Head-to-Head Feature Comparison
| Framework | Rendering Model | Performance Rank (1-5, 5=Best) | UI Consistency vs. Fidelity | Community Maturity Rank (1-5, 5=Best) | Primary Frustration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flutter | Custom Engine (Skia) | 5 | Max Consistency | 5 (Leading Usage, Rapid Growth) | Larger App Size, Platform Channels complexity |
| React Native | Bridged Native APIs | 4 | High Fidelity (Native Components) | 5 (Highest Revenue, Established Enterprise) | JS Bridge Overhead Risk, Native Module Updates |
| .NET MAUI | Native UI Abstraction | 4 | High Fidelity (Native Components) | 3 (Growing, Microsoft Support Focus) | Early Maturity/Stability, Limited General Talent Pool |
| Kotlin Multiplatform | Logic Only (Native UI) | 5 | Max Fidelity (Pure Native UI) | 3 (Emerging/Rapid Growth Focus) | Tooling/Gradle Complexity, Kotlin/Native Memory Management |
| Ionic/Capacitor | Embedded Web View | 2 | High Consistency (Web Design) | 4 (Mature Web Ecosystem) | Web View Performance Ceiling, Reliance on Plugins |
| NativeScript | Direct Native API Access | 3 | High Fidelity (Native Components) | 2 (Niche/Limited Community Support) | Limited Resources, Framework Evolution Risk |
Economic and Revenue Viability
The slight revenue advantage held by React Native (generating $287 million versus Flutter's $283 million in Q4 2024) 4 suggests that React Native may have captured high-value market segments---such as finance, social media, or specific corporate tools---that exhibit higher average lifetime user values (LTV). For businesses prioritizing immediate revenue metrics, React Native demonstrates a marginal, quantifiable edge in economic maturity.
Enterprise adoption sentiment supports the viability of both. Flutter's maturity has surged, with the percentage of Chief Technology Officers (CTOs) who believe Flutter is suitable for large-scale applications rising from 71.2% to 85%.16 This rising trust confirms that both frameworks are mature solutions capable of handling significant complexity and scale.
Cross-Platform as the Default Standard
The data confirms that cross-platform development is moving from a tactical option to a default standard for many mobile projects. This acceleration is overwhelmingly driven by financial efficiency; cross-platform projects are consistently reported to cut costs by 30-45% and reduce development timelines from 8-12 months to 5-8 months.18 With the global mobile application market projected to reach $1.103 trillion by 2034 20, adopting a single codebase strategy (React Native or Flutter) is becoming essential for sustainable scale and growth velocity.
Actionable Investment Strategy:
- Prioritize Ecosystem Alignment: The technical merits of React Native and Flutter are nearing parity, supported by equivalent revenue generation capabilities.4 The choice should hinge on staffing strategy:
-
Select Flutter if the primary organizational goal is maximizing UI control, guaranteed rendering consistency across all platforms, and launching a greenfield project with a smaller, highly passionate talent pool.
