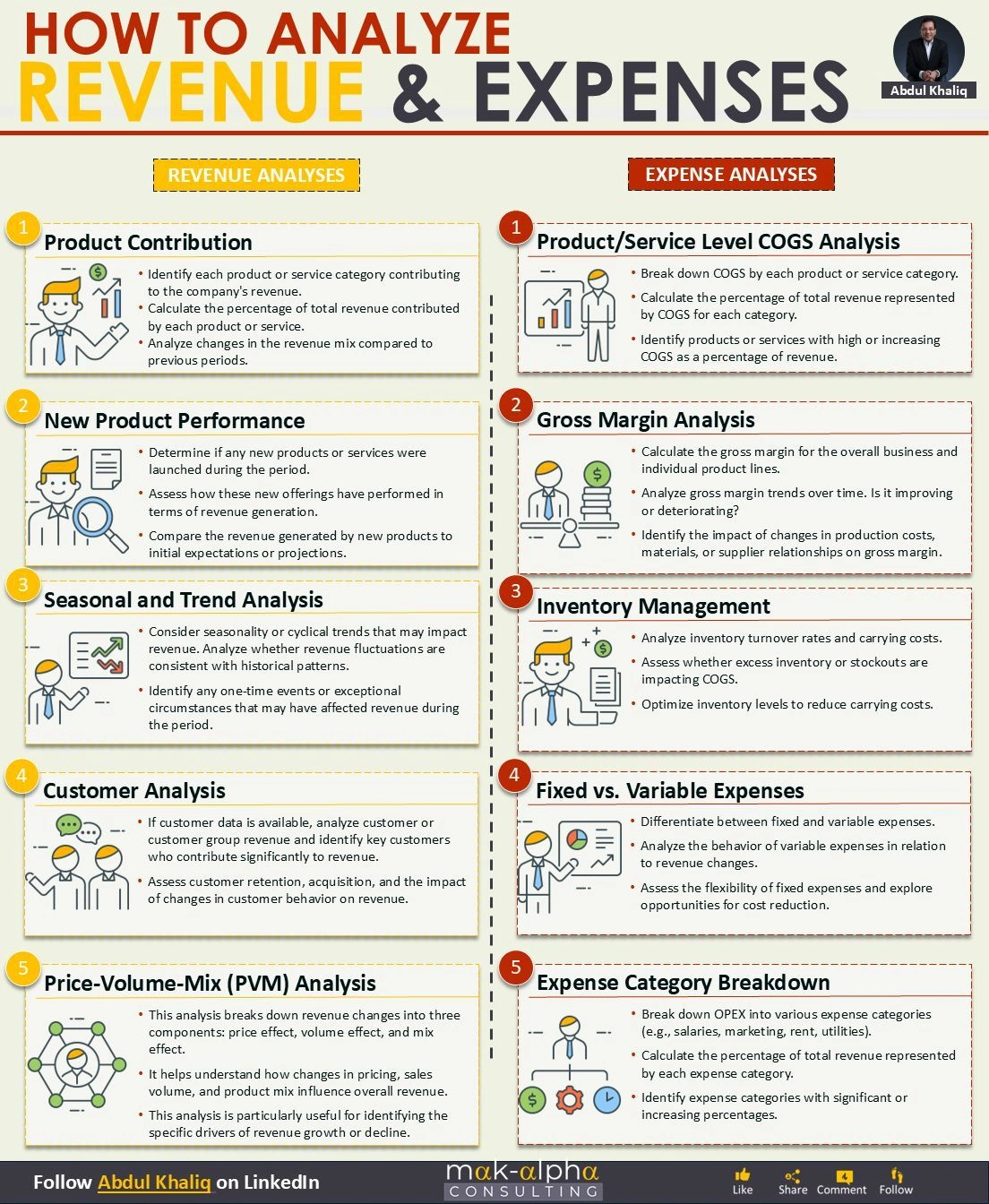
VC Terms
| Terms | Defintion |
|---|---|
| vertical start-up | A vertical startup, also known as a vertical-specific startup or industry-specific startup, is a type of startup company that focuses on addressing the needs and challenges of a specific industry or vertical market. Unlike generalist startups that aim to create a wide range of products or services, vertical startups specialize in a particular sector or niche. Vertical startups typically target industries that have unique characteristics, requirements, or pain points that can be addressed through specialized solutions. By focusing on a specific industry, these startups aim to provide tailored products, services, or technologies that cater to the specific needs of that industry. They often develop deep expertise and domain knowledge in the targeted vertical, allowing them to offer more specialized and effective solutions compared to broader, generalist competitors. Vertical startups can be found in various sectors, such as healthcare, finance, real estate, agriculture, transportation, and more. They leverage industry-specific knowledge, technology, and partnerships to create innovative solutions that improve efficiency, productivity, or customer experience within that industry. The advantages of vertical startups include: 1. Domain Expertise: By focusing on a specific industry, vertical startups can develop a deep understanding of the industry's dynamics, challenges, and opportunities. 2. Specialized Solutions: Vertical startups can develop highly specialized products or services that better meet the unique needs of the industry they target. 3. Market Differentiation: By catering specifically to one industry, vertical startups can differentiate themselves from broader competitors and establish a strong position within their niche. 4. Industry Network: Vertical startups often build strong relationships with industry players, including customers, suppliers, and partners, which can help with market access and business development. However, it's important to note that vertical startups may face challenges such as limited market size, industry-specific regulations, and potential dependence on a single industry's success. Successful vertical startups can expand horizontally by entering related verticals or by scaling their solutions across multiple industries once they have established a strong foothold in their initial target market. |
| Return on invested capital | |
| Economic Value Added | |
| Cost per ton mile | |
| Market Share | |
| Disruptive Innovation | |
| Revenue | Often referred to as gross revenue, simply the amount of money the company brought in through selling its products or services. |
| pre-revenue funding strategy | a plan for raising capital for a startup that has not yet generated any revenue. |
| Operating Expenses | These expenses are those associated with research and development, running the business (compensation and general expenses), and other accounting charges such as depreciation and amortization of capital expenses. For VCs, the most relevant for early stages are the Selling, General, and Administrative expenses — i.e. employee compensation and sales and marketing — and Research & Development. How realistic are the compensation figures modeled in the financial proformas and does headcount expectations match revenue growth? How aggressively does the company need to spend on marketing? Similarly, for companies that are manufacturing products, how adequately do revenues cover ongoing R&D? High amounts of R&D should be expected for early stage companies, and it should in fact consume the majority of capital. |
| Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) | Simply EBITDA less Depreciation and Amortization and is less commonly used that EBITDA given depreciation and amortization have different calculation methodologies that can distort EBIT when comparing time periods or among peers. |
| investment appraisal | the planning process used to determine whether an organization's long term investments such as new machinery, replacement of machinery, new plants, new products, and research development projects are worth the funding of cash through the firm's capitalization structures (debt, equity or retained earnings). It is the process of allocating resources for major capital, or investment, expenditures. An underlying goal, consistent with the overall approach in corporate finance, is to increase the value of the firm to the shareholders. |
| Venture Capital | By contrast, venture capital investment firms fund and mentor startups. These young, often tech-focused companies are growing rapidly and VC firms provide funding in exchange for a minority stake of equity—less than 50% ownership—in those businesses. |
