Risk Mgmt
A description of the potential risks and challenges involved in the business and how the company plans to mitigate them.

Risk Management
- Technical credibility based on portfolio of past projects
Greenfield software development refers to development work in a new environment with minimal pre-existing legacy code and free choice on tools, patterns, and architecture. is has the obvious advantage of allowing the thoughtful choice of the right architecture and tooling for the job, and no distraction from existing tech debt. The subtle downside is that, with so much choice and so few constraints, the risks of making poor decisions are higher. There is also usually a considerable bootstrap cost for new projects that is underestimated things like setting up testing, build systems, static code analysis, etc.
Brownfield software development refers to the opposite of greenfield, working with existing legacy systems. The tradeoffs are essentially inverted: for better or worse, you're stuck with the high-level decisions that have been made by those before you.
The largest risk in brownfield development is not invented here syndrome. Not invented here is the tendency for individuals to avoid taking responsibility for or paying sufficient attention to things they did not create themselves. In brownfield software development, this can lead to systematic underinvestment in understanding existing work, causing frustration and inefficiency in augmenting or modifying existing systems. I strongly encourage managers to make explicit space for a team to read and understand an existing system before asking them to modify it in any way. The time spent in comprehension upfront will be paid back by fewer surprises and faster velocity down the road.
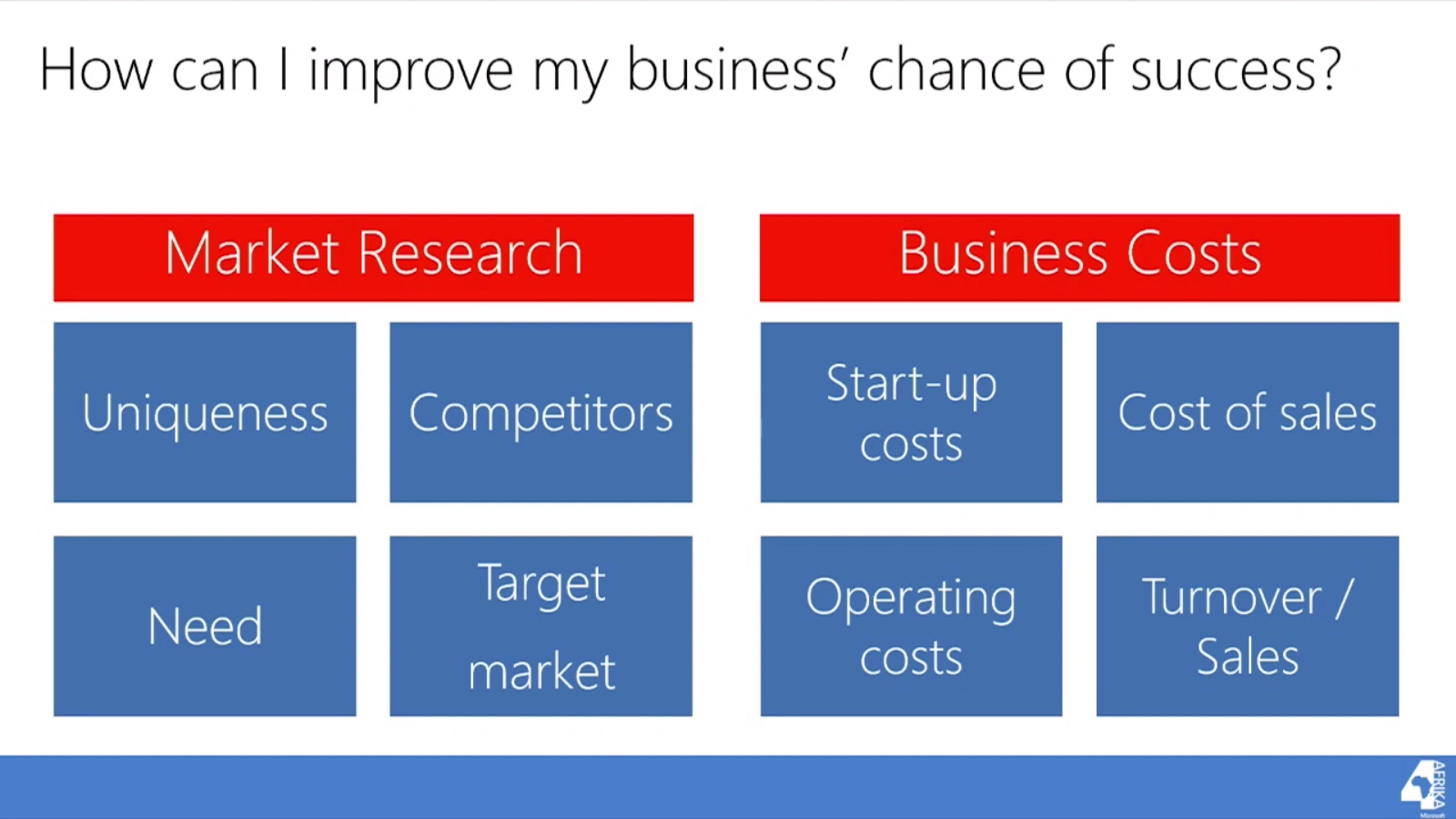
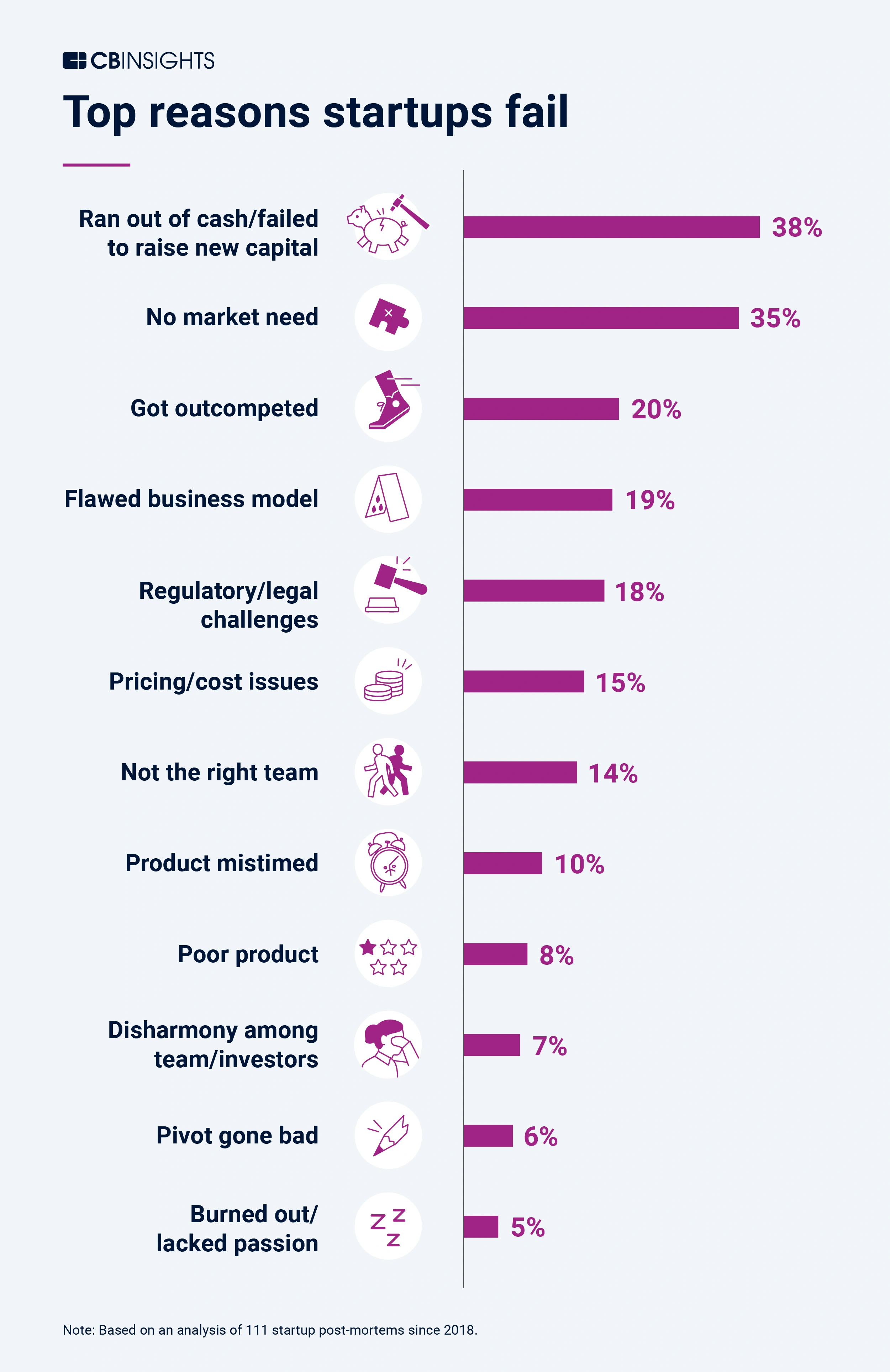
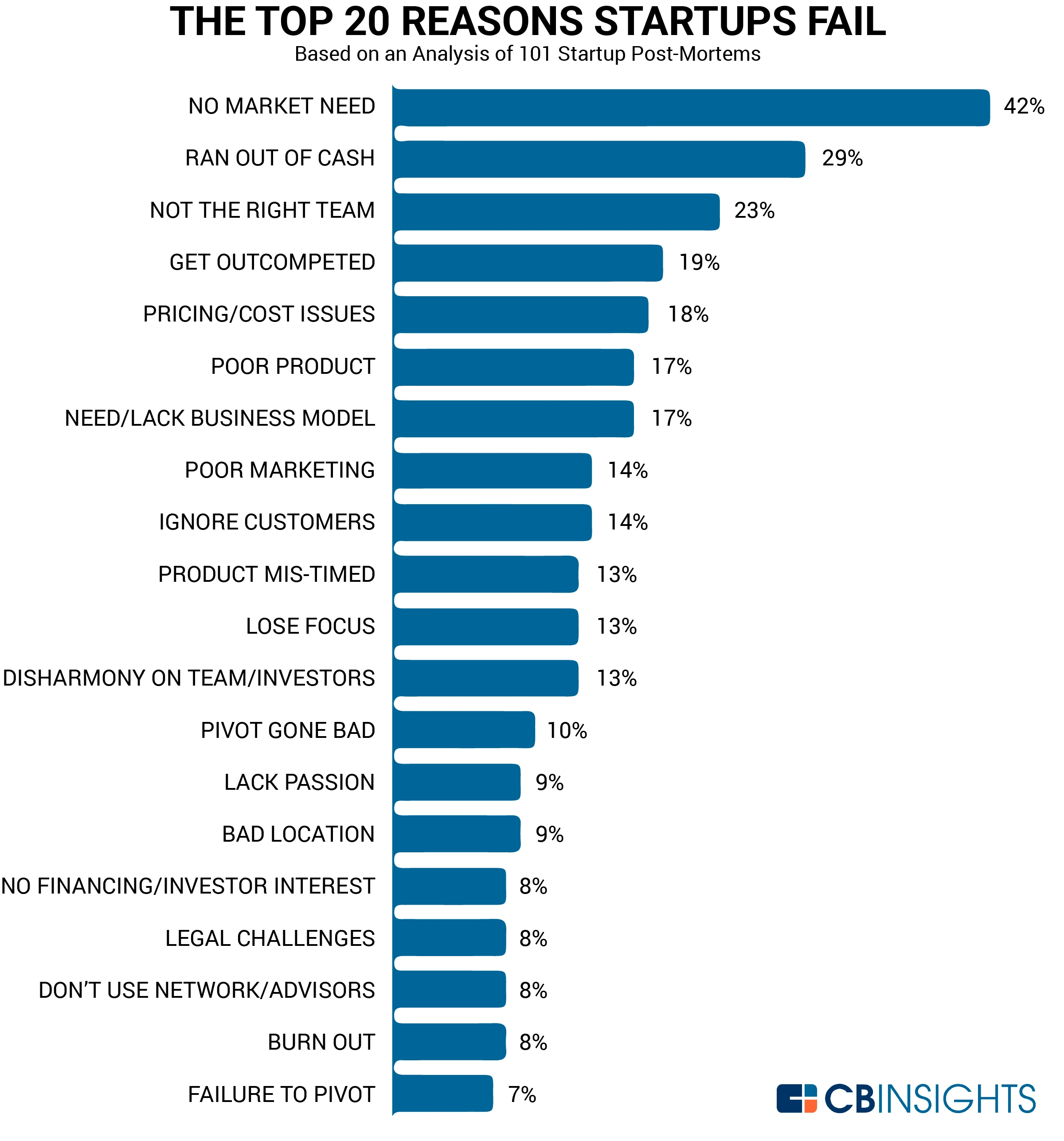
top reasons startups fail
14% - Ignore customers
13% - Lose Focus
13% - Disharmony within team OR with investors
9% Lack passion and committment
8% Don't connect / network / promote OR ask for help from advisors
8% Burnout
- We live in a world where working 50 years for someone is normal. but working for yourself for even a year is considered risky.
