Financial Planning
2025 Goal
239 work days per year * $500/day = $119,500 year 2 * $1,000 / day = $239,000 year 3 * $2,000 / day = $478,000 year 4 * $3,000 / day = $717,000
https://youtu.be/EJHPltmAULA?si=u8s_ZBO9evipD6lS

Table of Contents
Accounting
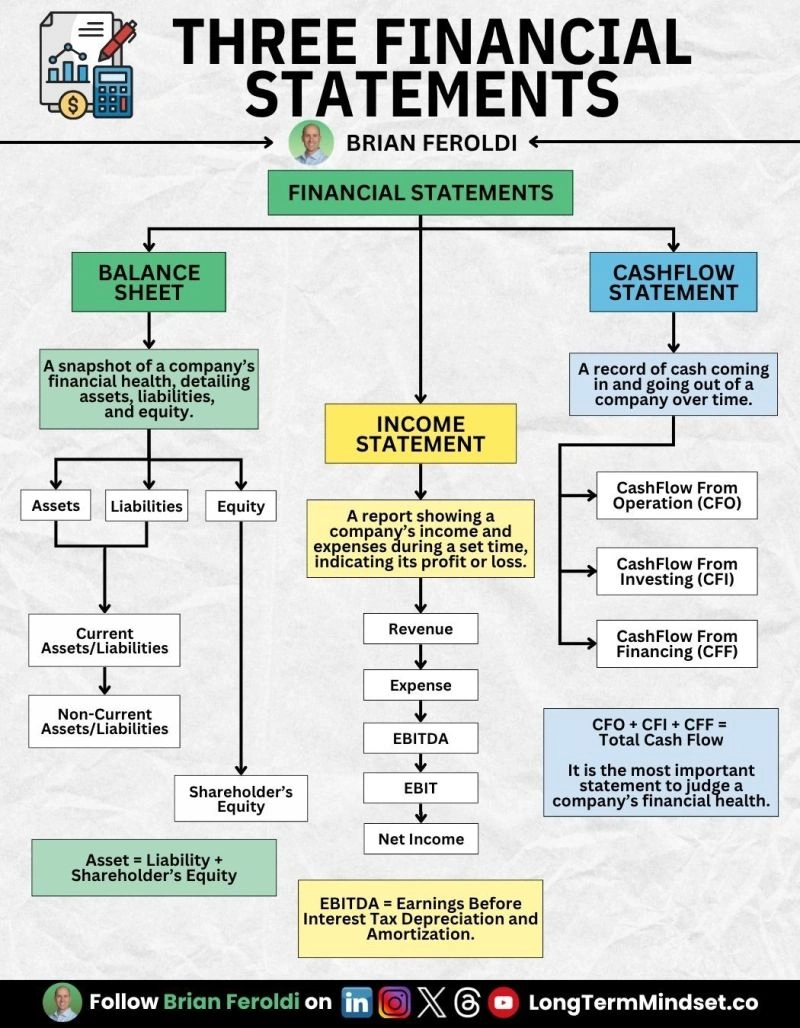
The income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement
Having a strong understanding of how the three financial statements work together and being able to digest a company’s financial proformas is critical
"The Valley of Death"
operating at a loss until reaching break-even revenue
3 Most Important Reports - Financial Statements
- Balance Sheet
- a list of a company's resources (assets) and obligations (liabilities)
- cash, property / equipment
- Income Sheet
- earnings
- Revenue
- Cash Flow Statement
- Cash Received
- Cash Paid
How to Separate Business from Personal
Separating business and personal finances is important because it helps to keep your business finances organized and makes it easier to track your business income and expenses. Here are some steps you can take to separate your business and personal finances:
Set up a separate business bank account: Open a separate bank account for your business. This account should be used exclusively for business transactions, such as receiving payments from clients and paying business expenses.
Use separate payment methods: Use separate credit cards and payment methods for business and personal expenses. This will help you avoid mixing business and personal expenses.
Keep receipts and records: Keep all of your business-related receipts and records organized and separate from your personal receipts and records.
Pay yourself a salary: If you are a sole proprietor or a single-member LLC, pay yourself a salary from your business account and use those funds for personal expenses.
Keep accurate records: Make sure to keep accurate and detailed records of all of your business transactions. This will make it easier to track your business income and expenses and to prepare your tax returns.
By following these steps, you can help ensure that your business and personal finances remain separate, making it easier to manage your business finances and stay on top of your financial obligations.
Sales Overhead
Sales overhead refers to the indirect expenses associated with the marketing and selling of a company's products or services. These costs are not directly tied to the production of goods or services but are necessary for the business to generate sales. Examples of sales overhead include:
- Printed Materials: Brochures, catalogs, and other printed marketing materials.
