BCG Matrix
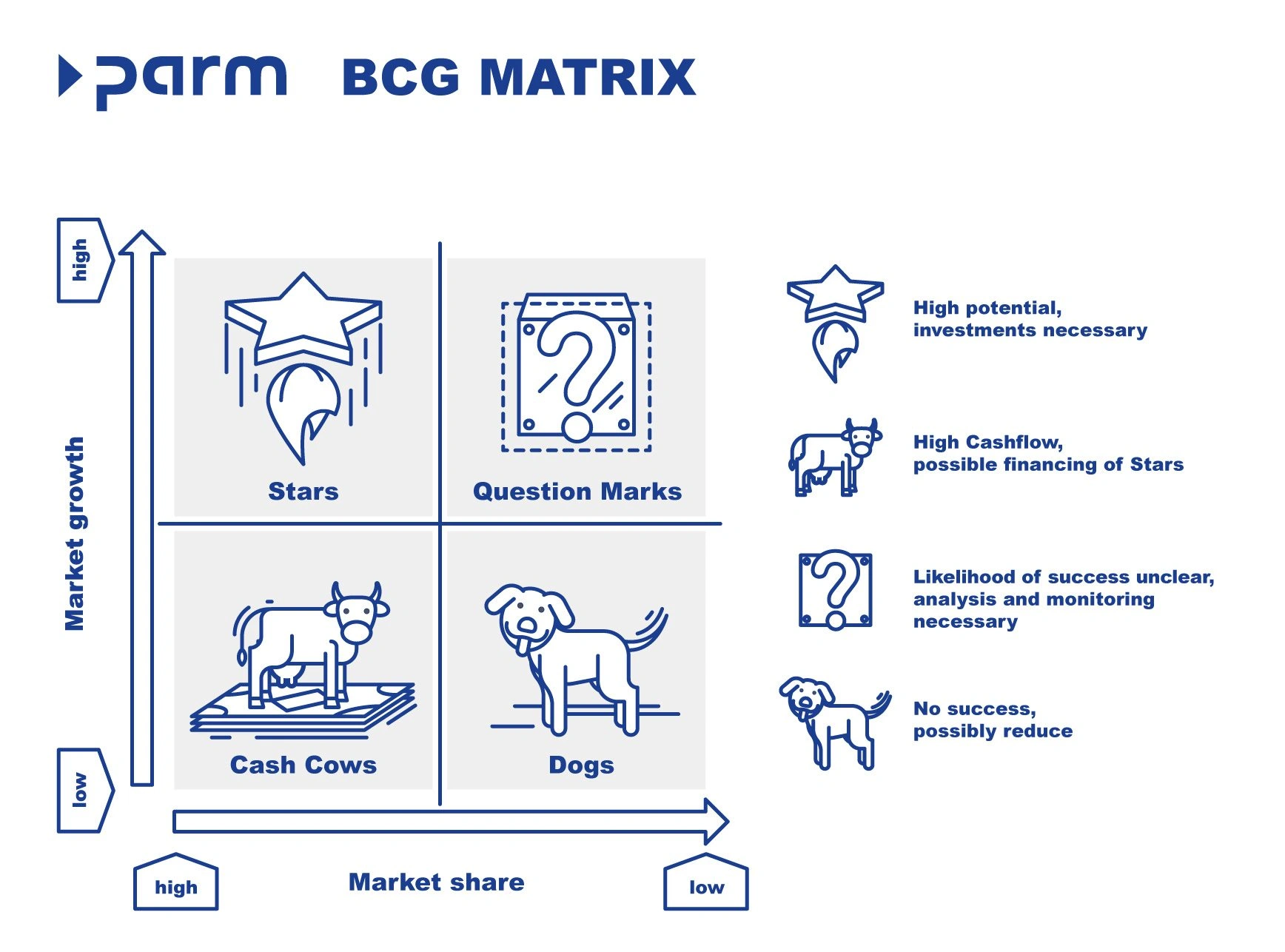
- you can apply the BCG Matrix to your service lines or client segments to strategically guide your agile product/service backlog and resource sprint planning.
The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix, or Growth-Share Matrix, is a pivotal strategic planning tool for analyzing a company's product or business unit portfolio to guide resource allocation and marketing strategy.
It classifies products into four quadrants based on two dimensions: Market Growth Rate (vertical axis) and Relative Market Share (horizontal axis).