- Entrepreneurship is like one of those carnival games where you throw darts or something. Middle class kids can afford one throw. Most miss. A few hit the target and get a small prize. A very few hit the center bullseye and get a bigger prize. Rags to riches! The American Dream lives on. Rich kids can afford many throws. If they want to, they can try over and over and over again until they hit something and feel good about themselves. Some keep going until they hit the center bullseye, then they give speeches or write blog posts about "meritocracy" and the salutary effects of hard work. Poor kids aren't visiting the carnival. They're the ones working it.
- Don't confuse experience with expertise. Having faced a problem doesn't guarantee that you've mastered the solution. Don't mistake expertise for wisdom. Having deep knowledge doesn't guarantee that you know when it applies.
financial risks
1. Revenue Dependence
- Client Concentration: Relying heavily on a small number of clients can create financial instability. If one major client leaves, it can significantly impact revenue.
- Project-Based Income: Many agencies work on a project basis, leading to inconsistent cash flow. This can make financial planning challenging.
2. Market Changes
- Industry Trends: Rapid changes in marketing trends (e.g., shifts to digital or changes in consumer behavior) can render existing strategies ineffective.
- Economic Downturns: Economic fluctuations can lead clients to cut marketing budgets, affecting agency revenues.
3. Competitive Pressure
- Increased Competition: As more agencies enter the market, pricing pressures can reduce profit margins.
- Service Differentiation: Failing to differentiate services can lead to decreased demand and loss of market share.
4. Client Retention
- High Churn Rates: If clients frequently leave for better options, it can lead to unstable revenue streams and increased acquisition costs.
- Satisfaction and Loyalty: Poor client satisfaction can harm retention rates and reduce referral opportunities.
5. Operational Efficiency
- Cost Management: Inefficient operations can lead to higher costs, affecting profitability.
- Staff Turnover: High turnover rates can lead to increased recruitment and training costs, impacting overall productivity.
6. Cash Flow Management
- Delayed Payments: Clients delaying payments can strain cash flow, making it difficult to cover operational costs.
- Inadequate Financial Planning: Poor budgeting and forecasting can lead to financial shortfalls and inability to invest in growth.
7. Sales Strategy Risks
- Ineffective Sales Processes: Outdated or ineffective sales strategies can hinder new client acquisition and revenue growth.
- Lack of Diversification: Failing to diversify service offerings can limit potential revenue streams and growth opportunities.
Mitigation Strategies
- Diversify Client Base: Aim for a broad client portfolio to reduce dependency on a few major clients.
- Adapt to Market Trends: Stay informed about industry trends and be agile in adjusting services to meet changing demands.
- Enhance Client Relationships: Focus on building strong relationships and improving client satisfaction to boost retention.
- Invest in Marketing and Sales: Continuously refine marketing and sales strategies to attract new clients and retain existing ones.
- Financial Planning: Implement robust financial management practices to monitor cash flow and prepare for potential downturns.
By addressing these risks, a small business marketing agency can create a more sustainable financial and sales momentum, leading to long-term success.
scalability Risks
Scalability risks for a small business marketing agency can hinder growth and operational efficiency. Here are some key areas to consider:
1. Resource Constraints
- Limited Staff: Small teams may struggle to handle increased workloads, leading to burnout and decreased quality of service.
- Skill Gaps: Lack of specialized skills can limit the agency’s ability to offer diverse services or adapt to new trends.
2. Operational Inefficiencies
- Manual Processes: Reliance on manual processes can slow down operations and make it difficult to scale efficiently.
- Technology Limitations: Outdated or inadequate technology can hinder productivity and limit the ability to manage larger projects.
3. Client Management
- Overcommitment: Taking on too many clients without the capacity to deliver can damage reputation and client relationships.
- Inconsistent Client Experience: As the client base grows, maintaining consistency in service quality can become challenging.
4. Market Saturation
- Competitive Landscape: In a saturated market, differentiating the agency’s services can be difficult, impacting growth potential.
- Changing Client Needs: Rapid changes in client expectations or industry standards can require quick adaptations that the agency may not be prepared for.
5. Financial Constraints
- Cash Flow Issues: Rapid growth can strain resources, leading to cash flow problems if not managed properly.
- Investment Requirements: Scaling often requires significant upfront investment in technology, marketing, or personnel that may not yield immediate returns.
6. Dependency on Key Personnel
- Knowledge Silos: Relying too heavily on specific individuals for key processes can create vulnerabilities if those employees leave.