-
Select React Native if optimizing for developer recruitment velocity, capitalizing on the vast existing JavaScript talent pool, and integrating into established enterprise processes are the highest strategic priorities, leveraging its existing dominance in job market volume.14
Immediate Legacy Migration: Organizations must formally fund and initiate the deprecation of all remaining Apache Cordova codebases. Migration to Capacitor is only warranted if the resulting application is strictly B2E or PWA-centric, capitalizing on Capacitor's efficiency in these specific areas.6 Any consumer-facing application currently built on Cordova should be migrated directly to either Flutter or React Native to avoid re-incurring future technical debt and to meet rising user expectations for performance.**
Cross Platform Development
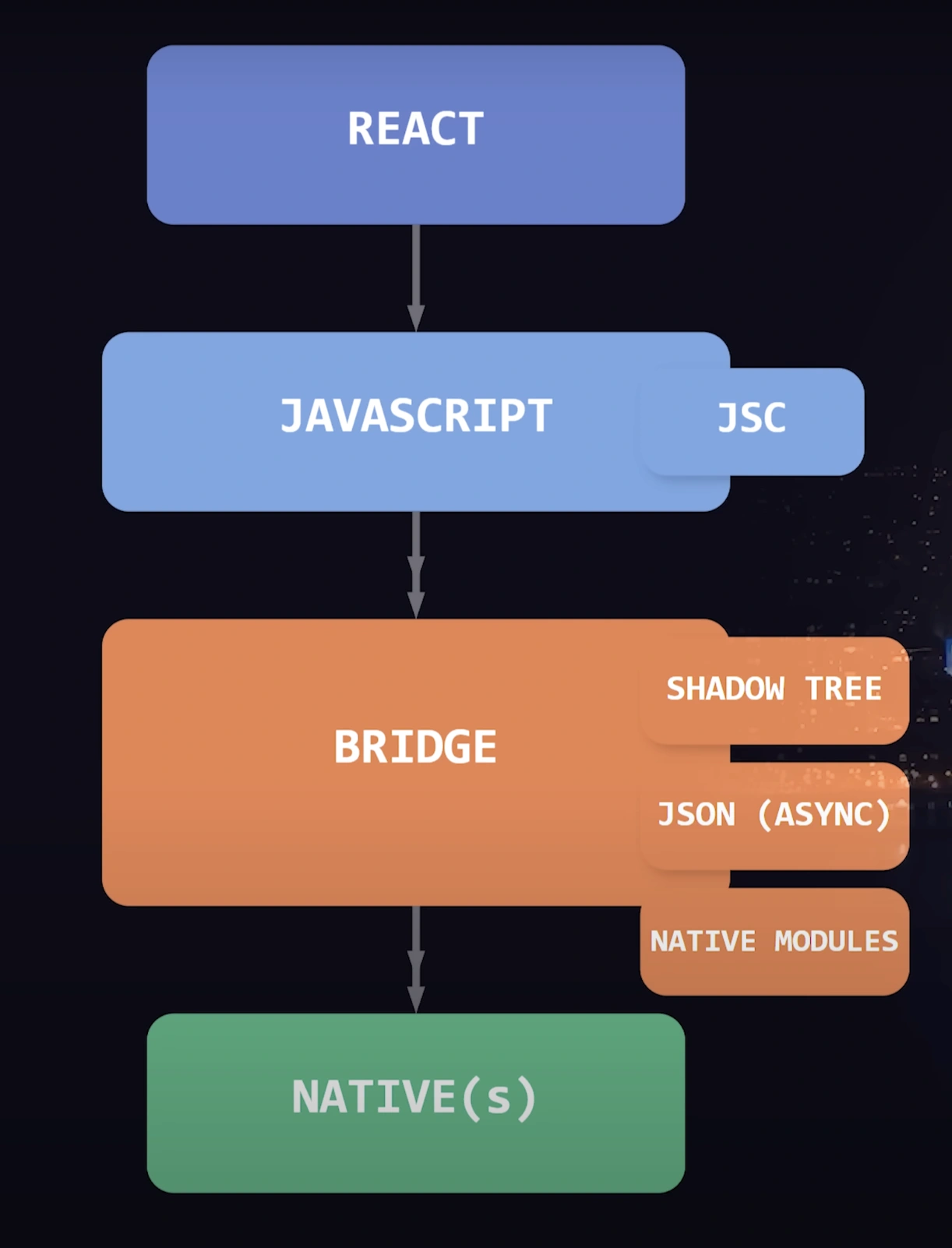
React Native is a popular framework for building mobile applications using JavaScript. It was developed by Facebook at the React.js Conf in January 2015 and was first released to the public in March 2015. React Native was created as a way to extend the benefits of React, a JavaScript library for building user interfaces, to mobile app development using familiar JavaScript and React concepts. React Native has become a popular choice for mobile app development due to its ability to bridge the gap between native performance and cross-platform development. It allows developers to leverage their existing JavaScript skills and build high-quality mobile applications with a native look and feel. The React Native community remains active, providing support, documentation, and a growing ecosystem of third-party libraries to enhance the development experience.
-
Focus on Cross-Platform Development: One of the key advantages of React Native is its ability to facilitate cross-platform development. It allows developers to write code once and deploy it on multiple platforms, such as iOS and Android. React Native achieves this by using native components and APIs, resulting in a highly performant and native-like user experience.
-
Community Growth and Adoption: React Native gained significant traction within the developer community due to its promise of code reusability and efficiency. Many companies and developers started adopting React Native for their mobile app development needs. Facebook itself used React Native for several of its own mobile apps, including Facebook, Instagram, and Messenger.
-
Continuous Development and Improvement: Since its initial release, React Native has undergone continuous development and improvement. Facebook and the React Native community have been actively maintaining and evolving the framework, introducing new features, performance optimizations, and bug fixes.
-
Expansion of Ecosystem: The React Native ecosystem has expanded rapidly, with the introduction of various community-driven libraries, tools, and plugins. These additions have helped to enhance the development experience and provide solutions for common mobile app development challenges.
