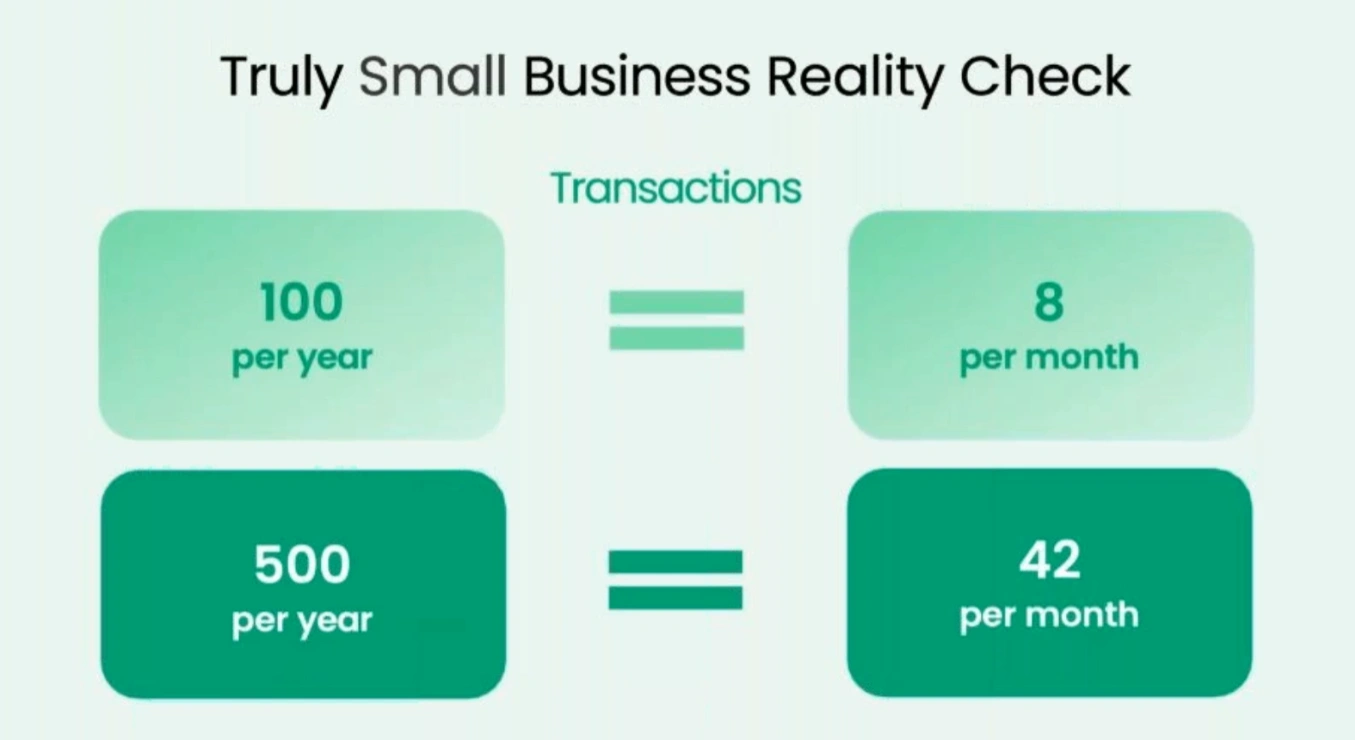
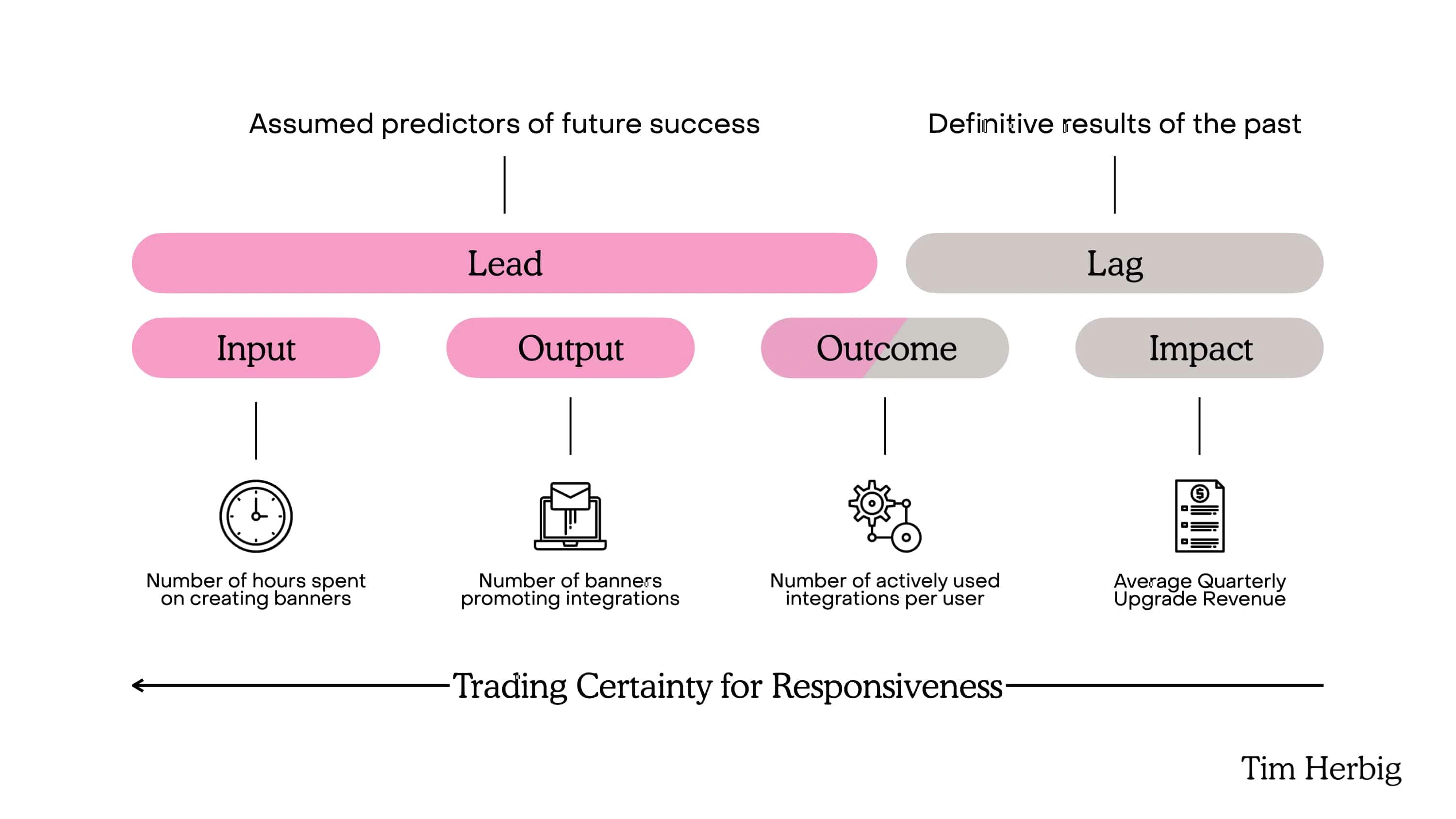
