React Native
Table of Contents
2025
React Native Isn't as Popular as You Think
| Node.js Version | LTS Status | React Native Version Compatibility | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20.13.1 | Active LTS | 0.73.x and above | Supports the latest React Native features; recommended for new projects. |
| --- | --- | --- | --- |
Key Points:
- Node.js 20.13.1 (Active LTS since April 2024, supported until April 2026) is compatible with React Native 0.73.x and later releases. The latest React Native version as of mid-2025 is around 0.74.x (based on the typical biannual release cycle), which aligns with Node.js 20.x.
- Earlier React Native versions (e.g., 0.68.x to 0.72.x) support Node.js 14.x to 18.x, but since 18.x is now in maintenance LTS (ending active support April 2025), it's less ideal for new development.
MacOS Sonoma Install Steps
brew install openJDK@17
environment var
set JAVA_HOME
brew install
brew install ios-deploy
https://shift.infinite.red/react-native-10-years-db9eb36c5af6
Upgrade
https://react-native-community.github.io/upgrade-helper/
Animations
- reactnativereanimated
- https://moti.fyi
Intro
VIDEO: After Trying React Native, I'll Never Use Anything Else
September 2024
 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=msErROjFY08
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=msErROjFY08
Tutorials
Verify Installed
npx react-native doctor
UI Libraries
- https://reactnativeelements.com
- nativewind.dev
- unistyl.es
- https://nativebase.io/
https://jscomplete.com/learn/javascript-for-react
Errors
react-native doctor

Unable to run simctl: Error: xcrun simctl help exited with non-zero code: 72
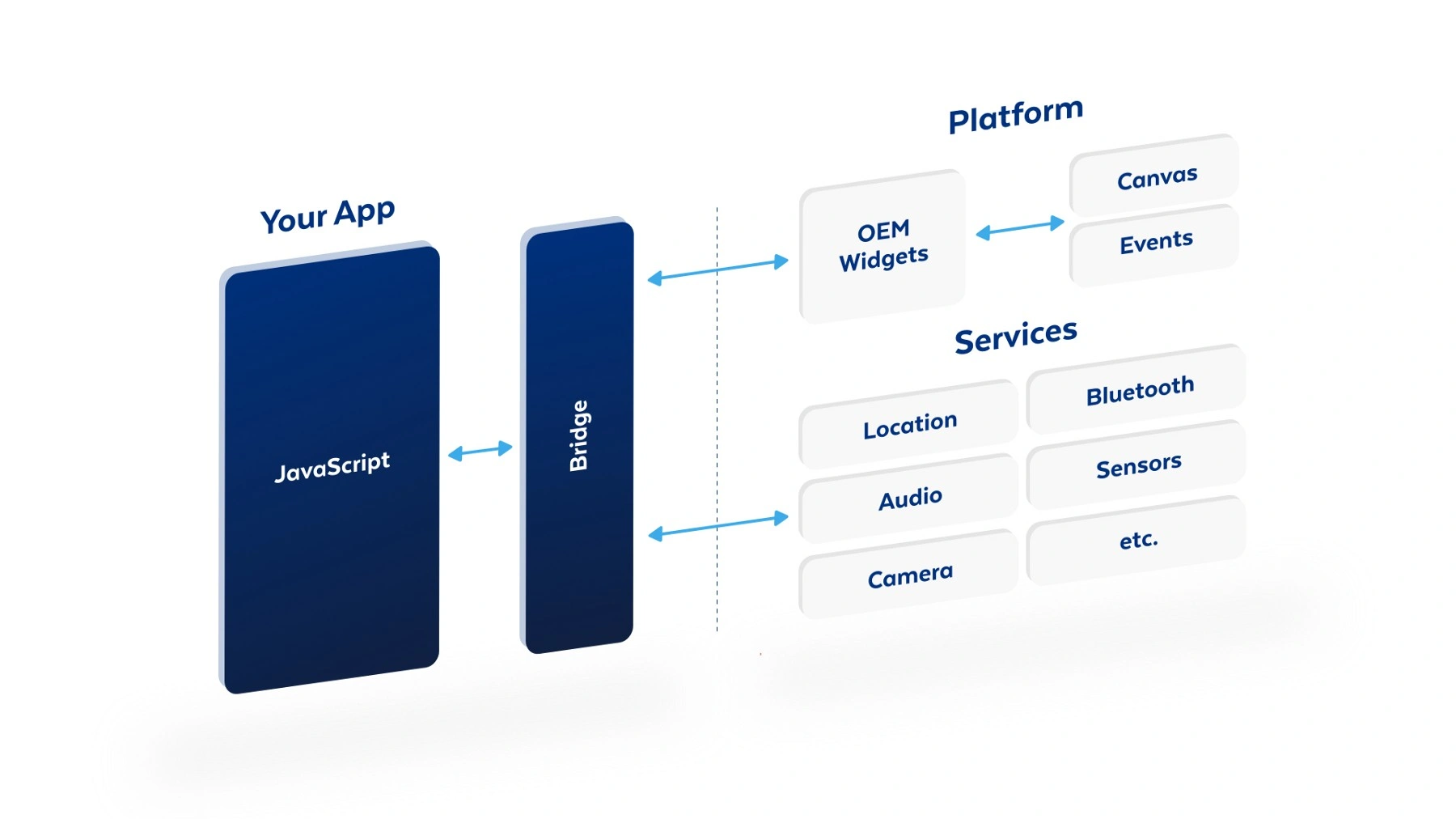
Accessing Native Code in Modules
- Accessing Platform specific code using Native modules in react native
- Leverage native APIs for deeper integrations with iOS/Android platforms
JSX
- Readability
- All the code for the page in a single file
Redux
- Stateful Component
- Stateless Component
Thunk allows to write an action creators that return a function instead of the typical action object. Where as redux-saga is a library that mainly focuses on easy handling of application side effects and more efficient for execution
step-by-step process of Redux-Thunk
Check what the incoming action is: If it is a regular action object, Redux-Thunk does not do anything and the action object is processed by the store’s reducer A thunk creator, which is an action creator that returns a thunk (a.k.a. asynchronous action creators)
2.The thunk itself, which is the function that is returned from the thunk creator and accepts dispatch and setState as arguments If the action is a function, Redux-Thunk invokes it and passes it the store’s dispatch and getState methods and any extra arguments (e.g., axios) 3. After the function runs, the thunk then dispatches the action, which will then update the state accordingly