📊 The Four BCG Matrix Quadrants and Marketing Strategies
The matrix provides prescriptive marketing and investment strategies for each product category:
| Quadrant | Description (Market Position) | Strategic Goal & Marketing Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| ⭐ Stars | High Market Growth, High Relative Market Share. Market-leading products in fast-growing markets. They consume significant cash to maintain their growth and competitive edge. | Build/Invest: Invest heavily to maintain market dominance, fund capacity expansion, and support product improvements. The long-term goal is for them to become Cash Cows as the market matures. |
| 💰 Cash Cows | Low Market Growth, High Relative Market Share. Mature, established, and dominant products in slow-growing markets. They generate more cash than they consume. | Hold/Harvest: Maintain market share with minimal investment. "Milk" the profits to fund Stars and promising Question Marks. Focus on efficiency, cost leadership, and defending current position. |
| ❓ Question Marks | High Market Growth, Low Relative Market Share. Products in fast-growing markets but with a low market share. They require significant investment to gain share, but the outcome is uncertain. | Invest or Divest (Triage): Carefully analyze potential. Invest aggressively (Build) if there is a realistic chance of becoming a Star, or divest/phase out (Harvest/Divest) if market share gains seem unlikely or too costly. |
| 🐕 Dogs | Low Market Growth, Low Relative Market Share. Products in slow-growing markets with low market share. They typically generate low or no profit and may tie up company resources. | Divest/Withdraw: Minimize investment or divest/liquidate the product line. Only keep them if they serve a specific strategic purpose (e.g., complement a Cash Cow, provide a niche service, or block a competitor). |
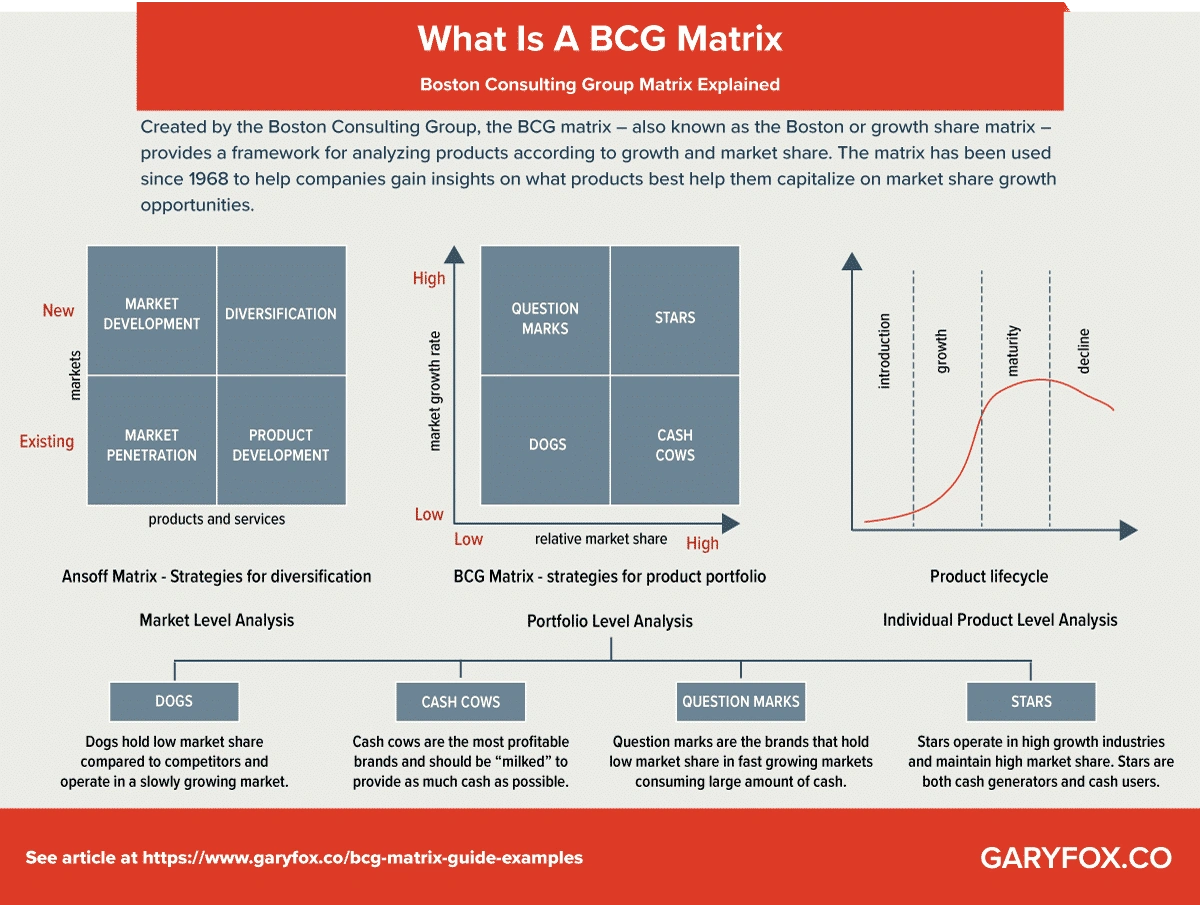
📈 BCG Matrix in the Marketing Planning Stages
The BCG Matrix is most relevant during the Strategic Analysis and Strategy Formulation phases of the overall marketing planning process:
1. Strategic Situation Analysis (Internal Assessment)
- Purpose: To assess the health and balance of the current product portfolio.
- BCG Role: The matrix serves as a visual framework to plot all Strategic Business Units (SBUs) or major product lines. This immediately highlights which products are driving current profit (Cash Cows), which promise future growth (Stars), which are speculative risks (Question Marks), and which are a drain on resources (Dogs).
- Output: A clear understanding of the company's competitive position and cash flow dynamics across its portfolio.
2. Marketing Strategy Formulation
- Purpose: To set objectives and define the core strategy for each product or SBU.
- BCG Role: The quadrant position directly informs the chosen generic strategy (Build, Hold, Harvest, Divest). This guides crucial decisions on resource allocation and long-term marketing objectives.
- Example: A strategy for a Star SBU will prioritize market expansion, aggressive promotion, and distribution, while a strategy for a Cash Cow will focus on maintaining customer loyalty and operational efficiency.
3. Resource Allocation and Budgeting
- Purpose: To determine where financial and human resources should be invested.
- BCG Role: The matrix provides the justification for prioritizing investment. Cash generated by Cash Cows is allocated to fund the aggressive marketing, R&D, and expansion needed for Stars and selected Question Marks. It also identifies where budget cuts (Dogs) can free up funds for more promising ventures.
4. Implementation and Control
- Purpose: To execute the plans and monitor performance.
- BCG Role: While less direct, the matrix provides performance benchmarks (market share and growth rate) for the control stage. The success of a Question Mark is measured by its movement toward the Star quadrant, and a Star's long-term health is confirmed if it eventually moves toward the Cash Cow quadrant as the market matures.