User Personas
- Demographics (age, gender, salary, location, education, family)
- Goals and challenges
- Value and fears
- Pain points or complaints
- Hobbies
- Where they get their news or other information
- Blogs they read
- Shopping preferences
- Apps used most frequently
- General lifestyle description
- Day in their life
- Work and/or school activities
- Relationship with friends
- Culture
- Relationship with technology
- How is free time spent?
- Social media usage
- Views on health and well-being
- Quotes from interviews
Developing User Personas (Who are the decision-makers within these segments?)
For each primary segment, let's create a representative persona. Remember, these are archetypes, not real people. Focus on their roles, goals, challenges, and how they make decisions.
Integrating into Your Marketing Plan
Now, how do you use these?
-
Website Content & Messaging:
- Homepage: Clearly state who you help (e.g., "Web Solutions for Professional Practices & Local Retailers" or "Helping Local Businesses Thrive Online").
- Service Pages: Tailor language to the pain points and goals of each persona.
- For Doctors/Lawyers: "Secure & Professional Websites for Your Practice," "Streamline Patient Intake," "Boost Your Online Reputation."
- For Retailers: "E-commerce Solutions that Drive Sales," "Showcase Your Products Beautifully," "Local SEO for Increased Foot Traffic."
- For Nonprofits: "Engage Donors & Amplify Your Mission," "Streamlined Online Giving."
- Case Studies: Feature diverse clients but frame them to resonate with your primary segments. "How We Helped Dr. Chen Increase New Patient Leads by 30%."
-
Portfolio Showcase:
- Organize your portfolio by industry or type of business if possible.
- Highlight the results you achieved for each client, not just the design. (e.g., "Increased online inquiries by 25%," "Improved website conversion rate").
-
Content Marketing (Blog, Social Media):
- Write blog posts directly addressing persona pain points:
- "5 Must-Have Website Features for Your Dental Practice"
- "Why Your Auto Dealership Needs a Mobile-First Website"
- "Storytelling Strategies for Nonprofit Websites"
- Share relevant industry news or tips on social media (LinkedIn for professional services, Instagram for visual-heavy retail).
- Write blog posts directly addressing persona pain points:
-
Targeted Outreach/Networking:
- Referral Partnerships: Seek referrals from industry-specific associations (e.g., local dental associations, chamber of commerce, legal bar associations).
- Networking: Attend local business expos, chamber meetings, or events relevant to your target segments.
- Online Ads (if budget allows): Target ads based on industry, job title, and interests on platforms like Google Search and LinkedIn.
- Cold Outreach: Craft personalized emails that speak directly to the persona's challenges.
-
Sales Pitches:
- During initial calls, actively listen to identify which persona's pain points the prospect exhibits.
- Tailor your pitch to emphasize the solutions that directly address their specific challenges and goals.
- Use language and examples that resonate with their industry.
- A business that does not have an IT employee on staff
- Small business with under 1 million in revenue
- Small business that is not affiliated with any franchise or chain
Creating an End User Profile
Typically, an end user profile consists of six items: demographics, psychographics, proxy product, watering holes, dav in the life, and biggest fears and motivators."° Demographics: Demographics are useful data in identifying your target end user, but they may not be entirely accurate when it comes to understanding your end user. For example, if you find out that your end users are all men in their 30s living in a particular geographic location, it doesn't tell you much about their attitudes or likes and dislikes. It is important to analyze demographics, but don't place too much emphasis on them
Psychographics: Psychographics is a method used to describe the psychological attributes (attitudes, values, or fears) of your target end users. Unlike demographics, which provide basic intormation about your users, psychographics present a more detailed overview, such as their aspirations, whom they admire, what they believe, and so on. However, it is difficult to get psychographic data and even harder to analyze for accuracv. For example, Facebook may be able to give you some information about users' likes and dislikes, but it's more difficult to pinpoint in-depth detail like fears.
Proxy product: Proxy products give you an idea of what else the user is likely to buy. For example, people who already buy from high-end fashion brands are more likely to buy an expensive piece of clothing. Proxy products can also display some demographic and psychographic characteristics. For instance, people who buy from farmer's markets rather than from potentially cheaper supermarkets may be interested in promoting sustainability. This group might also be interested in eco-friendly products, such as clothes made from recycled fabric or homemade skincare merchandise.
Watering holes: Watering holes are the places where users meet and swap information. They are also the best spots for word-of-mouth recommendations. There are many different types of watering holes, both formal and informal. Formal meeting places include work conferences or business meetings, while less formal watering holes include bars, fitness classes, and social media.