-
Support for Web and Other Platforms: React Native has expanded beyond mobile platforms. With projects like React Native for Web and React Native Windows, developers can now leverage React Native's capabilities to build applications for the web and Windows platforms, in addition to iOS and Android.
-
Version Updates: React Native has followed a versioning scheme, with regular releases introducing new features, improvements, and bug fixes. The versioning scheme started with React Native 0.1.x and has continued to evolve and mature over time. the latest stable version is React Native 0.72.
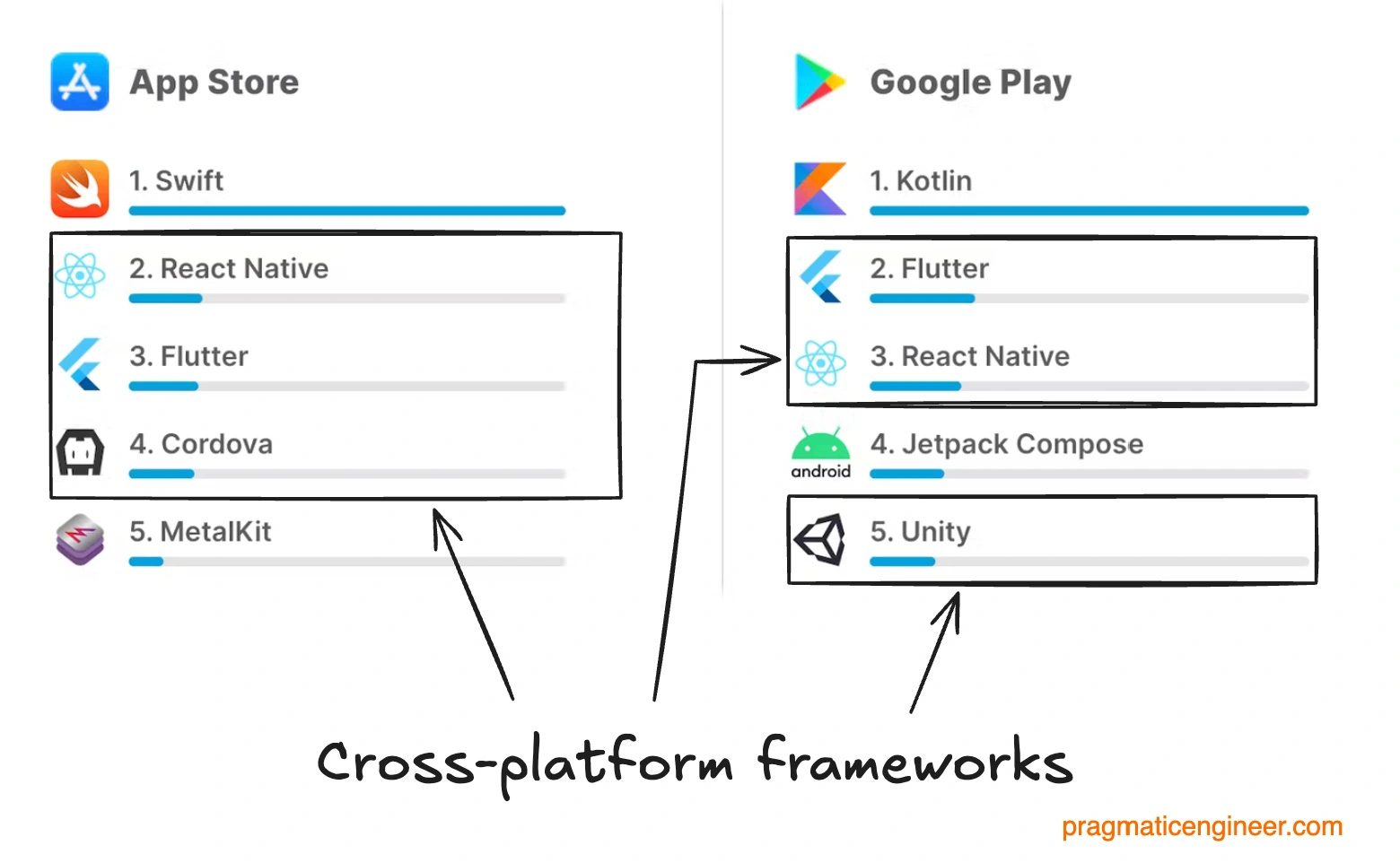
RN vs Flutter and Other Frameworks
https://newsletter.pragmaticengineer.com/p/cross-platform-mobile-development
React Native and Flutter
Both React Native and Flutter can be viable options for building a video conferencing iOS app, but each has its own advantages and drawbacks:
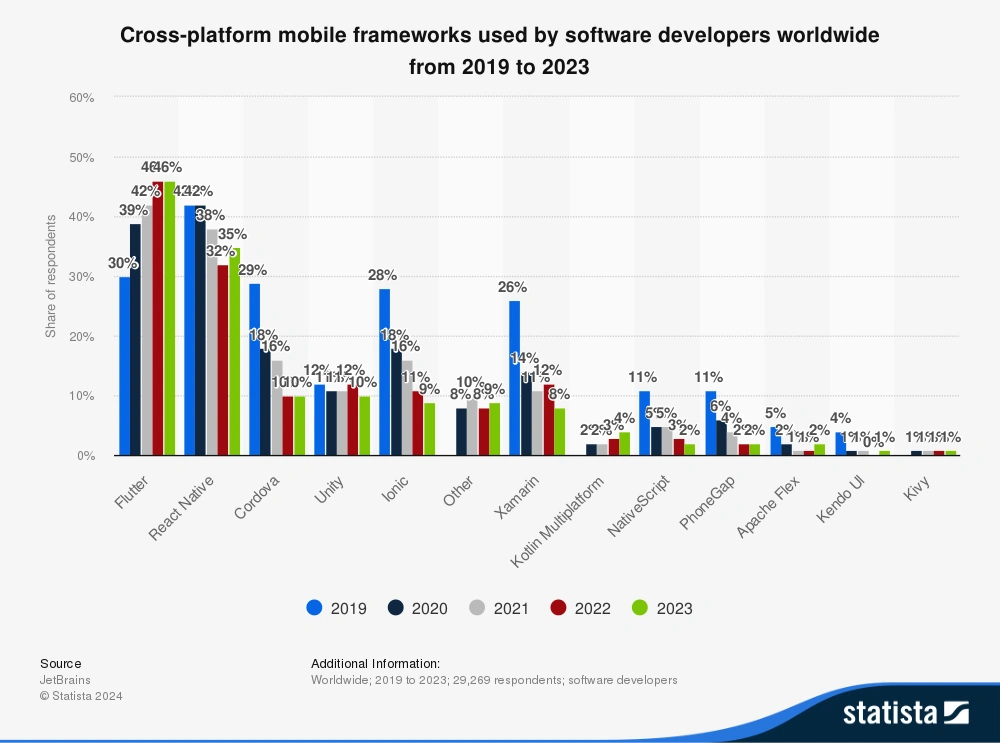
Flutter powers more apps, but React Native ones earn more revenue. It's hard to accurately measure developers' preferences, but determining the number of apps using each framework is easier. Appfigures did exactly this by tracking all apps released in a year and found that Flutter was used by 11% of apps released in 2024, while 7% used React Native:
Flutter:
- Pros:
- Potentially better performance: Flutter generally offers smoother performance compared to React Native, especially for complex animations and graphics, which can be crucial for video conferencing.
- Faster development: Flutter's hot reload functionality can accelerate development by allowing you to see changes reflected almost instantly.
- Single codebase: You write the app logic once in Dart, then it compiles for both iOS and Android, potentially saving development time.
- Cons:
- Steeper learning curve: Learning Dart, the programming language used in Flutter, might require more effort compared to JavaScript used in React Native.