- Leadership Gaps: Without strong leadership, scaling efforts may falter due to lack of direction or strategic vision.
7. Client Acquisition Challenges
- Marketing Effectiveness: Scaling often requires effective marketing strategies that may not be in place, leading to inconsistent client acquisition.
- Brand Recognition: As the agency grows, maintaining brand identity and recognition can become challenging.
Mitigation Strategies
- Invest in Training: Upskill current employees to fill any skill gaps and prepare for scaling.
- Automate Processes: Implement technology solutions to streamline operations and reduce manual workloads.
- Develop a Scalable Business Model: Create service packages that can be easily scaled without compromising quality.
- Focus on Client Experience: Standardize processes to ensure a consistent and high-quality client experience.
- Build a Strong Team: Hire strategically to ensure a well-rounded team capable of supporting growth.
- Financial Planning: Maintain robust financial management practices to support cash flow during scaling phases.
By proactively addressing these scalability risks, a small business marketing agency can position itself for sustainable growth while maintaining service quality.
systemic risks
These risks are inherent to the development process, market dynamics, and organizational structure. Here are some key systemic risks to consider:
- Inadequate Data Protection Policies: Failing to implement robust data encryption, improper data handling, and inadequate security measures can lead to data breaches and compromise user trust.
- Choosing the Wrong Platform or Technology Stack: Selecting an unsuitable platform or technology stack can limit the app's performance, scalability, and user reach, making it difficult to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Insufficient Budgeting and Financial Management: Poor budgeting and financial management can lead to overspending, delayed project timelines, and inadequate resource allocation, ultimately impacting the app's development and maintenance.
- Lack of Clear Product Requirements: Failing to define and prioritize product features can result in costly rework, delayed launches, and user dissatisfaction.
- Inadequate Risk Evaluation and Prevention: Neglecting to identify and mitigate risks throughout the development process can lead to project delays, cost overruns, and poor app quality.
- Dependence on Key Personnel: Relying too heavily on individual developers or team members can create a single point of failure, making it challenging to adapt to personnel changes or departures.
- Inadequate User Feedback Mechanisms: Failing to establish effective user feedback mechanisms can lead to poor user experience, low adoption rates, and negative reviews.
- Overemphasis on Features: Adding too many features can result in a cluttered and confusing user interface, leading to user frustration and abandonment.
- Inadequate Documentation and Control Systems: Lack of documentation and control systems can make it difficult to track project progress, resources, and budget, increasing the risk of project delays and cost overruns.
To mitigate these systemic risks, mobile app tech start-ups should:
- Implement robust data protection policies and security measures
- Conduct thorough market research and platform/technology stack evaluations
- Establish clear budgeting and financial management processes
- Define and prioritize product features through user research and feedback
- Identify and mitigate risks throughout the development process
- Foster a diverse and adaptable team structure
- Establish effective user feedback mechanisms
- Prioritize simplicity and user experience in feature development
- Maintain detailed documentation and control systems for project tracking and resource allocation.
Using a Risk Matrix for a Tech Startup
A risk matrix is a valuable tool for tech startups to identify, assess, and prioritize potential threats to their business. By understanding the likelihood and impact of various risks, startups can allocate resources effectively and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Steps to Use a Risk Matrix
-
Identify Potential Risks:
- Internal Risks: These can include technical failures, human errors, supply chain disruptions, and internal conflicts.
- External Risks: These can include market competition, economic downturns, regulatory changes, and cybersecurity threats.
-
Assess Likelihood and Impact:
- Likelihood: Rate the probability of each risk occurring on a scale (e.g., low, medium, high).
- Impact: Evaluate the potential consequences of each risk on your startup (e.g., financial loss, reputational damage, operational disruption).
-
Create the Risk Matrix:
- Axes: Plot likelihood on the x-axis and impact on the y-axis.
- Quadrants: Divide the matrix into quadrants based on high/low likelihood and high/low impact.
-
Prioritize Risks:
- Focus on high-impact, high-likelihood risks: These pose the greatest threat to your startup.
- Address medium-impact, high-likelihood risks: While less urgent, these risks still require attention.
-
Develop Mitigation Strategies:
- Create action plans: For each prioritized risk, develop strategies to reduce its likelihood or impact.
- Allocate resources: Assign responsibilities and budget for implementing mitigation measures.