Redux-Saga is a library that aims to make application side effects (e.g., asynchronous actions such as fetching data) easier to handle and more efficient to execute. The idea is that a saga is similar to a separate thread in your application that’s solely responsible for side effects.
The benefit to Redux-Saga in comparison to Redux-Thunk is that you can avoid callback hell meaning that you can avoid passing in functions and calling them inside. Additionally, you can more easily test your asynchronous data flow. The call and put methods return JavaScript objects. Thus, you can simply test each value yielded by your saga function with an equality comparison. On the other hand, Redux-Thunk returns promises, which are more difficult to test. Testing thunks often requires complex mocking of the fetch api, axios requests, or other functions. With Redux-Saga, you do not need to mock functions wrapped with effects. This makes tests clean, readable and easier to write. Redux-Thunk, however is great for small use cases and for beginners. The thunks’ logic is all contained inside of the function. Additionally, you do not need to learn a new function type, generators, and the keywords and methods associated with this function type. In conclusion, there are tradeoffs for each middleware and depending on your project, you can decide which middleware is most fitting for your code.
Global Store | Keep track of changes to the tree
higher-order component (HOC) A higher-order component (HOC) is an advanced technique in React for reusing component logic. HOCs are not part of the React API, per se. They are a pattern that emerges from React’s compositional nature.
touchable components
React Native provides several components that respond to touches in a way that is consistent with the native behavior. These touchable components include:
-
TouchableHighlight: When pressed, it dims the button and fires an event. This is best used for buttons or links that need to visually respond to being touched. -
TouchableOpacity: This component makes the view slightly transparent when touched. It's less visually intrusive thanTouchableHighlightand is often used for icons or to wrap custom components. -
TouchableWithoutFeedback: As the name suggests, this component allows you to handle touch events without any feedback on the UI. It's useful when you need to capture a press action on a component without changing its appearance. -
TouchableNativeFeedback: This component provides touch feedback for Android in the form of a ripple effect that originates from the point of touch. It's Android-specific and helps maintain the Material Design look and feel. -
Pressable: Introduced in React Native 0.63,Pressableis a core component that can detect various stages of press interactions. It is more flexible than the other touchable components and can be customized to fit a wide variety of use cases.Pressablecan be used to detect simple presses, long presses, and even more complex gestures if needed.
