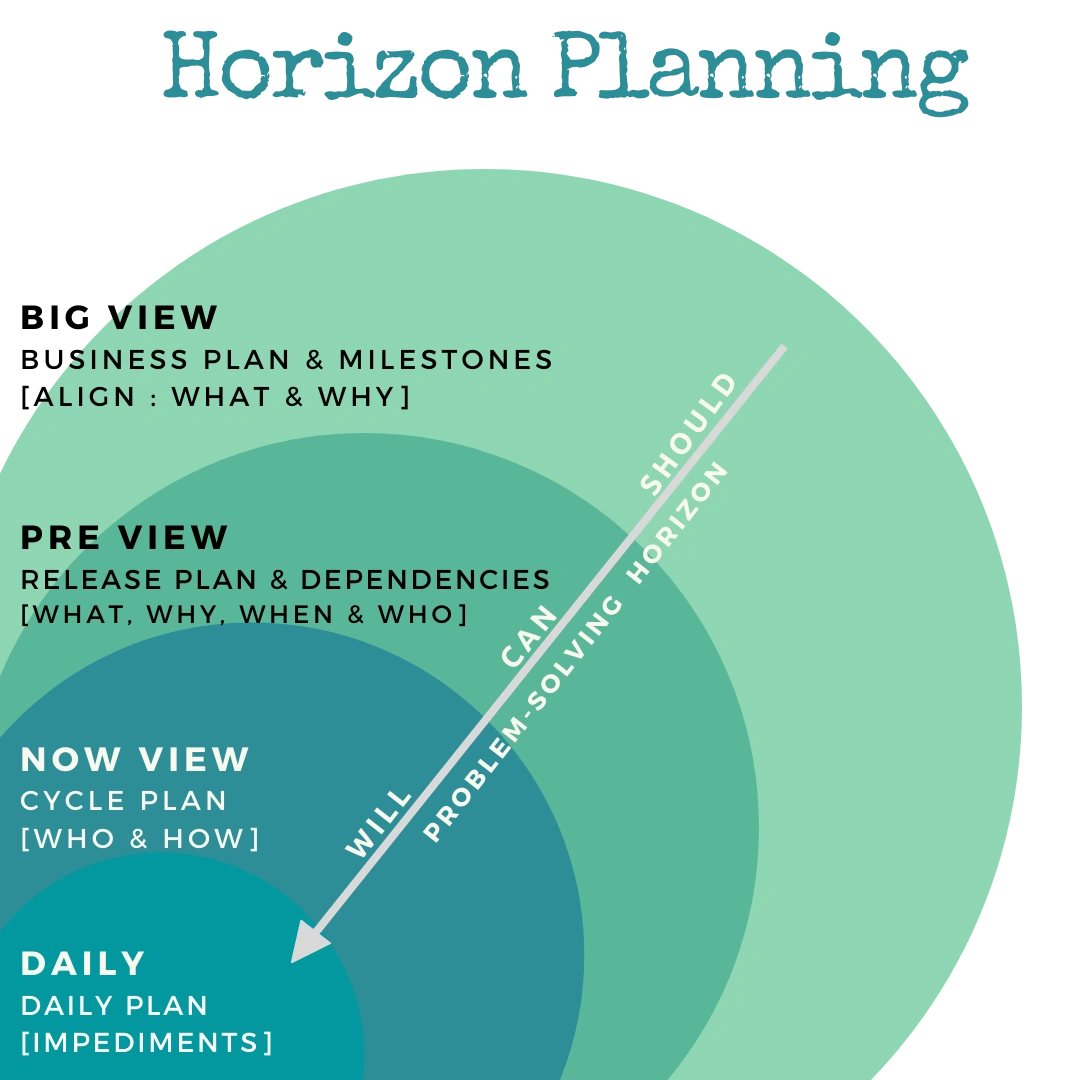
Horizontal planning
A planning tool where each horizon represents a different timescale.
