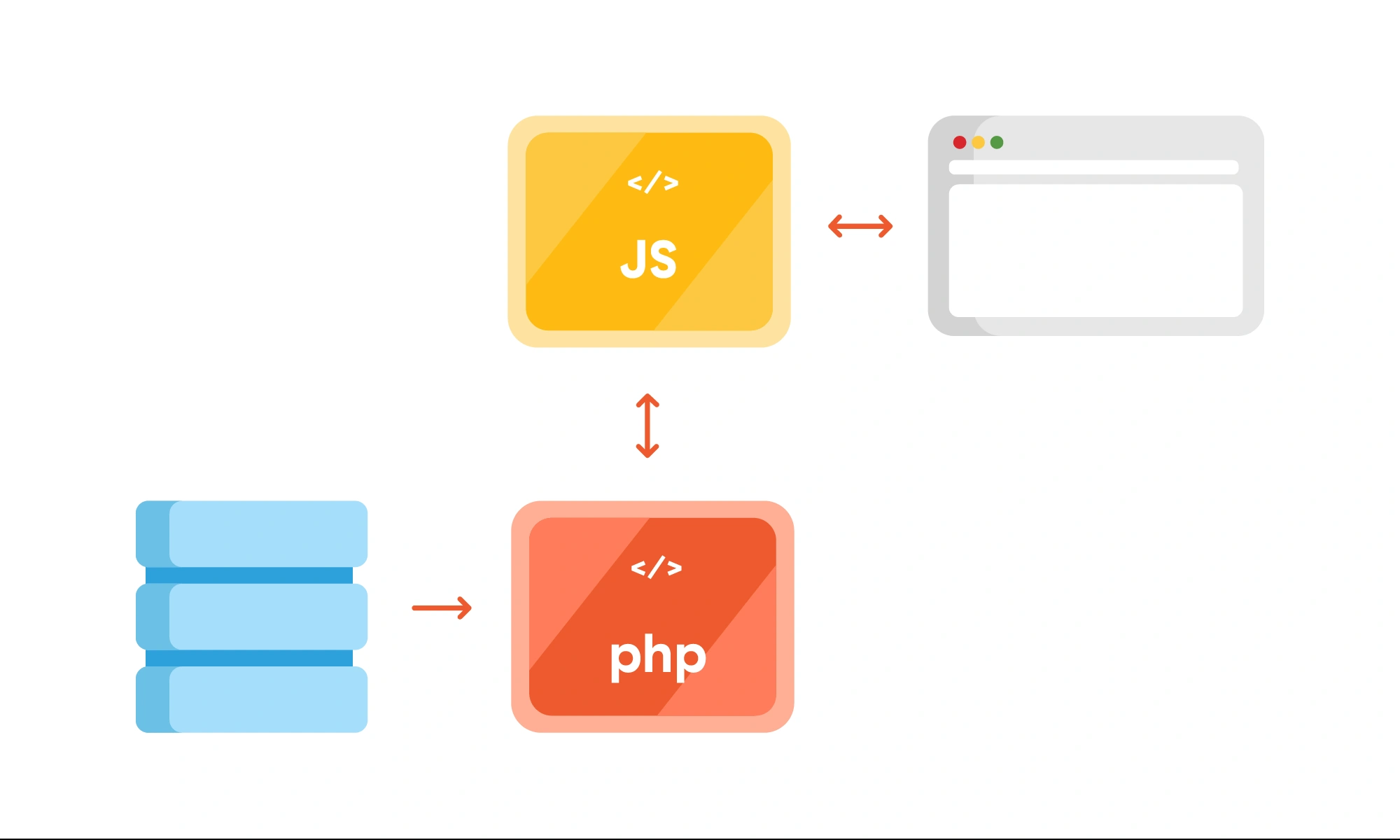
Headless CMS
Blogging
- 3x posts per week
- News
- Opinion
- Humor
- Controversy
- Blog Posts with Intention
- Advertorial
- Advertisement + editorial
AEM
-
Component Development: Creating and configuring AEM components using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to build the front-end structure and functionality of web pages. This involves designing reusable components and templates that can be easily integrated into AEM.