Day in the life: One of the most useful ways entrepreneurs can create a profile of their end users is to walk in their shoes for a day. This method is particularly effective after you have spent some time observing and talking to a group of end users. Creating this real-world story puts all the data into perspective and provides a deeper insight into the behavior of your potential customers. As serial entrepreneur Les Harper says, "If you can get into their shoes and see their needs from their point of view, then you can take your experience and your entrepreneurial drive and really satisfy them."
Biggest fears and motivators: Find out what keeps your end users awake at night and identify their top priorities in order to understand their biggest fears and motivators. This exereise is best carried out by sitting with a group of end users, making a comprehensive list of all their concerns, and asking them to score their priorities from highest to lowest. By the end of the exercise, you will have a list of their top five priorities, which will be a useful addition to all the research you have carried out so far.
Buyer Persona 1
- Demographics
- Characteristics
- Marketing mix
- Psychologoical
- Sociocultural
- Situational
Buyer Persona 2
- Demographics
- Characteristics
- Marketing mix
- Psychologoical
- Sociocultural
- Situational
Buyer Persona 3
- Demographics
- Characteristics
- Marketing mix
- Psychologoical
- Sociocultural
- Situational
- Marketing Program
- product strategy
- price strategy
- promotion strategy
- place/distribution strategy
- 5 year sales projection
- organization
- Implementation Plan
- Evaluation
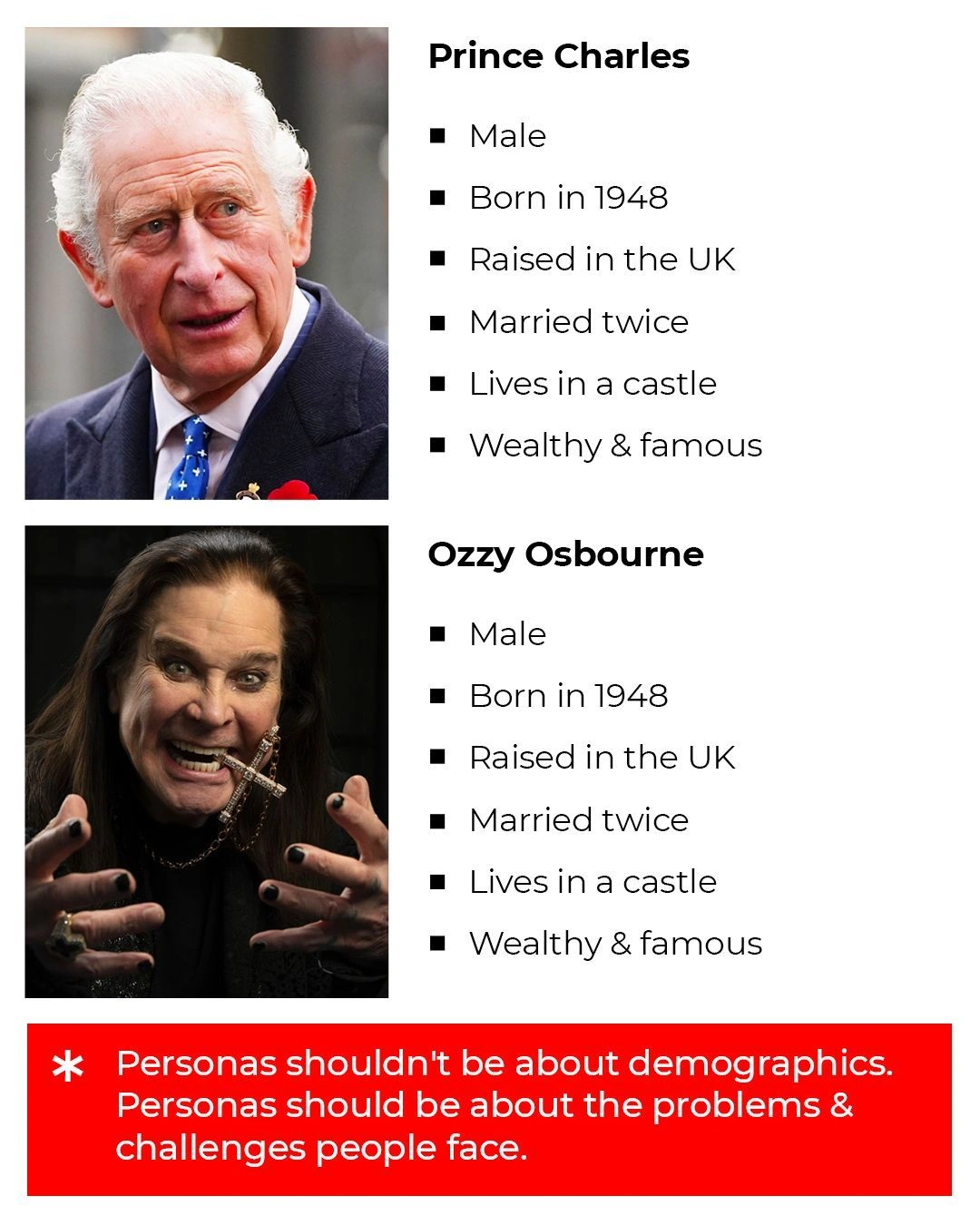
2 different people, same persona
User personas: User personas are fictional representations of the different types of users that will be using the website. They help define the needs, goals, and behaviors of the target audience and inform the content strategy.
