Audit Risks
refer to the potential for financial misstatements or irregularities that may trigger an examination by tax authorities or auditors. Understanding these risks is crucial for maintaining compliance and ensuring the integrity of financial reporting.
key aspects:
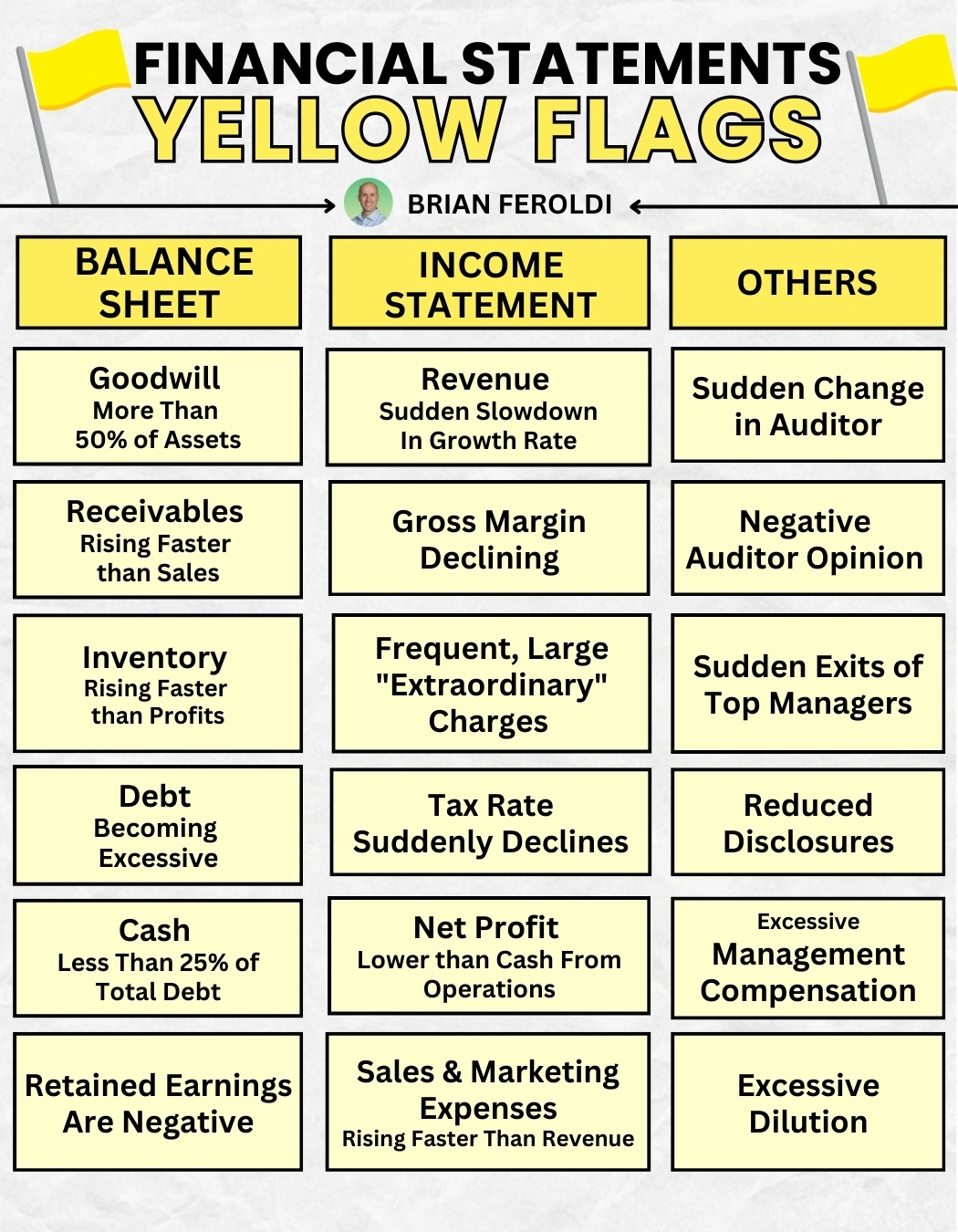
1. Types of Audit Risks
- Inherent Risks: These are risks that exist due to the nature of your business or industry. For example, cash-intensive businesses may have higher risks due to the potential for underreporting income.
- Control Risks: These arise from the possibility that a company's internal controls may not prevent or detect misstatements in financial reports. Weak internal controls can lead to errors or fraud.
- Detection Risks: This refers to the risk that auditors will not catch errors or fraud during an audit. This can be influenced by the effectiveness of the audit procedures used.
2. Common Audit Triggers
- Unusual Transactions: Significant or unusual transactions that deviate from normal business practices can raise flags.
- Discrepancies in Financial Records: Inconsistencies between financial statements and supporting documentation can lead to scrutiny.
- High Expense Ratios: Expenses that appear excessive relative to revenue may prompt a deeper investigation.
3. Mitigation Strategies
- Maintain Accurate Records: Thorough and accurate bookkeeping reduces the risk of errors and misstatements.
- Implement Strong Internal Controls: Establishing checks and balances within financial processes can help prevent fraud and errors.
- Regular Audits: Conducting internal audits can help identify potential issues before they become significant problems.
- Educate Staff: Training employees on compliance and ethical practices can reduce the risk of unintentional errors.
4. Consequences of Audit Risks
- Financial Penalties: Misstatements can lead to fines or penalties imposed by tax authorities.
- Reputational Damage: Audit findings can harm a business’s reputation, affecting customer trust and relationships.
- Operational Disruption: An audit can disrupt business operations, requiring time and resources to address findings.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing audit risks is essential for a small business LLC to ensure compliance and maintain financial integrity. Implementing robust internal controls, accurate record-keeping, and regular audits can help mitigate these risks effectively.