-
Template Creation: Developing AEM templates that define the overall structure and layout of web pages. This includes designing and coding HTML and CSS to create the base layout and containers for AEM components.
-
Content Integration: Integrating the front-end components and templates with AEM's content management system. This involves mapping the AEM components to the appropriate content fields and ensuring the proper rendering and display of content.
-
Style Customization: Customizing the appearance and styling of AEM components and templates to match the desired design and branding guidelines. This includes modifying CSS styles, applying themes, and ensuring consistency across the website or web application.
-
Responsive Design: Implementing responsive design techniques to ensure that the website or web application is optimized for various devices and screen sizes. This involves using media queries, flexible grids, and other responsive design practices to adapt the layout and styling based on the device being used.
-
Front-End Optimization: Optimizing the performance and loading speed of the website or web application. This includes minifying CSS and JavaScript files, optimizing image assets, and implementing caching strategies to improve overall performance.
-
Cross-Browser Compatibility: Testing and ensuring that the website or web application works correctly across different web browsers and browser versions. This involves identifying and fixing any inconsistencies or issues that arise during cross-browser testing.
-
Collaboration with Back-End Developers: Collaborating with back-end developers to integrate the front-end components with the server-side logic and data retrieval. This may involve working with AEM APIs, implementing data bindings, and handling dynamic content.
-
User Experience (UX) Implementation: Implementing the user experience design provided by UX designers. This includes translating design mockups into interactive and functional web interfaces, ensuring consistent branding and visual appeal.
-
Troubleshooting and Bug Fixing: Identifying and resolving front-end issues and bugs that may arise during development or testing. This involves debugging code, conducting cross-browser testing, and working closely with the development team to address any issues.
-
Version Control and Deployment: Using version control systems (e.g., Git) to manage code repositories and collaborating with the development team to ensure smooth deployment of front-end changes to the AEM environment.
- https://webflow.com/
- https://www.contentful.com/
- https://www.sanity.io/
- https://firecms.co/
- https://itnext.io/connecting-angular-6-to-wordpress-ee0055686a70
- https://www.netlifycms.org/
WordPress or Drupal 8
- https://jamstack.org/headless-cms/
- https://www.sanity.io/
- https://flatlogic.com/blog/best-headless-cms/
- https://www.storyblok.com/
- https://www.datocms.com/
Contentful
Unlike traditional CMS platforms, Contentful adopts a "headless" approach, decoupling the content management backend from the presentation layer. This means that content can be created and organized independently of how it is displayed, allowing for greater flexibility and reusability across different applications and platforms.
-
Content Modeling: Contentful allows users to define and structure content using a flexible data model. Content types can be created to represent different types of content, with customizable fields and relationships between content entries.
-
Content Creation and Editing: Contentful provides a user-friendly interface for creating and editing content. It supports various content formats, including text, images, videos, and more. Content creators can collaborate, preview changes, and schedule content publication.
-
Content Delivery: Content stored in Contentful can be delivered through APIs to any digital platform or application, including websites, mobile apps, IoT devices, and more. This allows for consistent content delivery across multiple channels.
-
Localization and Internationalization: Contentful supports multilingual content management, enabling businesses to create and manage content in multiple languages. It provides features for translating and localizing content, making it suitable for global organizations.
-
Versioning and Workflow: Contentful includes versioning and workflow features that allow users to track changes, review and approve content, and maintain content governance. This helps teams collaborate effectively and ensures content quality and consistency.
-
Integrations and Extensibility: Contentful offers a wide range of integrations and extensions to extend its functionality. It integrates with other tools and services, such as e-commerce platforms, analytics tools, marketing automation systems, and more.
Contentful is often favored by developers and content teams looking for a flexible and API-driven CMS. Its headless architecture allows for faster development, easier content reuse, and the ability to deliver content to any channel or device. It is suitable for a wide range of use cases, including websites, mobile apps, digital signage, e-commerce, and more.