The user persona process is a UX research method used to create fictional representations of the different types of users who will be using a website, product, or service. User personas are created based on data collected through user research, including user interviews, surveys, and observation. The user persona process typically involves the following steps:
By using the user persona process, UX designers can create a better understanding of the target audience and design solutionsthat meet their needs and preferences. Personas help designers empathize with users and make design decisions that are based on user needs, rather than assumptions or personal preferences. This ultimately leads to a better user experience and higher user satisfaction.
Conduct user research: Conduct research to identify the needs, goals, behaviors, and pain points of the target audience. This may include user interviews, surveys, and observation.
Identify user segments: Identify common user segments based on the research, such as age, gender, occupation, and level of expertise.
Define user personas: Use the research and user segments to create fictional representations of the different types of users who will be using the website or product. Each persona should include a name, photo, job title, demographics, behaviors, and goals.
Refine and validate the personas: Refine and validate the personas through additional user research and feedback from stakeholders. This helps ensure that the personas accurately represent the target audience and can be used effectively in the design process.
Use the personas in the design process: Use the personas to inform the design process, including decisions about content, layout, functionality, and user flows. Personas help ensure that the design is aligned with the needs and goals of the target audience and supports a positive user experience.
Not using user personas as part of the UI/UX design process can lead to several problems, including
Lack of user focus: Without user personas, design teams may not have a clear understanding of who their users are, what their needs and goals are, and how they use the product. This can lead to design decisions that prioritize the preferences of the design team or stakeholders over the needs of the users.
Inconsistent design decisions: Without user personas, design teams may make inconsistent design decisions that do not align with the needs of the target audience. This can lead to a fragmented user experience that is difficult to navigate, causing frustration and decreased engagement.
Misalignment with business goals: Without user personas, design teams may not have a clear understanding of how the product fits into the overall business goals. This can lead to design decisions that do not align with the business objectives, resulting in a product that does not meet the needs of the target audience or the business.
Reduced usability and accessibility: Without user personas, design teams may not consider the needs of users with different levels of experience, abilities, or preferences. This can lead to a product that is difficult to use or inaccessible to certain groups, resulting in a poor user experience.
Increased development costs: Without user personas, design teams may not have a clear understanding of the requirements of the product, which can lead to changes and revisions during the development process. This can increase development costs and delay the time to market, as well as reduce the quality of the final product.
Overall, using user personas as part of the UI/UX design process is essential for creating a user-centered design that meets the needs and goals of the target audience. User personas provide a clear understanding of the user's needs, preferences, behaviors, and goals, which can inform design decisions and ensure that the product is both usable and valuable to the target audience.
User Segmentation
Sorting Order Visitor
- Segmentation by Referrer / Traffic source
- Segmentation by Visitor Type
- Segmentation by Location / Geography Visit
- Segmentation by Content Viewed
- Segmentation by Landing Page Type Hit
- Segmentation by Action taken Visitor
- Segmentation by Value
- Segmentation by Demographics.
- Segmentation by Engagement
- Segmentation by Technology platform
based on "demographic & pyschographic segmentation"
- Target Audience
- geographic
- demographic
- psychographic
- total market: http://www.census.gov/econ/smallbus.html
- estimated obtainable market:
- Northeast
- Southeast
- tri-state area
- Segmentation
- user personas
- niche
- market demand
- buying patterns
- why do they need a professional website
- macro trends
- responsive web design
- how to go after opportunities
- sales pitch to local businesses with poorly designed or very basic websites and discuss the potential in investing in