Horizon one is generally short term (days/weeks) Horizon Two is medium (months) Horizon Three long term (years)
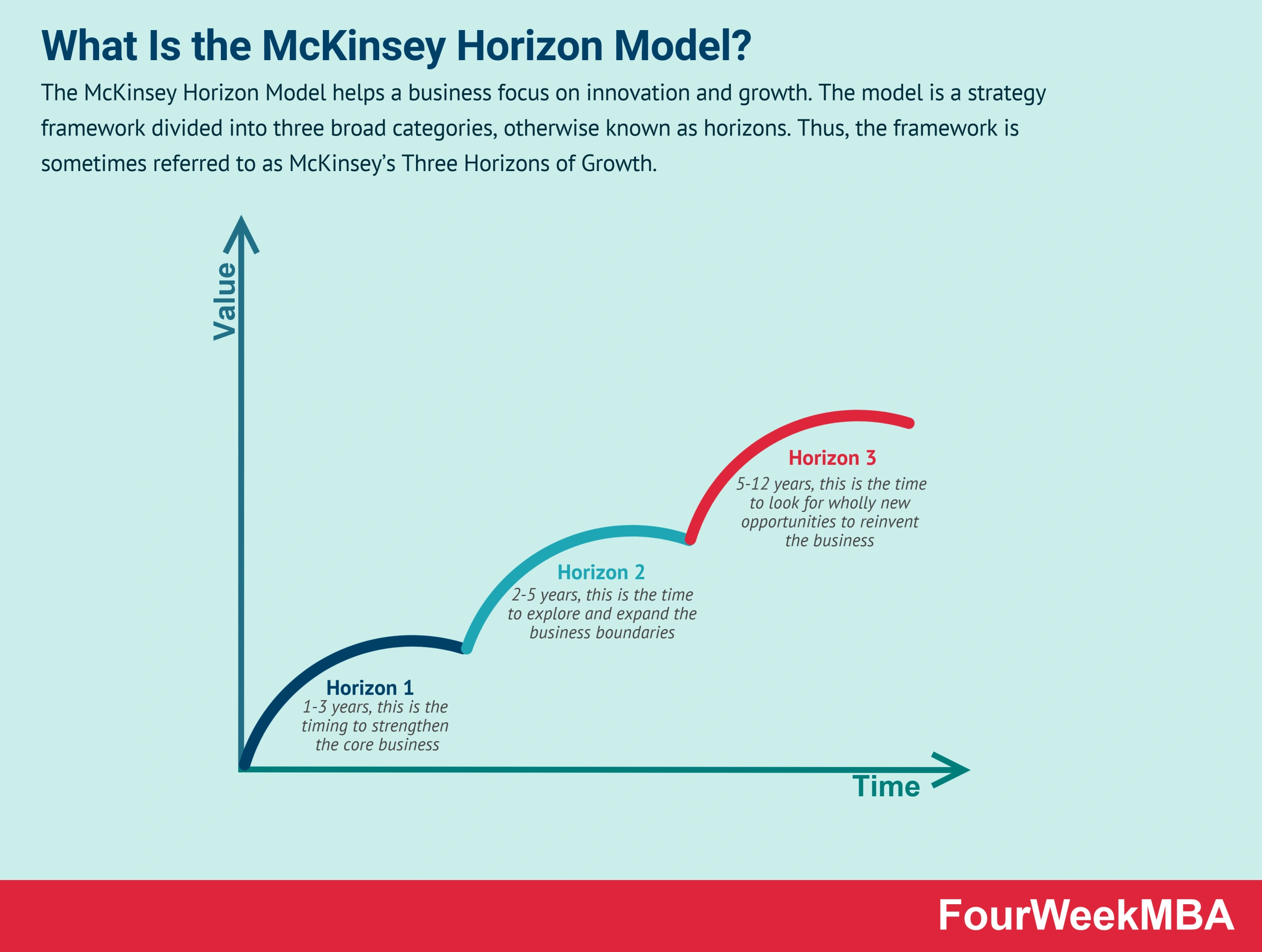
Horizontal planning in Agile project management is a strategy that emphasizes the parallel progression of tasks or features across different teams or disciplines. Unlike traditional vertical planning, which focuses on completing one phase before moving on to the next, horizontal planning allows for multiple activities to occur simultaneously, promoting efficiency and collaboration. This approach is particularly effective in Agile environments where cross-functional teams work together to deliver increments of value in short cycles.
Key Principles of Horizontal Planning
-
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Encourages teams with different expertise to work together, breaking down silos and fostering a culture of open communication and shared responsibility.
-
Parallel Task Execution: Allows for the simultaneous progression of multiple tasks or features, which can reduce the overall project timeline and increase flexibility in responding to changes.
-
Incremental Delivery: Focuses on delivering small increments of value frequently, enabling continuous feedback and adjustments based on stakeholder input and market changes.