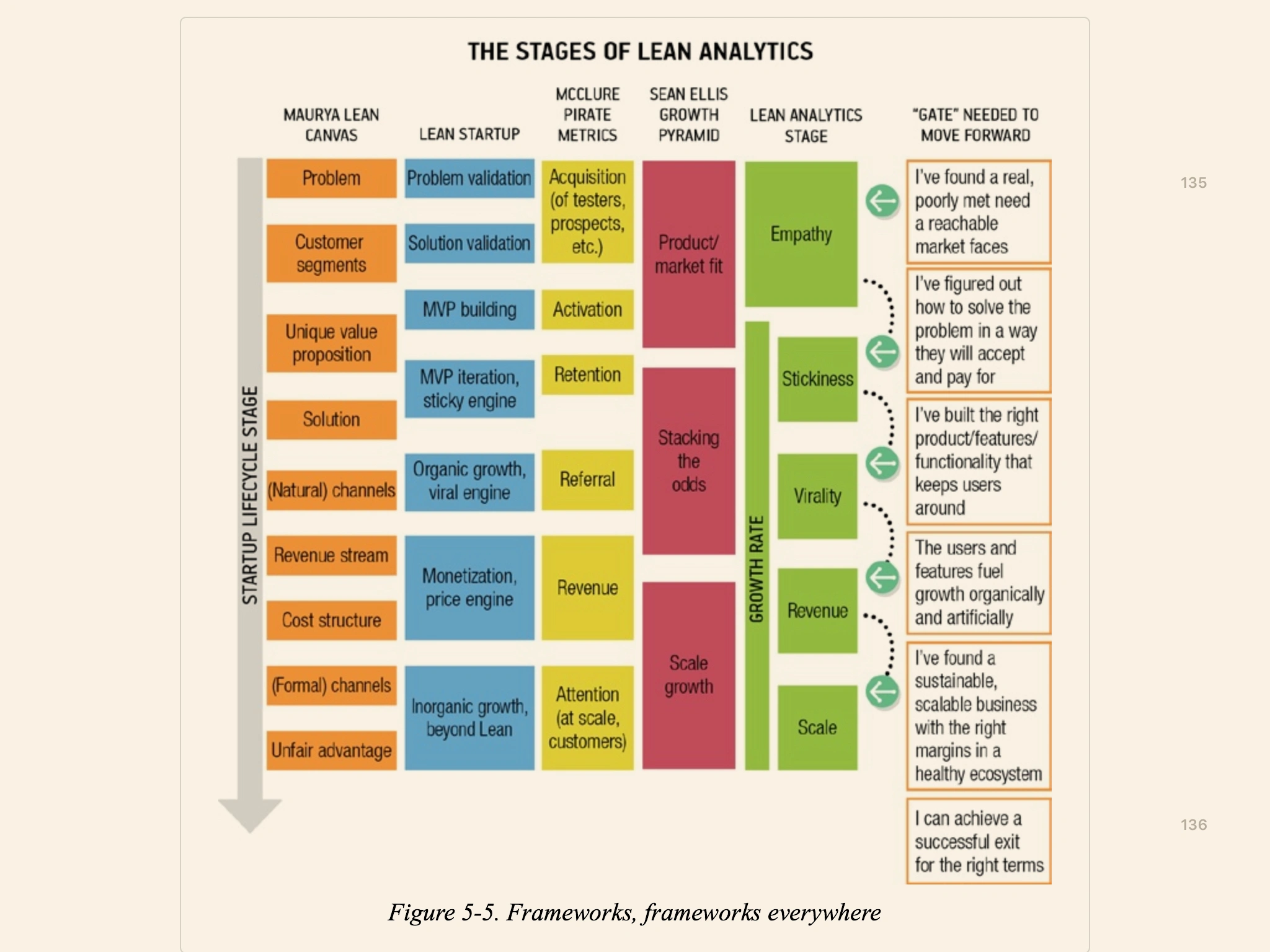
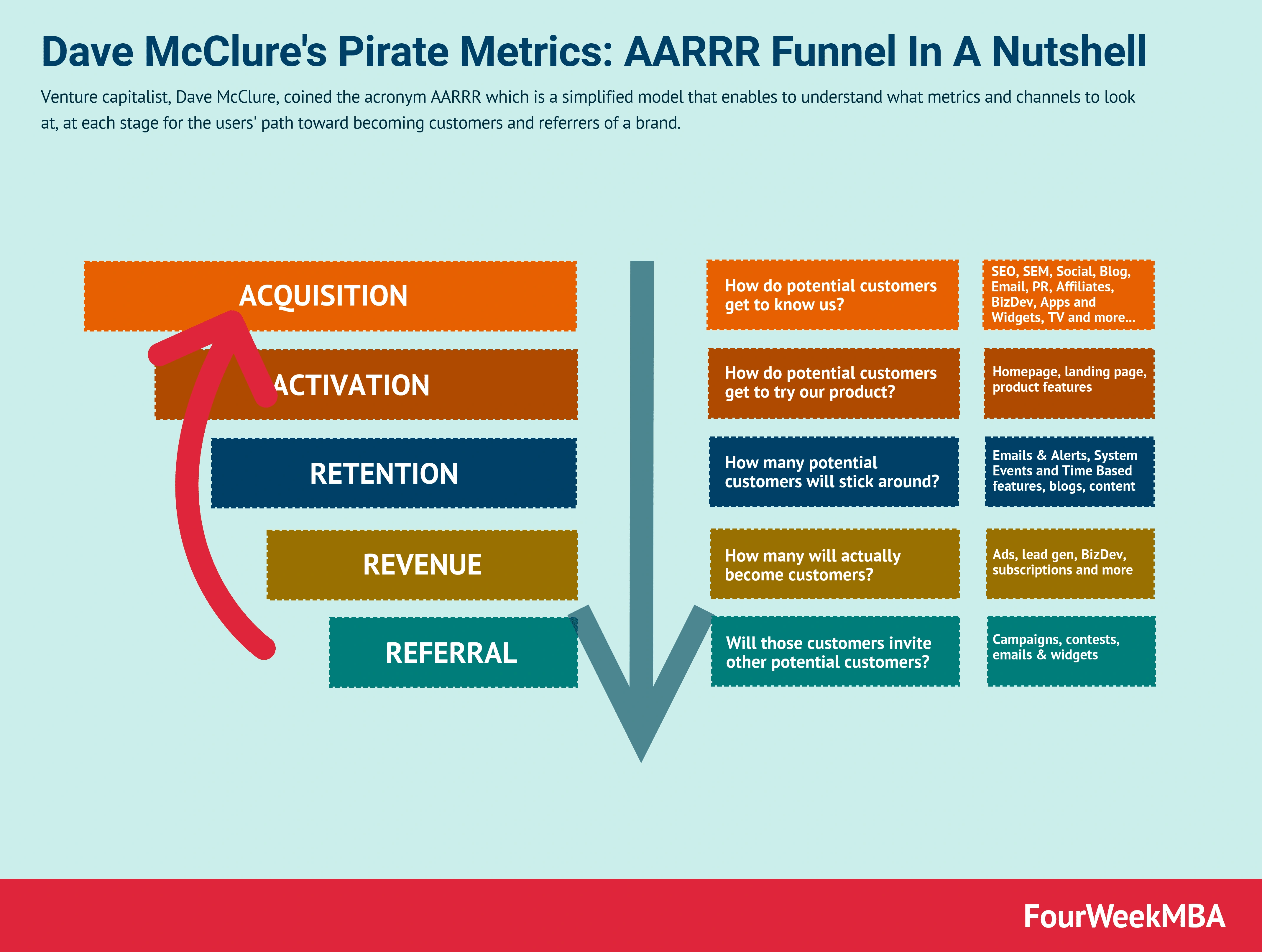