- Television Commercials: Advertising expenses for television ads.
- Sales Personnel Commissions: Payments made to sales staff based on their sales performance.
- Trade Shows: Costs associated with exhibiting at trade shows and conferences.
- Paid Advertisements: Expenses for placing advertisements in various media channels.
- Sales Staff Salaries: Wages paid to sales representatives and managers.
Sales overhead is a component of the broader category of selling and distribution overheads, which also includes distribution-related expenses. Understanding and managing these costs is crucial for businesses to control their overall expenses and improve profitability.
There are a number of methods that businesses can use to track and manage overhead costs related to sales. Here are a few common ones:
-
Budgeting: One of the most common methods for managing overhead costs is to create a budget that outlines all of the expenses associated with sales operations. This can help businesses to set realistic targets for sales revenue and control expenses by monitoring actual spending against the budget.
-
Cost allocation: As mentioned earlier, overhead costs are often allocated to the product or service on a per-unit basis, in order to determine the true cost of producing and selling the product or service. This can be done using various methods, such as activity-based costing, which assigns overhead costs to specific activities or processes that generate them.
-
Performance metrics: Businesses can track and manage overhead costs by monitoring performance metrics related to their sales operations, such as sales per employee, sales per square foot of retail space, or sales per marketing dollar spent. By analyzing these metrics, businesses can identify areas where they may be overspending on overhead costs and take steps to reduce them.
-
Technology solutions: There are a variety of software tools and cloud-based solutions that can help businesses track and manage overhead costs related to sales. These tools can automate processes like expense tracking and reporting, and provide real-time visibility into spending and budget performance.
Overall, tracking and managing overhead costs is an important aspect of running a successful sales operation, and businesses should carefully consider the methods and tools that will work best for their specific needs and circumstances.
Monthly Expenses
| Monthly Expenses | Definition |
|---|---|
| General and administrative (G&A) | expenses are incurred in the day-to-day operations of a business and may not be directly tied to a specific function or department within the company. General expenses pertain to operational overhead expenses that impact the entire business. Administrative expenses are expenses that cannot be directly tied to a specific function within the company such as manufacturing, production, or sales. G&A expenses include rent, utilities, insurance, legal fees, and certain salaries. |
Budget Management CASH BUDGETS ARE ROADMAPS
- Define your time period
- Milestones
- Trigger rewards
Revenue Growth Model research on trends and changes in the market, customer demographics, skill levels, our people work hard to stay ahead of the curve to ensure that we are giving our clients the best and most effective solutions for their needs.
disruption prediction
Payment System Model
- Open Loop
- Closed Loop
- Paypal
- Western Union Income https://stripe.com/en-gb/payments/payment-links
80% >> business expenses 20% MKTG 20%
20% Wages
| Budget | Category | COST |
|---|---|---|
| Software Licenses | Adobe Creative Cloud | ? |
| Voice | cloudphone.com | |
| PRODUCT / MARKET FIT | Paid research, Competitive analysis, Focus groups | |
| PRODUCT TESTING | User testing sessions, Testing software | |
| PRODUCT RELEASES | Product management/release software, Launch event, Paid advertising, PR | |
| CONTENT | White papers, Case studies, Product demo videos | |
| SEARCH | CPC, CPM | |
| DISPLAY & RETARGETING | CPC, CPM | |
| AFFILIATE | CPC, CPM | |
| SOCIAL | Facebook Ads, Twitter Ads, LinkedIn Ads, Pinterest Promoted Pins, Instagram Ads | |
| LEAD GENERATION | Content discovery platform (e.g. Outbrain), Dedicated email send - fixed cost, Dedicated email send - CPL (cost per lead) |
Financial Analysis
- ROI Forecast / Balance Sheet Projection
- cash flow chart
- Break Even Analysis
Monetization Strategies
Developer passive income
Staffing Model
contract terms vs business needs
https://www.ycombinator.com/documents
- Create a Comprehensive Budget: Develop a detailed budget that outlines projected income and expenses, including marketing costs, operational expenses, and potential investments.
- Track Cash Flow Closely: Regularly monitor cash inflows and outflows to identify potential shortfalls and make adjustments accordingly.
- Prioritize Expenses: Identify essential expenses and prioritize them over discretionary spending to ensure the business remains financially stable.
- Maximize Efficiency: Implement processes and systems that maximize efficiency, reducing waste and minimizing unnecessary expenditures.
- Diversify Income Streams: Explore alternative revenue streams to reduce dependence on a single source of income and increase financial stability.
- Build an Emergency Fund: Set aside a portion of the business's income in an easily accessible savings account to cover unexpected expenses or cash flow shortfalls.