Example Risk Matrix for a Tech Startup
| Risk | Likelihood | Impact | Quadrant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cybersecurity breach | High | High | Quadrant I (High-Impact, High-Likelihood) |
| Market competition | Medium | Medium | Quadrant II (Medium-Impact, High-Likelihood) |
| Supply chain disruption | Low | High | Quadrant III (High-Impact, Low-Likelihood) |
| Technical failure | High | Low | Quadrant IV (Low-Impact, High-Likelihood) |
Tips for Effective Risk Management
- Involve your team: Encourage input from various departments to identify potential risks.
- Regularly review and update: As your startup evolves, reassess risks and adjust mitigation strategies.
- Utilize risk management software: Tools can help automate the process and provide valuable insights.
- Consider risk transfer: Explore insurance options to mitigate certain risks.
By effectively using a risk matrix, tech startups can proactively manage potential threats and increase their chances of long-term success.
Would you like to explore specific risks or discuss how to create a risk matrix for your startup? https://www.isitdownrightnow.com/
OPSEC Operational Security
OPSEC, or Operational Security, is a risk management process that involves identifying, controlling, and protecting sensitive information to prevent adversaries from obtaining critical insights. It aims to safeguard operational activities and maintain confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information in order to achieve mission success.
Operational Security (OPSEC) best practices for a tech startup leveraging cloud platforms like AWS or GCP involve implementing stringent access controls, regularly updating and patching systems to address vulnerabilities, encrypting sensitive data in transit and at rest, conducting frequent security audits, and utilizing cloud-native security tools for monitoring unusual activities. Employing multi-factor authentication, configuring network security groups effectively, adhering to the least privilege principle for access permissions, and providing comprehensive cybersecurity training for employees are essential measures to enhance overall OPSEC in the cloud environment.
For a tech startup utilizing cloud platforms like AWS or GCP, OPSEC best practices include implementing strong access controls, regularly updating and patching systems, encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest, conducting regular security audits, monitoring for unusual activities using cloud-native security tools, and providing cybersecurity training for employees to ensure awareness of potential threats and vulnerabilities. Additionally, employing multi-factor authentication, configuring network security groups effectively, and adopting a least privilege principle for access permissions contribute to a robust OPSEC posture in the cloud environment.
Risk Mitigation
examples of human-related factors that can contribute to project delays
-
Lack of clear communication: Poor communication among team members, stakeholders, or clients can lead to misunderstandings, delays in decision-making, and a lack of alignment on project goals and requirements.
-
Inadequate project planning and management: Insufficient planning, improper resource allocation, ineffective task delegation, or inadequate project management can result in missed deadlines, scope creep, and overall project inefficiencies.
-
Skill gaps or resource constraints: If team members lack the necessary skills or expertise to complete their assigned tasks, it can lead to delays as they may require additional training or assistance. Similarly, resource constraints, such as limited manpower or access to necessary tools, can impede progress.
-
Team conflicts or turnover: Internal conflicts, personality clashes, or high turnover rates within the project team can disrupt workflow, decrease morale, and cause delays in completing tasks or making critical project decisions.
-
Dependencies on external parties: When a project relies on external vendors, contractors, or partners, delays can occur if there are miscommunications, delays in deliverables, or unforeseen issues on their end.
-
Scope changes or indecisiveness: If there are frequent changes in project requirements, scope, or objectives, or if key stakeholders are indecisive or have conflicting priorities, it can lead to project delays as tasks may need to be reworked or additional approvals are required.
-
Inadequate risk management: Failure to identify and mitigate potential risks, such as not addressing known vulnerabilities or underestimating the impact of certain risks, can result in unexpected issues arising during the project, causing delays.
Risk Management
Overall, risk management requires a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating potential risks. By having strong policies, procedures, and protocols in place, as well as a commitment to ongoing risk management, web development businesses can minimize their exposure to risk and protect their long-term success.