Metrics
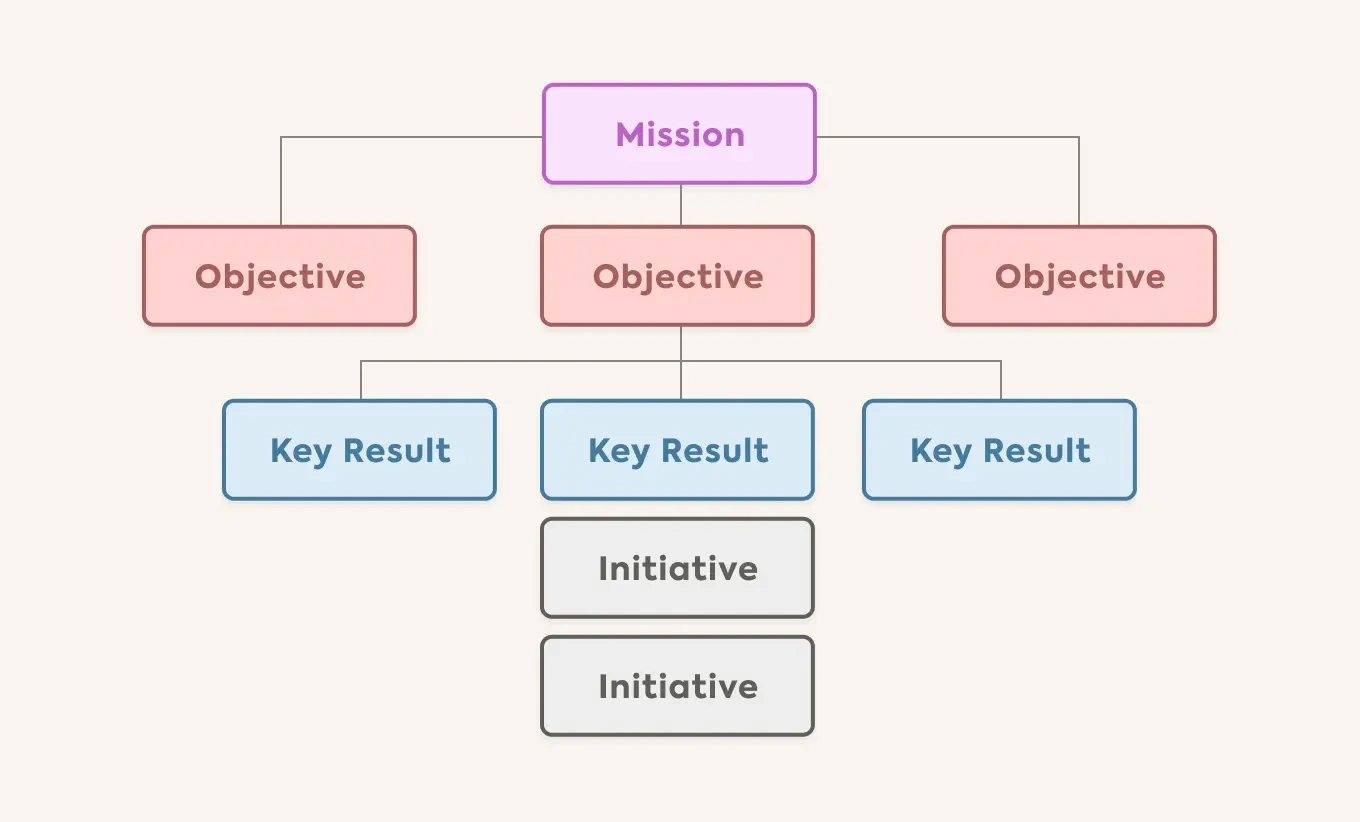
KPI & OKR Categories
- financial