- Smaller community: While growing, Flutter's community and available resources might be slightly smaller than React Native's.
- Limited native features: Integrating certain native iOS features might require more work compared to React Native.
React Native:
-
Pros:
- Larger developer community: React Native has a larger and more established community, making it easier to find solutions and support.
- Wider range of libraries: React Native boasts a wider selection of third-party libraries specifically designed for video conferencing functionalities.
- Potentially easier access to native features: Integrating native iOS features might be more straightforward due to the use of JavaScript bridges.
-
Cons:
- Potentially lower performance: React Native apps might experience slightly slower performance compared to Flutter, especially for demanding functionalities like video conferencing.
 }
}- Slower development cycles: Hot reloading in React Native isn't as seamless as Flutter's, potentially impacting development speed.
- Two codebases: You need to maintain separate codebases for iOS and Android, potentially doubling the development effort.
Choosing for an iOS video conferencing app:
- If performance is a top priority: Flutter might be the better choice due to its potentially smoother rendering and animations.
- If development speed is crucial: Consider your team's familiarity with Dart and React Native. If they're comfortable with JavaScript, React Native might offer a quicker start.
- If access to native features is important: React Native might be more straightforward for integrating specific iOS functionalities.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific requirements, team expertise, and priorities. It's recommended to carefully evaluate your needs and weigh the pros and cons of each framework before making a decision.