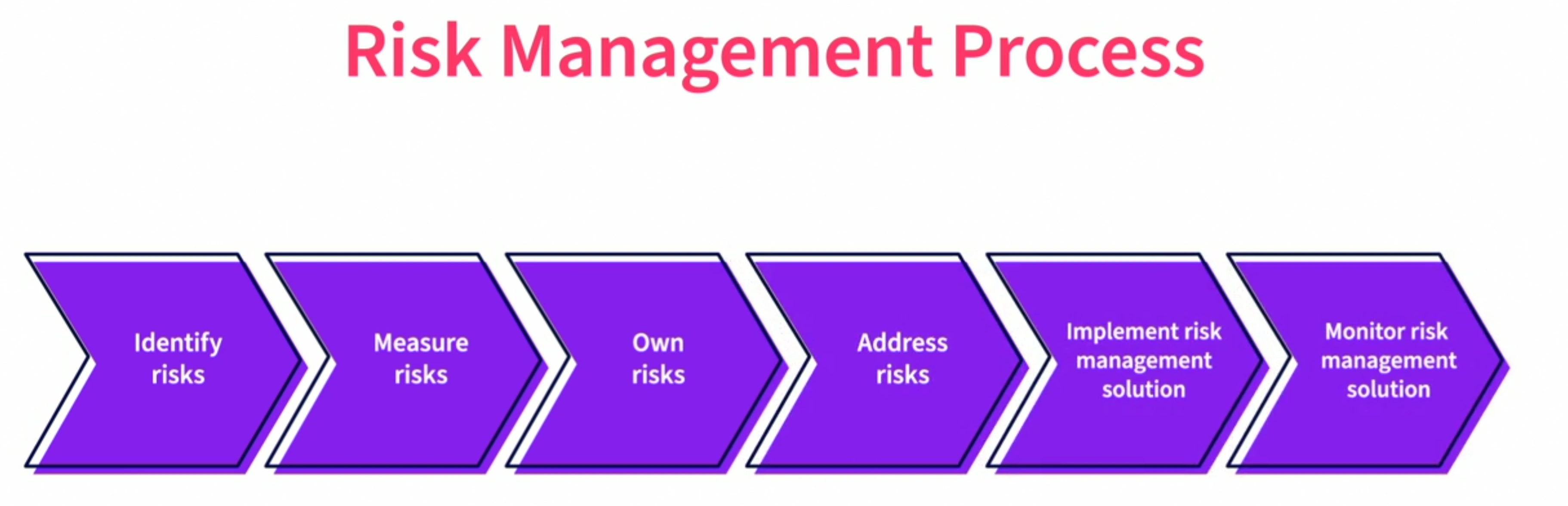
| Terms | definition |
|---|---|
| Upside Risk | opportunities for profits |
| Downside Risk | potential for losses |
| operational risk | insufficient controls, poor leadership, incompetence, things can go wrong day to day operations |
| strategic risks | lack of investment, or over-invest |
Legal Risks: Web development businesses face a variety of legal risks, including breach of contract, copyright infringement, and liability for data breaches or other security incidents. It's important to have contracts and agreements in place with clients, as well as strong security protocols to protect client data.
Financial Risks: Web development businesses may face financial risks such as cash flow issues, bad debt, and project cost overruns. It's important to have sound financial management practices in place, such as accurate budgeting, invoicing, and payment tracking.
Project Risks: Web development projects may face risks such as scope creep, missed deadlines, and technical issues. It's important to have a project management methodology in place, such as agile or waterfall, as well as clear communication with clients to manage expectations and address any issues that arise.
Cybersecurity Risks: Web development businesses may be targeted by cyber attackers seeking to access sensitive data or disrupt business operations. It's important to have strong cybersecurity measures in place, such as firewalls, anti-virus software, and regular data backups.
Human Resource Risks: Web development businesses may face human resource risks such as employee turnover, professional misconduct, and employment law violations. It's important to have clear policies and procedures in place for hiring, training, and managing employees, as well as compliance with employment laws.
Reputation Risks: Web development businesses may face reputation risks such as negative reviews, social media backlash, or public relations crises. It's important to have a crisis management plan in place, as well as a strong commitment to ethical business practices and customer service.
old notes
RISK ANALYSIS
Key differentiators are • We strive to ensure a quick and easy launch of the website as well as feedback. • First payment is due upfront to start the project, which includes the full package the second payment is due after 45 days. • encourage • Your project duration will • That will help build the perfect website. New Jersey community owned business other web designers only interact via phone and email. We make sacrifices to keep it a locally run business to ensure a high level of quality and build valuable relationships with our clients. • Pricing we deliver quality software to our consumers at a fraction of the going market rate
The following section breaks down the general risk associated with the development and establishment of the company. It displays the market, technology, operational, management, and legal risks that are associated with our company and the web design industry as a whole. This risk analysis allows potential investors to be aware of what might go wrong in starting or during the lifespan of the business.