- user
- acquisition
- sales
- marketing
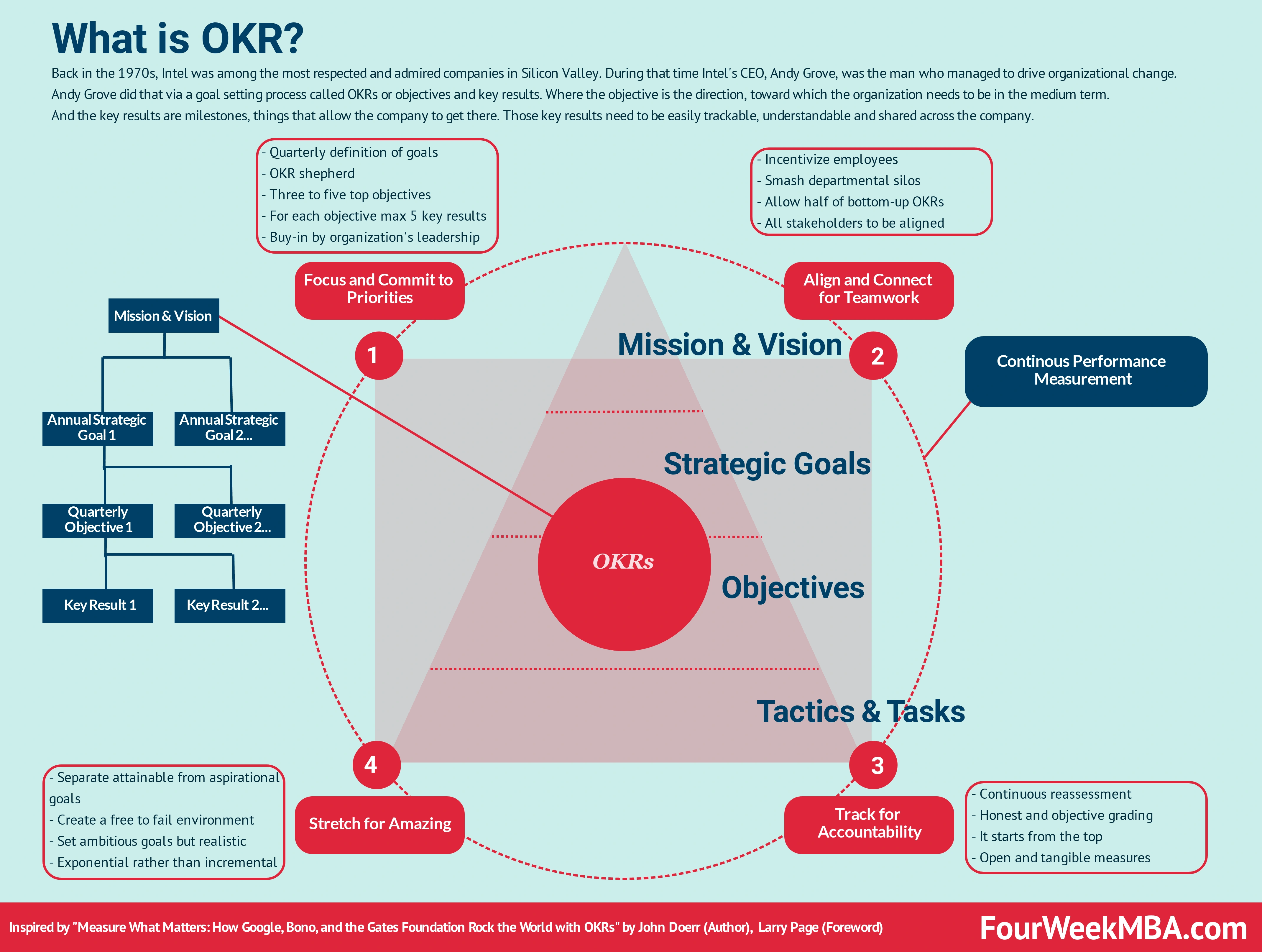