Each of these components has its own set of props that can be used to customize its behavior, such as onPress, onLongPress, underlayColor for TouchableHighlight, activeOpacity for TouchableOpacity, and so on. Choosing the right touchable component depends on the specific needs of your application and the visual feedback you want to provide to your users.
Common Issues with DOM Event Methods in React Native
AnimationEvent
Issue: Animations not triggering or behaving unexpectedly.
Solution: Ensure that the animation library (e.g., react-native-reanimated) is properly installed and configured. Verify that the animation methods are correctly implemented and that the components are properly wrapped with animation containers.
KeyboardEvent
Issue: Keyboard not dismissing or causing layout issues.
Solution: Use Keyboard.dismiss() to programmatically dismiss the keyboard. Ensure that the KeyboardAvoidingView component is used to handle keyboard interactions and prevent layout issues.
InputEvent
Issue: Input fields not responding to user input or losing focus.
Solution: Ensure that the TextInput component is correctly implemented with proper props such as onChangeText and value. Verify that the input fields are not being unmounted or losing focus due to re-renders.
MouseEvent
Issue: Mouse events not working as expected on web versions of React Native apps.
Solution: Use the react-native-web library to ensure compatibility with web-specific mouse events. Verify that the event handlers such as onMouseEnter, onMouseLeave, and onClick are correctly implemented.
isTrusted
Issue: Events not being recognized as trusted, leading to unexpected behavior.
Solution: Ensure that events are being dispatched correctly and that they originate from user interactions. Avoid manually dispatching events unless necessary, and ensure that the event properties are correctly set.
General Tips
- Always test your app on both Android and iOS devices to ensure consistent behavior across platforms.
- Use the React Native Debugger and other debugging tools to inspect and troubleshoot event-related issues.
- Keep your dependencies up to date to benefit from the latest bug fixes and improvements.
Common Issues with HTML DOM Events in React Native
DragEvent
Issue: Drag and drop functionality not working as expected.
Solution: React Native does not natively support drag and drop events. Use third-party libraries like react-native-drag-sort or react-native-draggable to implement drag and drop functionality. Ensure that the components are properly configured and that the drag events are correctly handled.
BeforeUnloadEvent
Issue: Handling app state before the user navigates away or closes the app.
Solution: React Native does not support the beforeunload event. Use the AppState API to detect when the app is about to go to the background or is closed. Implement appropriate logic to save the app state or prompt the user.
FocusEvent (blur and focusin)
Issue: Input fields losing focus unexpectedly or not gaining focus.
Solution: Ensure that the TextInput components have the correct onBlur and onFocus handlers. Verify that the components are not being re-rendered unnecessarily, which can cause them to lose focus. Use KeyboardAvoidingView to manage keyboard interactions.
MouseEvent (dblclick, mouseenter)
Issue: Mouse events not working on web versions of React Native apps.
Solution: Use the react-native-web library to ensure compatibility with web-specific mouse events. Implement event handlers such as onDoubleClick, onMouseEnter, and onMouseLeave to handle mouse interactions.
DropEvent
Issue: Drop events not being recognized or handled.
Solution: React Native does not natively support drop events. Use third-party libraries like react-native-drag-sort to implement drop functionality. Ensure that the drop zones are correctly defined and that the drop events are properly handled.
MediaEvent (ended, stalled)
Issue: Media playback issues such as videos not ending or stalling.
Solution: Use the react-native-video library to handle media playback. Ensure that the onEnd and onStalled event handlers are correctly implemented to manage media playback states.
ToggleEvent
Issue: Toggle events not working as expected.
Solution: React Native does not have a native toggle event. Use state management to handle toggle functionality. Implement custom toggle components or use libraries like react-native-switch to manage toggle states.
VolumeChangeEvent
Issue: Volume changes not being detected or handled.
Solution: Use the react-native-sound or react-native-video libraries to manage audio and video playback. Implement the onVolumeChange event handler to detect and handle volume changes.
ErrorEvent
Issue: Errors not being caught or handled properly.
Solution: Use the ErrorBoundary component to catch JavaScript errors in the component tree. Implement global error handling using console.error and ErrorUtils to capture and log errors. Ensure that network requests and other asynchronous operations have proper error handling.
General Tips
- Test your app on both Android and iOS devices to ensure consistent behavior across platforms.
- Use debugging tools like React Native Debugger to inspect and troubleshoot event-related issues.
- Keep your dependencies up to date to benefit from the latest bug fixes and improvements.
- Refer to the official React Native documentation and community resources for best practices and solutions to common issues.