MARKET RISKS
Market risk is the ability to successfully deliver the product to the market to a sizable portion of customers. Our market risk starts and ends with our ability to get in front of prospective customers either in person or via a wide array of marketing tools online in order to attract clients and gain market share. Our business model is fairly simple in that our sales will drive our development, which will in turn drive more sales as a result of several quality products that we offer. The market already exists and is not particularly dominated by any one company as previously noted in our market research section. Our job will be to persuade customers that we can deliver services and products beyond their needs. The only major change in consumer behavior that we can anticipate deals with customers’ voluntary decision and their satisfaction with our dashboard analytics software and online reputation management services.
TECHNOLOGY RISKS
Our technology risk lies in whether or not we can deliver our products on budget and on time to our customers. We are confident that we can manage our clients’ projects in a timely manner in a cost-effective manner. We can achieve this through our lean business model and by setting realistic and appropriate client deadline demands. We also know that we can stay at the forefront of any technological advancements and practices in the web design and development industry.
OPERATIONAL RISKS
The major operational risk that we face is balancing our sales accounts with development capabilities. At the very beginning, we might have more resources available than clients signed up for business. As time progresses, this trend might reverse and we might end up with too many projects in a small amount of time for our development capabilities. We hope to accommodate this by engaging in a driven sales strategy early on and potentially outsourcing development work outside of the company should the need arise.
RAID Log
A RAID log is a project management tool used to track and manage risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies (or decisions) throughout a project's lifecycle. It helps project managers identify potential risks, document assumptions, address issues promptly, and manage dependencies to ensure project success. The RAID acronym stands for:
- Risks: Potential problems that could negatively impact the project.
- Assumptions: Conditions that must be true for the project to proceed as planned.
- Issues: Problems that have already occurred and need resolution.
- Dependencies: Tasks or conditions that must be completed or met for the project to progress.
Go / No-go Decisions
Regarding go/no-go decisions for SaaS startups, these are critical decision points where the startup evaluates whether to continue or halt development based on specific criteria. These criteria typically include:
- Market validation: Ensuring there is a viable market for the product.
- Product viability: Confirming the product meets user needs and solves problems effectively.
- Financial health: Assessing whether the startup has sufficient resources to continue development.
- Technical feasibility: Verifying that the technology can be developed within the given timeframe and budget.
If these criteria are met, the decision is "go," and the startup continues with development. If not, the decision is "no-go," and the startup may need to pivot, seek additional resources, or terminate the project.
MANAGEMENT RISKS
Management risk is that which is associated in leading the team and making internal business decisions. Our team has several years of experience across broad business lines that include IT, sales, finance, and project management. We are confident that we can make the best possible business decisions given the circumstance. We are prepared to hire talented people and outside consultants to help manage our business if need be as we are flexible and open to innovate strategies to grow our business.
LEGAL RISKS
IPR: intellectual property rights INTERNATIONAL SCHEDULE OF CLASSES OF GOODS AND SERVICES. acceptable identification of goods and services TMEP
Legal risk refers to loss of business that can result from any potential lawsuits directed at the founders or business as a whole. We have limited these risks through the incorporation of our business as well as the recent purchase of insurance. Our intellectual property is also protected as all of our business partnerships and dealings are required to sign a form stating our company rights and their own rights. We are not infringing on any other company’s patents or copyrights. Even more so, we can limit our liability by handling our business in a professional manner with ethics and best practices being our priority. Can an unregistered mark used by an early-stage startup be poached? Most definitely. Does it happen in practice? Very rarely. Against that context, it is up to each founding team to make a cost-benefit assessment of whether it is worth front-loading the legal expense (usually about $2K to $3K for a federal registration) to guard against that risk. The usual answer is no. But, for any really valuable name, it should be yes. From my experience, in practical terms across a range of early-stage startups, it can easily be said, however, that 90+% do not bother with such registration at the start on cost-benefit grounds.
Strategies to Enhance Performance Under Pressure
-
Reframe Your Mindset: View high-pressure situations as opportunities to demonstrate resilience and leadership rather than threats.
-
Pause Before Reacting: Take a moment to breathe and assess the situation to respond thoughtfully instead of impulsively.
-
Develop Contingency Plans: Prepare strategies for potential high-stress scenarios to enable swift and effective responses.
-
Practice Under Simulated Pressure: Engage in role-playing exercises to build confidence and improve decision-making in stressful conditions.
-
Maintain Physical Well-Being: Incorporate regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and relaxation techniques to keep your body and mind resilient.
-
Establish Resilient Routines: Adopt daily habits such as journaling or structured problem-solving to strengthen your stress management skills.