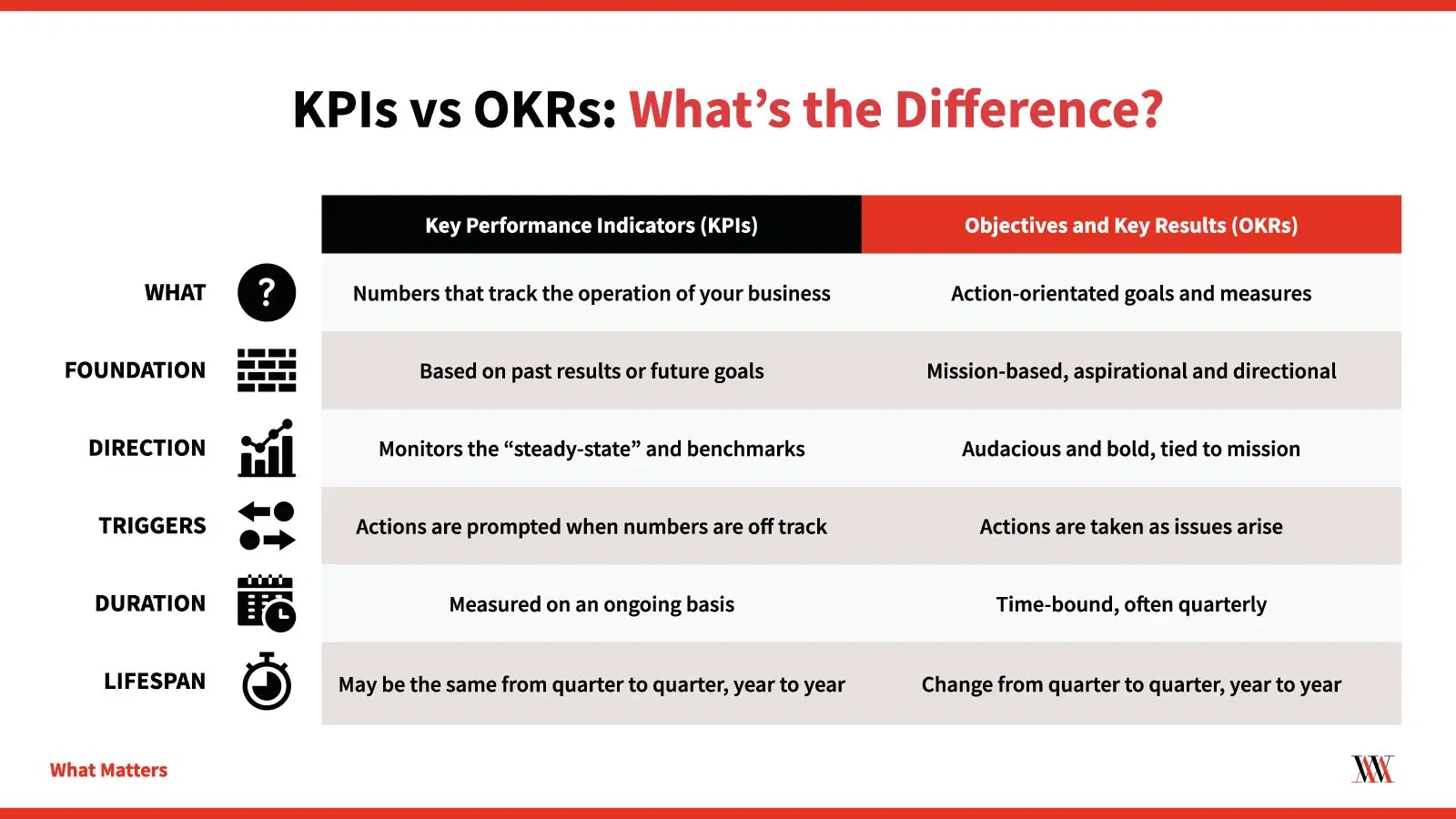
KPIs vs OKRs
That's a fantastic application of the term, particularly relevant given your role in running an agile tech firm!