| Private equity investment firms | often take a majority stake—50% ownership or more—in mature companies operating in traditional industries. PE firms usually invest in established businesses that are deteriorating because of operational inefficiencies. |
| Market Exposure | The absolute amount of funds or the percentage of a portfolio that is invested in a given security https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/capital-markets/market-exposure/ Market exposure refers to the dollar amount of funds or percentage of a broader portfolio that is invested in a particular type of security, market sector, or industry. Market exposure is usually expressed as a percentage of total portfolio holdings, for instance, as in 10% of a portfolio being exposed to the oil and gas sector or a $ 50,000 in Tesla stock. Market exposure represents the amount an investor can lose from the risks unique to a particular investment or asset class. It is a tool used to measure and balance risk in an investment portfolio. Having too much exposure to a particular area can indicate a portfolio needs to undergo broader |
| What Is Net Exposure? | Net exposure is the difference between a hedge fund’s long positions and its short positions. Expressed as a percentage, this number is a measure of the extent to which a fund’s trading book is exposed to market fluctuations. Net exposure can be contrasted with a fund's gross exposure, which does not offset long and short positions. Net exposure is therefore often a more accurate measure of a fund's amount-at-risk. |
| single member LLC | entity is totally separate from you |
| S Corp | (Pass through entity) saves you the most on taxes, but the downside is more administrative burdens. run a formal payroll, pay yourself, tax withholdings, 1120S tax return |
| C Corp | pay higher taxes. corporate income tax expense |
| LP - limited partner | |
| GP - general partner | |
| solopreneur | angel check |
| tech start-up is pre-revenue | |
| Runway | This is the operating loss per month. To calculate runway, take the amount of available capital and divide by the monthly burn rate to get the number of months until your start-up runs out of cash. the calculation will be dependent on consistent expenses and revenues, so any anticipated changes or fluctuations should be considered in addition to this basic formula. |
| Cohort Analysis and Churn | Take all of the users who joined a product in a given time frame (usually a week). Then calculate how many of these users engaged with the product over every successive week. Churn is slightly different and is calculated by taking the number of users who leave and dividing by the number of total users (regardless of start time). |
| CAC | the average cost of acquiring a customer and typically includes any costs associated with advertising, sales, marketing, and onboarding. It’s natural as your company grows for CAC to increase since you’ll be spending more to capture a bigger piece of your TAM. |
| Total Addressable Market | This is the total amount of money spent in a startup’s defined space. |
| 10x ARR | |
| end market | |
| top line growth | The top line refers to a company's revenues or gross sales. Therefore, when a company has "top-line growth," the company is experiencing an increase in gross sales or revenues. |
| bottom line | The bottom line is a company's net income, or the "bottom" figure on a company's income statement. More specifically, the bottom line is a company's income after all expenses have been deducted from revenues. These expenses include interest charges paid on loans, general and administrative costs, and income taxes. A company's bottom line can also be referred to as net earnings or net profits. |
| Lean Startup Methodology | |
| Lean Startup | |
| User Interface development | create new features, pages, widgets in web applications or hybrid mobile/hybrid desktop web applications |
| due diligence example: kevin o'leary | |
| inflation hedge | |
| quantitative tightening | |
| yield curve inversion | |
| rally | |
| liquidity | |
| Valuation | the process of determining the monetary worth or value of a startup company based on factors such as its assets, intellectual property, market potential, growth prospects, and comparable industry benchmarks. |
| extreme market conditions |
Cram Down
The TechCrunch article "Cram downs are a character test for VCs and founders" by Steve Blank discusses the challenges startups face during financial crises, particularly the phenomenon of "cram downs." These occur when venture capitalists (VCs) provide funding under harsh new terms, often diluting the value of existing shares and forcing founders to accept unfavorable conditions to keep their companies alive.