-
Flexibility and Adaptability: Supports the Agile principle of responding to change over following a fixed plan, allowing teams to pivot quickly when necessary without derailing the entire project.
Implementing Horizontal Planning
-
Define Clear Objectives: Start by defining clear objectives and outcomes for the project. This ensures that all teams are aligned and working towards a common goal.
-
Identify Dependencies: Map out the dependencies between tasks and teams. This helps in planning parallel workstreams effectively and avoiding bottlenecks.
-
Establish Communication Channels: Set up regular communication channels and meetings, such as daily stand-ups or integration reviews, to ensure that teams are synchronized and can address issues promptly.
-
Use Visual Management Tools: Implement visual management tools, like Kanban boards or Scrum boards, to track progress across teams and facilitate coordination.
-
Foster a Culture of Collaboration: Encourage a culture of collaboration and mutual support among teams. This can involve cross-team pairings, shared learning sessions, or joint problem-solving workshops.
Benefits of Horizontal Planning
-
Increased Efficiency: By allowing tasks to progress in parallel, horizontal planning can significantly reduce the time to market for new features or products.
-
Enhanced Flexibility: This approach provides the flexibility to adjust priorities and shift resources as needed, without disrupting the overall project flow.
-
Improved Quality: Cross-functional collaboration and continuous feedback loops help in identifying and addressing issues early, leading to higher quality outcomes.
-
Greater Stakeholder Satisfaction: Incremental delivery ensures that stakeholders see continuous progress and can provide input throughout the project, leading to greater satisfaction with the final product.
Horizontal planning aligns well with the Agile methodology, offering a dynamic and collaborative approach to project management that can drive efficiency, quality, and stakeholder satisfaction.
The Value Realization Gap
Asses the delivered value vs. proposed value; understand & communicate the value realization gap.
What is the value realization gap?
The value realization gap refers to the disparity between the expected value or benefits derived from a project, initiative, or investment and the actual value realized in practice. It is often observed in business contexts where there is a disconnect between the intended outcomes and the actual results achieved.
The value realization gap can occur due to various factors:
-
Misalignment of Goals and Objectives: When the goals and objectives of a project or initiative are not clearly defined or communicated, there can be a lack of alignment between the intended outcomes and the actions taken to achieve them. This can result in a gap between what was expected and what was achieved.
-
Incomplete or Inaccurate Requirements: Inadequate understanding or documentation of requirements can lead to a gap between the expected value and the actual outcomes. If the requirements are not well-defined or if they do not accurately reflect the needs and expectations of stakeholders, the delivered solution may fall short of meeting the intended value.
-
Poor Execution or Implementation: Even with well-defined goals and requirements, poor execution or implementation can result in a gap between the expected value and the actual outcomes. Factors such as inadequate planning, improper resource allocation, technical challenges, or lack of expertise can contribute to this gap.
-
Lack of Monitoring and Measurement: Failure to effectively monitor and measure the progress and outcomes of a project can make it difficult to identify and address any deviations from expected value. Without proper tracking and measurement mechanisms, it becomes challenging to take corrective actions in a timely manner.
-
External Factors and Changes: External factors, such as market conditions, regulatory changes, or technological advancements, can impact the value realization of a project. If these factors are not adequately considered or if they change significantly during the course of the project, it can result in a gap between expected and actual outcomes.
To address the value realization gap, organizations can take several steps:
-
Clear Goal Setting and Communication: Ensure that the goals and objectives of a project or initiative are well-defined, communicated, and understood by all stakeholders. This clarity helps to align efforts and expectations.
-
Robust Requirements Analysis: Invest time and effort in gathering and analyzing requirements to ensure they are comprehensive, accurate, and aligned with stakeholder needs. This helps in setting realistic expectations and delivering value accordingly.
-
Effective Project Management: Implement strong project management practices to ensure proper planning, resource allocation, and execution. Regular monitoring, tracking, and timely interventions can help bridge the gap between expected and actual value.
-
Continuous Monitoring and Measurement: Establish mechanisms for monitoring and measuring progress and outcomes throughout the project lifecycle. This enables proactive identification of any deviations from expected value, allowing for timely corrective actions.
-
Flexibility and Adaptability: Recognize that external factors and changes may impact the value realization. Build flexibility and adaptability into project plans, allowing for adjustments and contingencies as needed.
By addressing the value realization gap, organizations can enhance their ability to deliver projects and initiatives that align with expectations and generate the intended value for stakeholders.