In agile people performance management, maladaptive behaviors are processes, individual actions, or cultural remnants of a traditional/waterfall model that actively impede the agile team's ability to be flexible, collaborate, learn continuously, and deliver iterative value.
📉 Examples of Maladaptive Behaviors
These behaviors are "maladaptive" because they undermine the core adaptive traits required by an agile environment, leading to reduced productivity, lower morale, and a failure to meet customer needs quickly.
| Category | Maladaptive Behavior | Impact on Agile Adaptation |
|---|---|---|
| Individual/Team | Hero Culture: An individual consistently acts as the sole expert, hoarding knowledge and monopolizing problem-solving. | Undermines collective ownership and cross-functionality; creates a single point of failure and slows the team down when the "hero" is absent. |
| Individual/Team | Withholding or Gatekeeping Feedback: Fear of conflict or reprisal leads to avoiding honest conversation in Retrospectives or one-on-ones. | Destroys psychological safety and cripples the ability to enact continuous improvement (Inspect and Adapt). |
| Process/Structure | Rigid Annual Review Cycle: Performance evaluations are conducted only once a year based on fixed goals set 12 months prior. | Directly opposes the need for real-time feedback, goal adaptation to changing market needs, and continuous coaching. |
| Process/Structure | Focusing Solely on Utilization (Busy-ness): Measuring performance based on how many hours an individual spent "working" or how full their capacity is. | Incentivizes task inflation and multitasking over delivering customer-centric value (working software); ignores the value of learning and collaboration. |
| Leadership/Managerial | Micro-management of How: Managers dictate the specific technical steps or solutions rather than setting a clear outcome or goal. | Undermines self-organizing teams and empowerment, leading to dependency and disengagement. |
| Leadership/Managerial | Gaming the Metrics (Velocity Inflation): Pressure to increase story point velocity leads teams to inflate estimates rather than improving the actual process. | Creates a false sense of progress, corrupts the use of data for predictive planning, and destroys transparency. |
To manage performance adaptively, you need to shift the focus from managing individual output (maladaptive) to coaching and enabling high-performing, self-correcting teams (adaptive).
Would you like to explore strategies for replacing one of these specific maladaptive behaviors with an adaptive agile practice?
Analytics and Reporting
The marketing agency will provide regular analytics and reporting on the performance of the marketing campaigns, including metrics such as website traffic, social media engagement, and advertising ROI.
- Prescriptive Analytics
- Diagnostic Analytics: answer to the question "what happened", Diagnostic analytics try and then figure out "Why did this happen".
- predictive analytics
If it’s not being measured it’s not being managed
Table of Contents
Lead Gen is a shared KPI between sales and marketing
- If it’s targeted & outbound → Sales
- If it’s scalable & inbound → Marketing
- Handoff at Stage 2 (Discovery Call) → Marketing → Sales
KPIs
Measuring Return on Investment (ROI) in digital marketing
Measuring Return on Investment (ROI) in digital marketing involves tracking and analyzing the financial performance of marketing campaigns and activities to determine their effectiveness and profitability. Here are some steps to measure ROI in digital marketing:
Set Clear Goals
Clearly define your marketing objectives and goals. These goals could include increasing website traffic, generating leads, improving sales, or enhancing brand awareness. Specific, measurable goals will provide a basis for evaluating ROI.
Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identify the key metrics that align with your goals. For example, if your goal is to increase website conversions, KPIs may include conversion rate, cost per conversion, and revenue generated from conversions. KPIs should be relevant, quantifiable, and directly tied to your objectives.
Establish Tracking Systems
Implement tracking mechanisms to gather data related to your KPIs. This can be done through web analytics tools, conversion tracking pixels, CRM systems, or custom tracking codes. Ensure that you have the necessary infrastructure in place to accurately track and attribute results to specific marketing efforts.
Assign Values to Conversions
Assign a monetary value to each conversion or desired action. This value can be based on average customer lifetime value, average purchase value, or any other relevant financial metric. It allows you to calculate the revenue or value generated by your marketing efforts.
Calculate Costs
Determine the costs associated with your digital marketing activities. This includes expenses such as advertising spend, agency fees, content creation costs, software subscriptions, and staff salaries dedicated to marketing efforts. Ensure that you consider both direct and indirect costs.
Calculate ROI: Once you have the data on revenue generated and costs incurred, you can calculate ROI using the following formula
ROI = (Revenue - Cost) / Cost * 100. This will give you a percentage value representing the return on your marketing investment.
Analyze and Optimize
Continuously analyze your ROI data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. Compare the performance of different campaigns, channels, or strategies to determine which ones are delivering the highest ROI. Use these insights to optimize your marketing efforts and allocate resources effectively.
It's important to note that measuring ROI in digital marketing may not always be straightforward, especially when attributing conversions to multiple touchpoints or considering long-term customer value. However, by establishing clear goals, tracking relevant metrics, and consistently evaluating performance, you can gain valuable insights into the effectiveness of your digital marketing initiatives and make informed decisions to optimize your ROI.
- usability-based KPIs
- Revenue
- Market Share
- Client Satisfaction
- Return Purchases
- Estimated vs. Actual Project Budget
- Estimated vs Actual Project Time
- Lead Time Per Project: Lead time refers to how much time a project takes from request to final delivery.
common KPIs
UI KPIs
o roll-over (hover) o clicks o interaction
Metric Types
- std
- participation
- video
- calculated
- mobile
- lifetime
Segmentation
Metrics
- Lead-to-sales conversion ratio
https://startupdevkit.com/types-of-startup-kpis-metrics-to-measure-with-examples/
Actionable Metrics Vocab
- Market
- Market Segmentation
- Market Aggregation
- opposite of segmentation; form a single group and handle all users in the same way
- Personalization:
- localized
- username identity
- Personalized Email responses
- https://econsultancy.com/blog/63622-a-five-step-roadmap-for-using-personalisation-in-ecommerce#i.ost7kajljfotz4
- User Persona
- ROI
personalization
Welcome Screen
Targeted Content
- based on geolocation assumed from ip address
user behavior tracking
amazon redshift amazon EMR
mine user behavior to improve results
- session info: queries/results, clicks, purchases
- document boosting / promoted results
- rank expression
- add query field to store keywords searched
- synonym creation between query keywords and clicked results
key metrics for founders
key quantitative metrics that venture capitalists use to evaluate early-stage startups. financial metrics are crucial for any startup, and some companies are funded by venture capitalists simply for having a great balance sheet and statement of cash flows.
Examples of metrics include monthly revenue growth, revenue run rate, gross and net margins, burn rate and runway, K-value (a measure of virality), proportion of mobile traffic, cohort analysis and churn, and cost of acquiring a customer. The guide provides benchmarks for each metric and explains their importance in the evaluation process.
monthly revenue growth, revenue run rate, gross and net margins, burn rate, and runway
For investors, your burn rate and runway, illustrate the efficiency of your business, your ideal fundraising timeline, and your company’s capital needs. While startups often keep their operations and expenses relatively lean until their first fundraise, VCs want to know how you plan to sustainably invest back into your company with new capital infusions while still considering healthy spend management and runway.

- user metrics are essential for VCs to assess the quality of a startup. Key user metrics include K-value (a measure of virality), proportion of mobile traffic, cohort analysis, and churn.
- acquisition and marketing metrics, which go to the core of a business model and its sustainability.
- understand the cost of acquiring a customer and payback, which are essential metrics for subscription companies and most other startups.
while the metrics are essential, the relevant weight any one metric will hold in a VC’s decision will depend on the type of startup and the VC’s opinion about which metrics matter and which do not.