Key points include:
-
Definition: A cram down differs from a down round; it involves significant changes to stock agreements and often results in a reverse split of shares, drastically reducing their value.
-
Motivations: VCs justify cram downs as good business, but the practice is often viewed as exploitative. The author criticizes the moral ambiguity within the venture capital industry.
-
Founders’ Dilemma: Faced with the potential collapse of their companies, founders may feel compelled to accept these terms, rationalizing their decisions despite the negative impact on employees and early investors.
-
Ethical Considerations: The article emphasizes the importance of ethical decision-making and encourages founders to recognize their options, including walking away from a bad deal.
-
Advice: Founders should take time to assess their situations and seek advice, rather than jumping into potentially harmful agreements. The article advocates for maintaining relationships with investors and making informed choices that prioritize long-term integrity over immediate survival.
Overall, the article warns against the pressures of accepting cram downs and encourages founders to think critically about their decisions in times of crisis.
Financial planning
Financial planning for a SaaS mobile app startup is the strategic process of outlining financial goals, estimating funding needs, and creating a budget to guide the company's financial decisions. This involves forecasting revenue, expenses, and cash flow over a specific period, typically 3-5 years, and identifying potential risks and opportunities.
financial model
A financial model, on the other hand, is a quantitative tool used to project the company's financial performance based on various assumptions and scenarios. It's a dynamic spreadsheet that allows you to manipulate variables like customer acquisition cost, churn rate, and pricing to see how they impact key metrics like revenue, profitability, and cash burn. While financial planning is the overarching strategy, the financial model is the engine that drives the projections and informs decision-making.
Price elasticity
Price elasticity in economics is a measure of how responsive the quantity demanded or the quantity supplied of a good or service is to a change in its price. It is calculated as the percentage change in quantity divided by the percentage change in price.
-
If the value is greater than 1 (elastic), a small price change leads to a proportionally larger change in quantity.
-
If the value is less than 1 (inelastic), a price change leads to a proportionally smaller change in quantity.
-
If the value is equal to 1 (unitary elastic), the percentage change in quantity equals the percentage change in price.
How to Calculate EBITDA
EBITDA draws on multiple pieces of information:
- Net income
- Interest expense
- Taxes
- Depreciation: This is when a tangible asset's value, such as equipment and commercial real estate, reduces over time.
- Amortization: This is when an intangible asset's value, such as a patent, copyright, or trademark, reduces over time.
Some of these terms, like taxes and interest, are easier to understand. Others, like depreciation and amortization, are less straightforward because they represent value --- how much assets that are used over time are worth. While businesses are still using these assets, they can be expensed as a tax deduction. Depreciation and amortization determine how much businesses can deduct for their assets each year.
To calculate EBITDA, start with your business's revenue and then subtract the cost of goods sold. Once you have that amount, subtract operating expenses, such as salaries and rent. Expenses for interest, taxes, and depreciation aren't considered in EBITDA, hence the "before", but when you do subtract them, what you're left with is your net income.
Calculating your business's EBITDA can help you gain a better understanding of its financial health. By keeping track of its earnings, you can set your small business up for a more profitable future.
beachhead market: the biggest difficulty is making the transition between early adopters and the early majority; he calls this the "chasm." Crossing the chasm involves focusing your resources on a single, primary market first, known as a beachhead market, before winning over that market and then using that momentum to dominate larger markets.
- The customers in that market buy similar products.
- Those customers have similar expectations of value.
- The customers use word of mouth to communicate to others in similar regions or professional organizations."